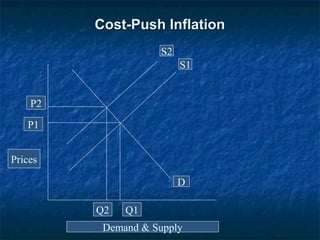
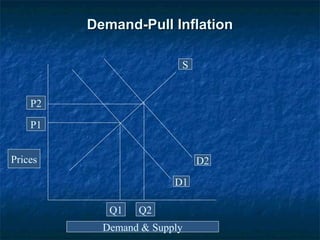
This document discusses the effect of inflation on Pakistan's economy. It defines inflation as a general and progressive increase in prices where the value of goods rises faster than the value of money. The document outlines the different types of inflation including cost-push inflation, which occurs when businesses raise prices to maintain profits in response to higher production costs, and demand-pull inflation, which arises when aggregate demand exceeds supply. The consumer price index is used to measure inflation. Some factors that can cause inflation in Pakistan are natural calamities, indirect taxes, rising import prices, and shortages in production factors. The document recommends policies like tight monetary policy, contractionary fiscal policy, and increasing domestic production to help control inflation.











![Calculate the inflation rate from 2010 toCalculate the inflation rate from 2010 to
2011 and from 2011 to 20122011 and from 2011 to 2012
Inflation10-11 = [(CPI 2011 – CPI 2010)/CPI 2010] x 100Inflation10-11 = [(CPI 2011 – CPI 2010)/CPI 2010] x 100
Inflation10-11 = [(124.14 – 100)/100] x 100Inflation10-11 = [(124.14 – 100)/100] x 100
Inflation10-11 = 24.14%Inflation10-11 = 24.14%
Inflation11-12 = [(CPI 2012 – CPI 2011)/CPI 2011] x 100Inflation11-12 = [(CPI 2012 – CPI 2011)/CPI 2011] x 100
Inflation11-12 = [(146.21 – 124.14)/124.14] x 100Inflation11-12 = [(146.21 – 124.14)/124.14] x 100
Inflation11-12 = 17.78%Inflation11-12 = 17.78%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inflationresearch-130525144804-phpapp02/85/Inflation-research-16-320.jpg)




