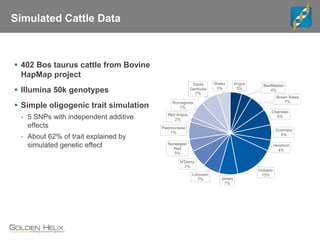
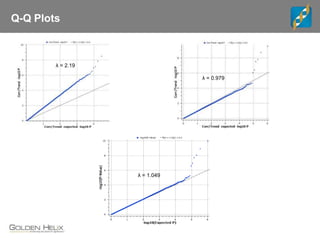
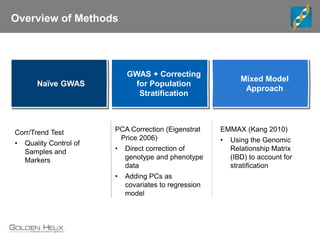
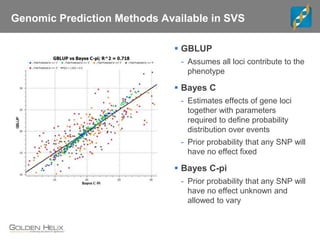
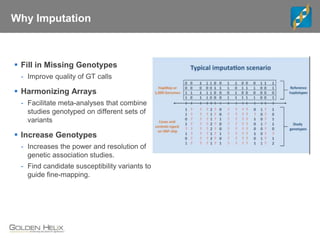
The document discusses the use of genomic tools for GWAS, genomic prediction, and imputation, highlighting the capabilities and features of the SNP & Variation Suite (SVS) for data management and analysis. It presents a workflow using simulated cattle data and various genomic prediction methods that improve breeding value calculations and assist in identifying genetic markers. The document also emphasizes the importance of imputation in enhancing the quality and resolution of genetic research.