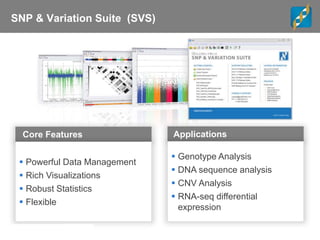
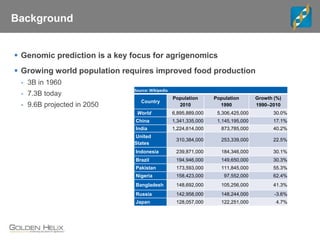
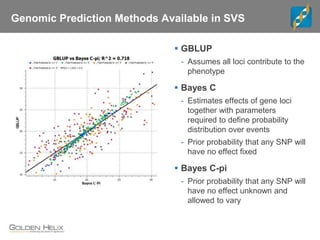
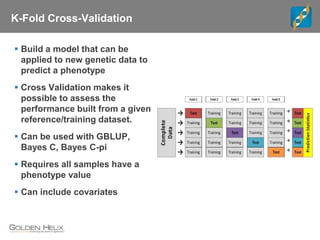
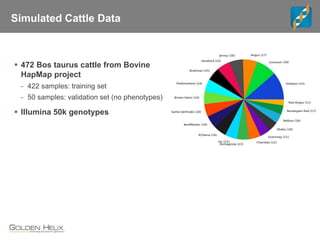
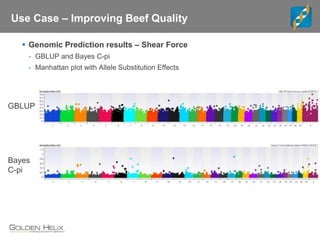
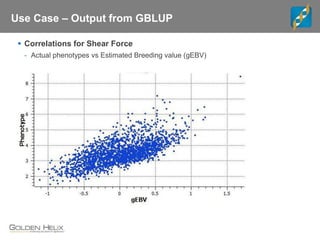
Golden Helix is a global bioinformatics company specializing in genomic prediction methods for agrigenomics, focusing on improving food production through enhanced breeding values. Their software leverages various methods such as GBLUP and Bayesian approaches to optimize genetic analysis and predict traits in large populations, exemplified through studies on cattle for enhanced beef quality. The document highlights their services, features, and a successful case study identifying genetic markers linked to beef palatability.