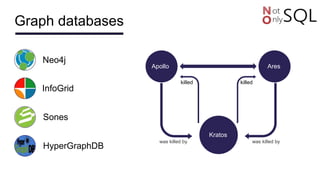
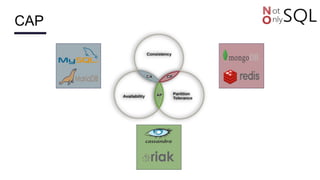
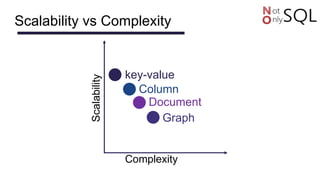
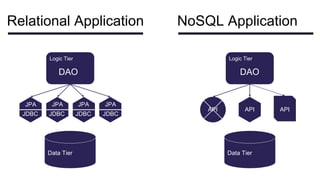
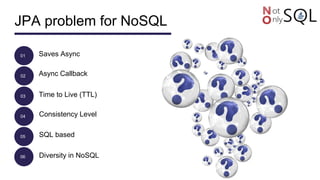
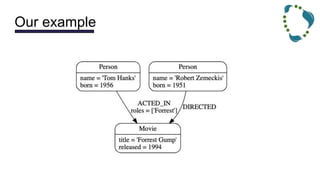
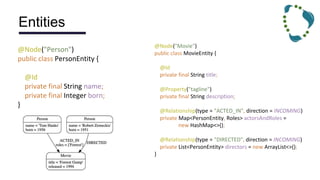
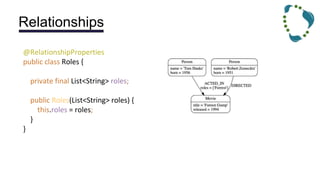
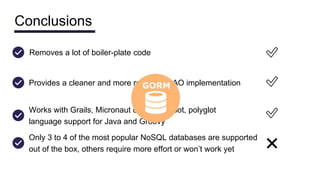
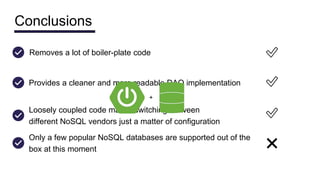
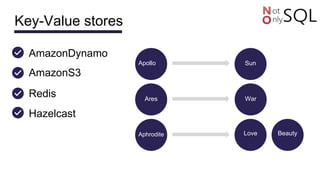
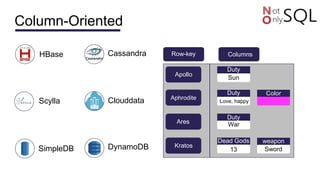
This document discusses NoSQL databases and frameworks for using them with Java applications. It summarizes the advantages of NoSQL databases, different types including key-value, column-oriented, document and graph databases. It also discusses frameworks like NoSQL Endgame that aim to provide a common API for working with multiple NoSQL databases from Java code. However, it notes that fully supporting all NoSQL databases and scenarios is still a challenge for such frameworks.










![Document stores
{
"name":"Diana",
"duty":[
"Hunt",
"Moon",
"Nature"
],
"siblings":{
"Apollo":"brother"
}
}
ApacheCouchDB
MongoDB
Couchbase](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eclipsecon2021nosqlendgame-211006171923/85/EclipseCon-2021-NoSQL-Endgame-13-320.jpg)