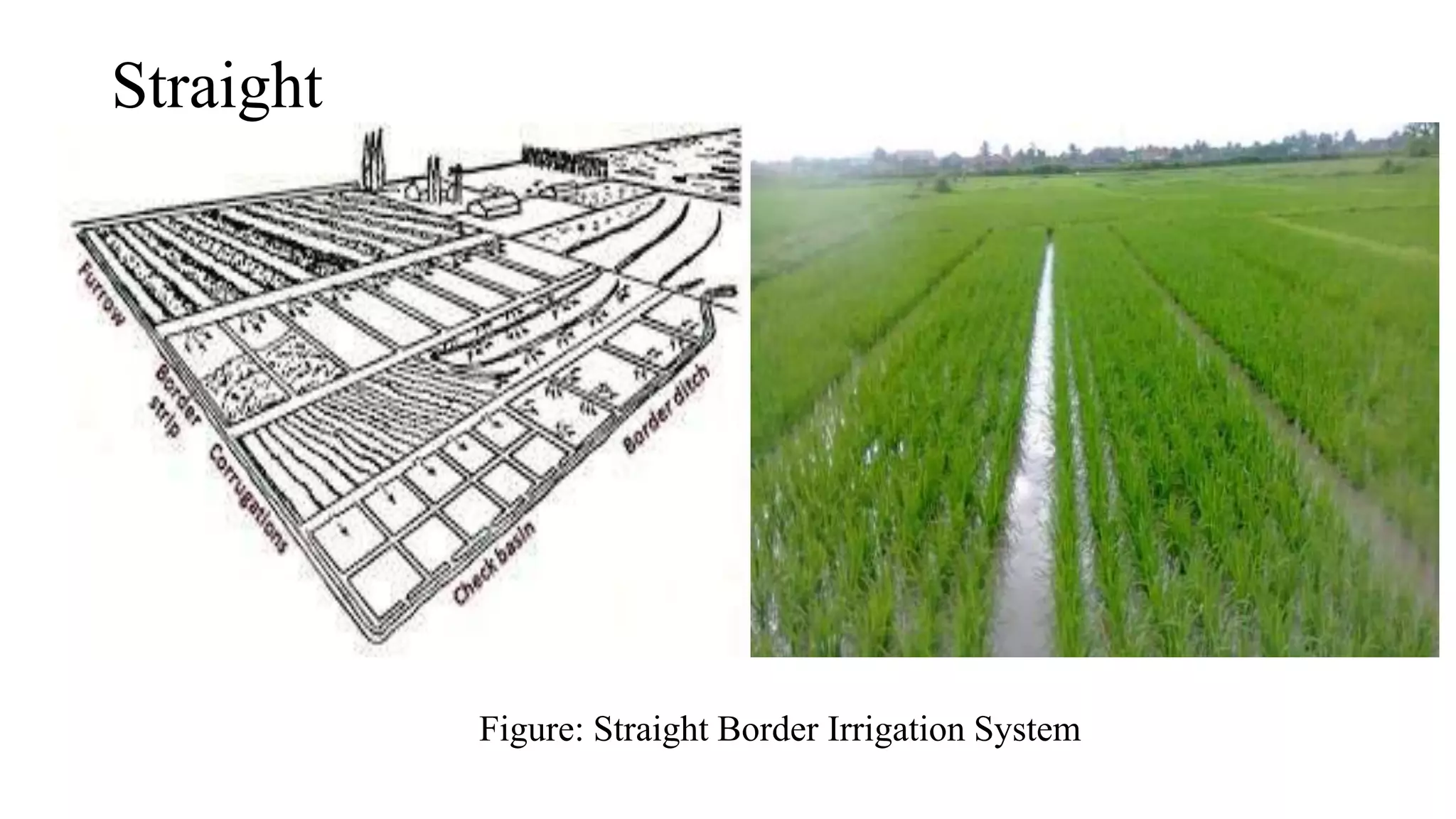
Border irrigation is an old system used in Bangladesh to irrigate crops like wheat. It involves putting a large volume of water in a defined border area at the top of a field to flush it down the slope in a uniform pattern. It works best on larger farms and fields with uniform slopes between 0.05-2%. There are two types - straight borders that run straight down slopes and contour borders that run along elevation contours. The system has advantages like earlier irrigation and less labor than flood irrigation. However, it requires setting up the water distribution across the top of fields and does not work as well on fields with side slopes.