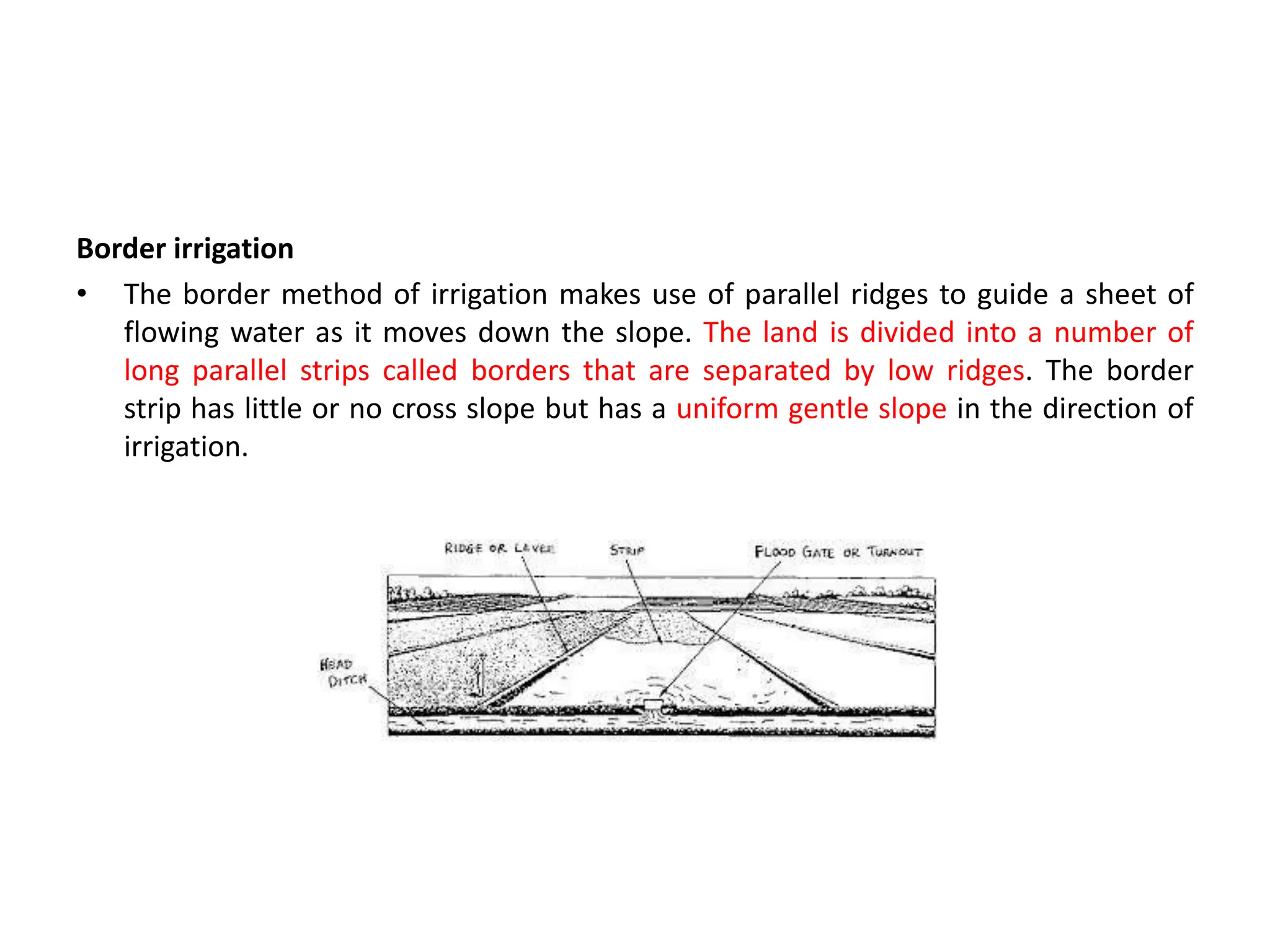
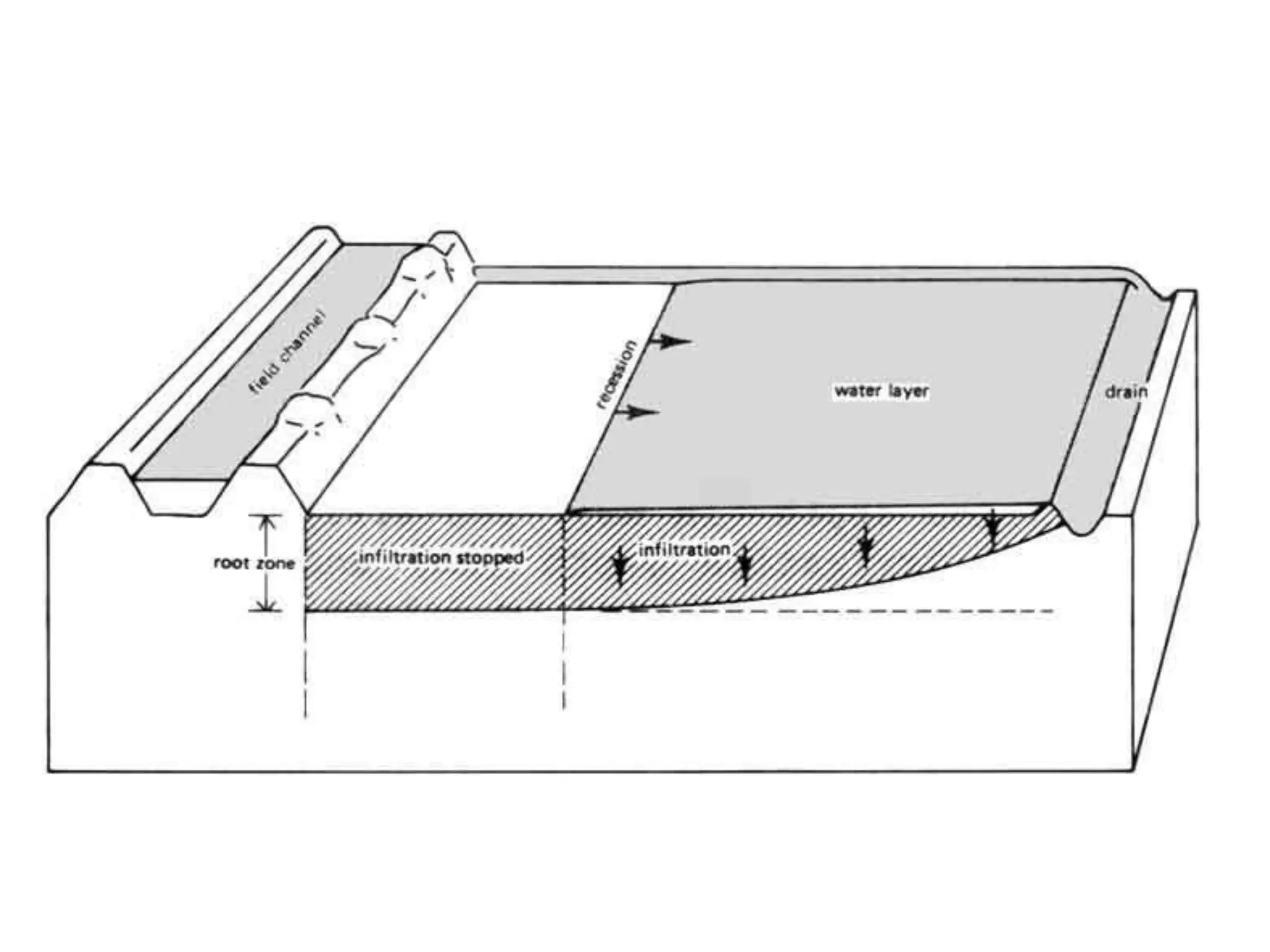
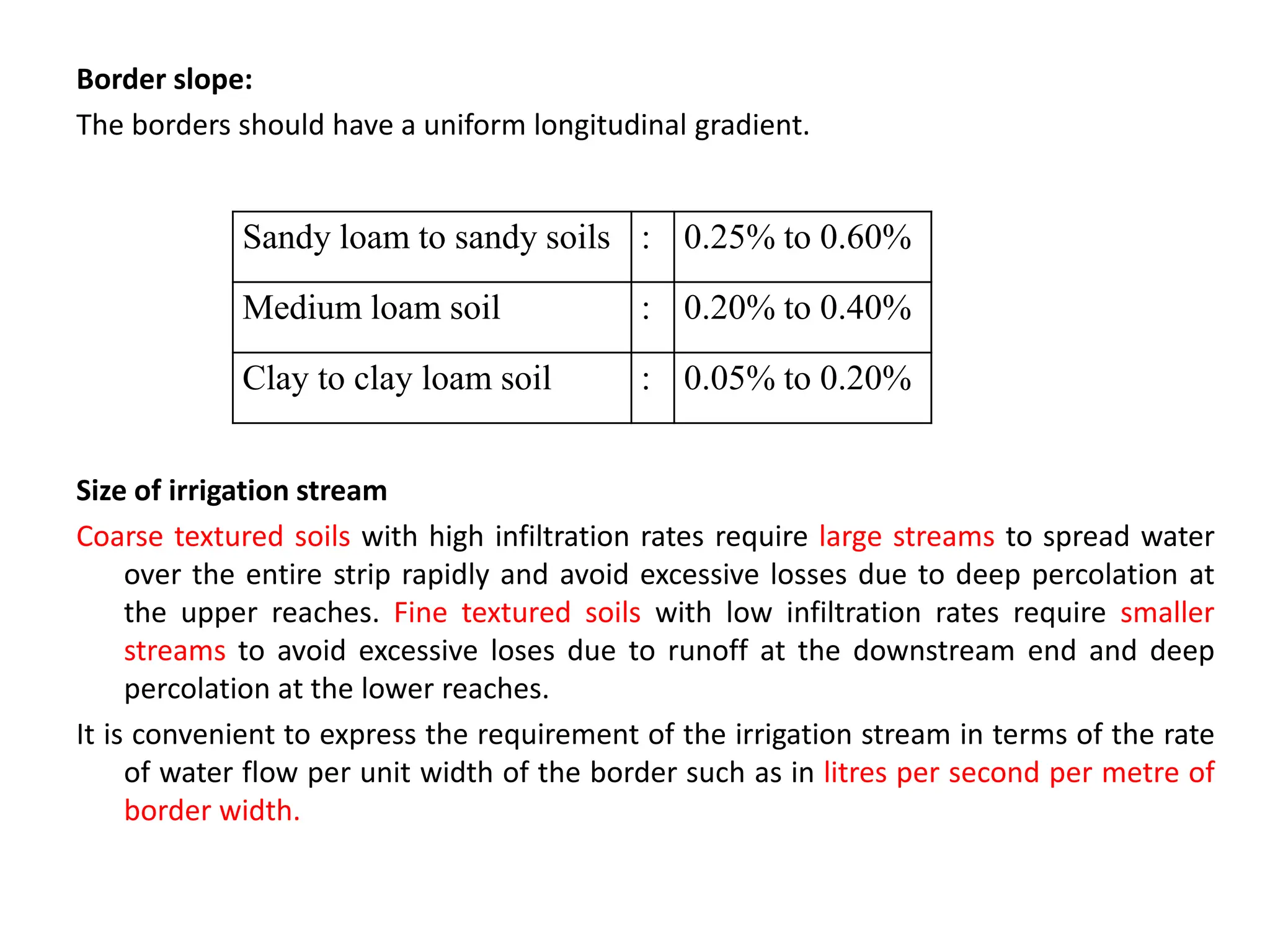
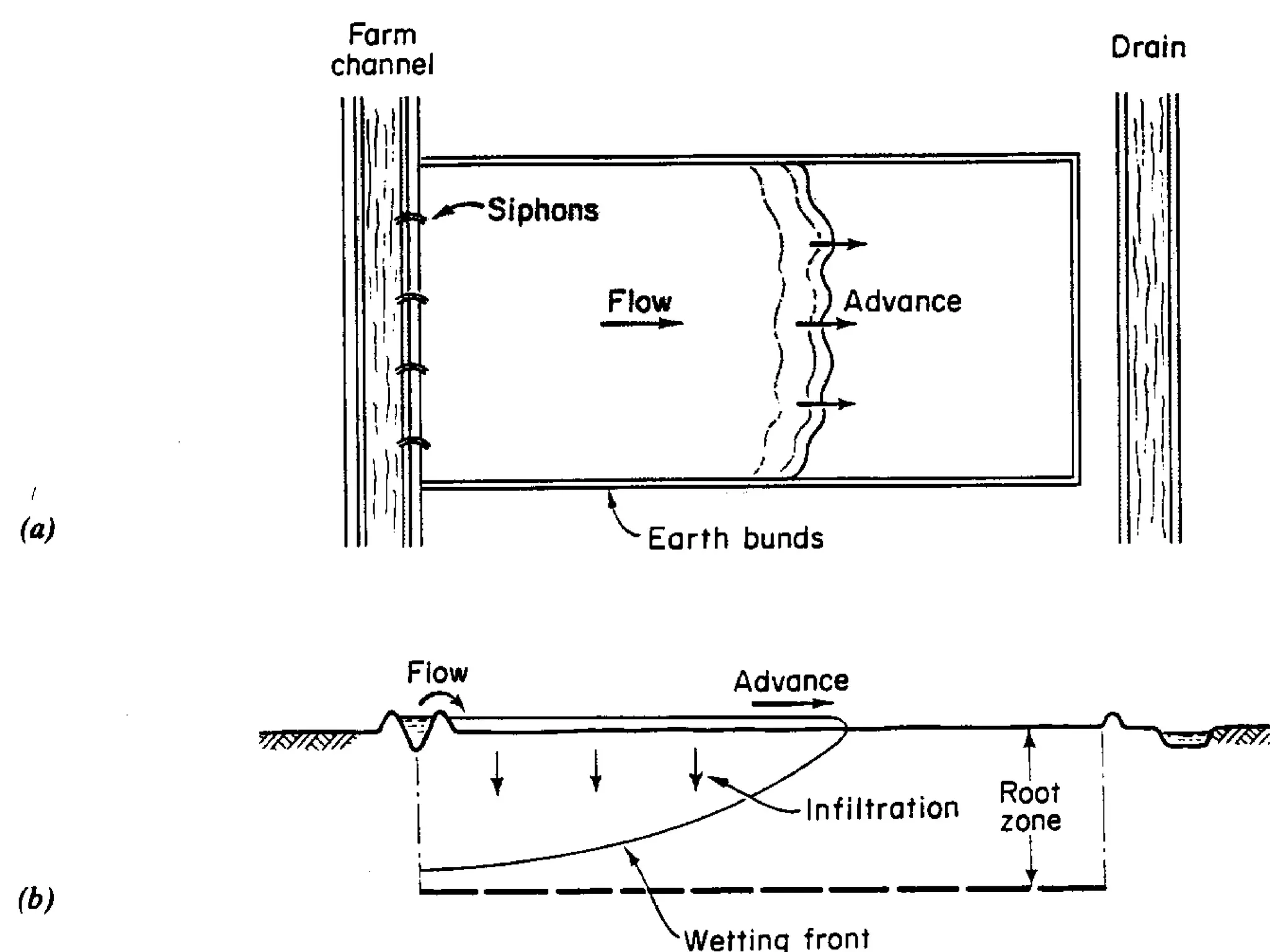
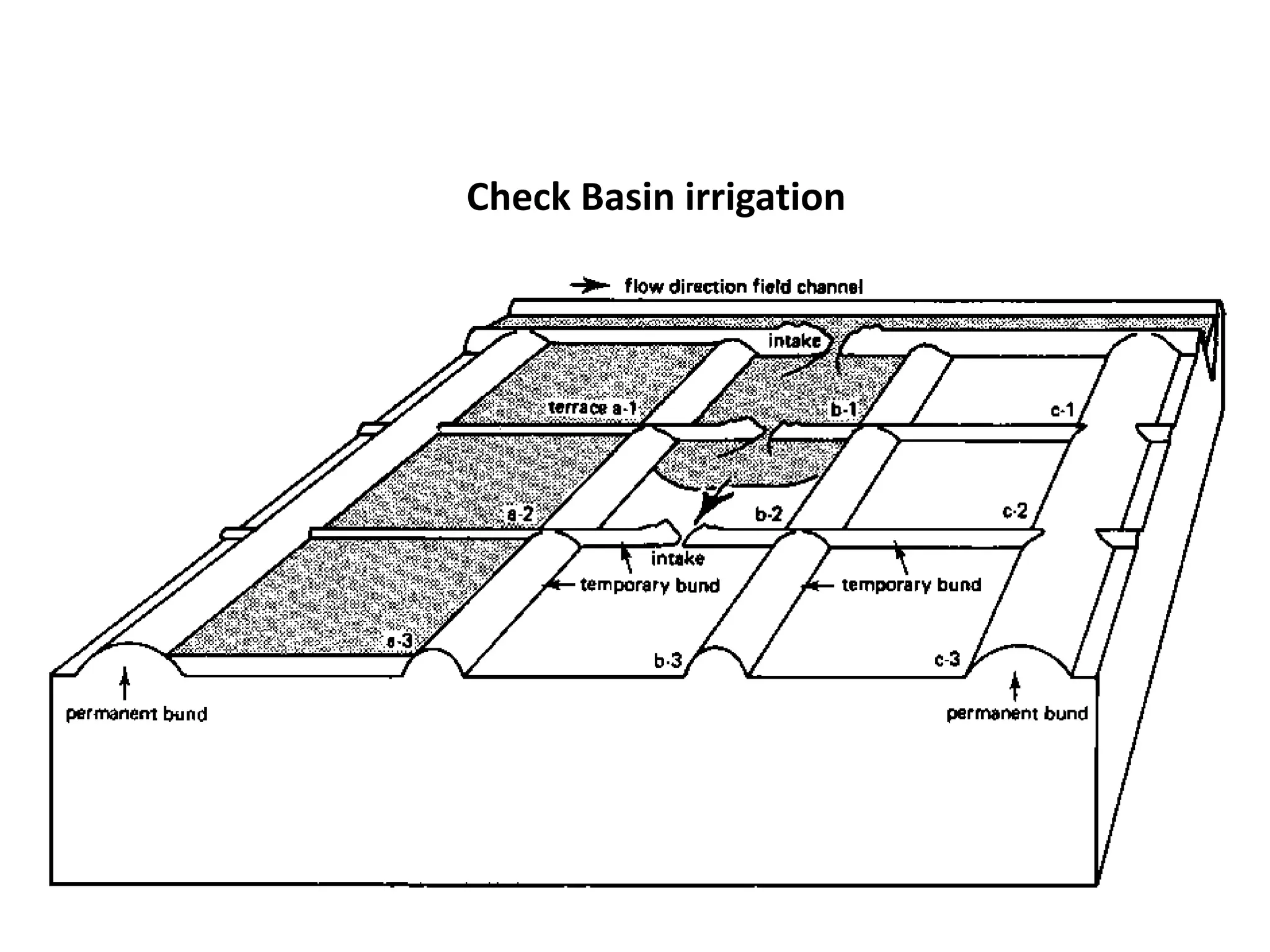
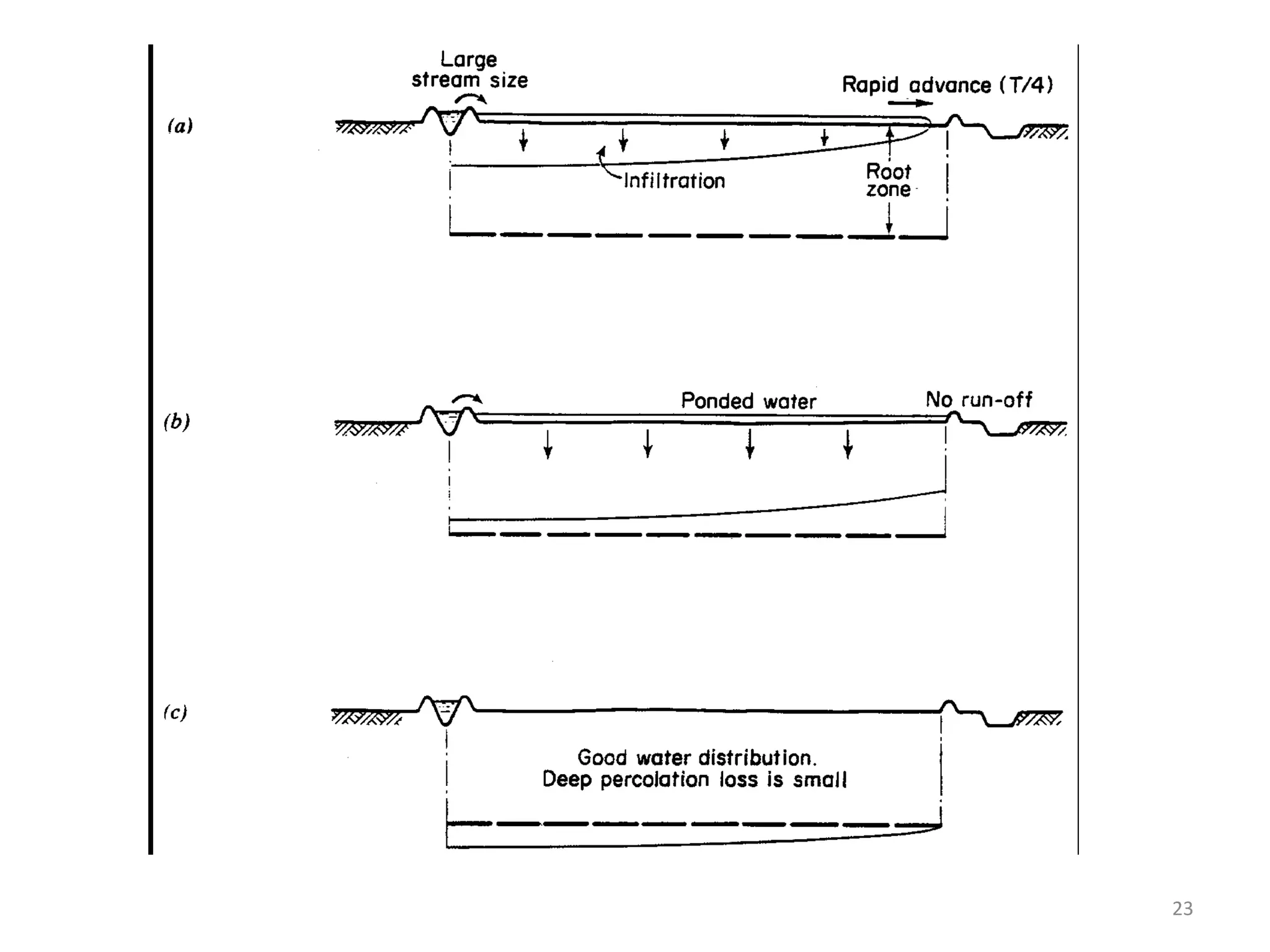
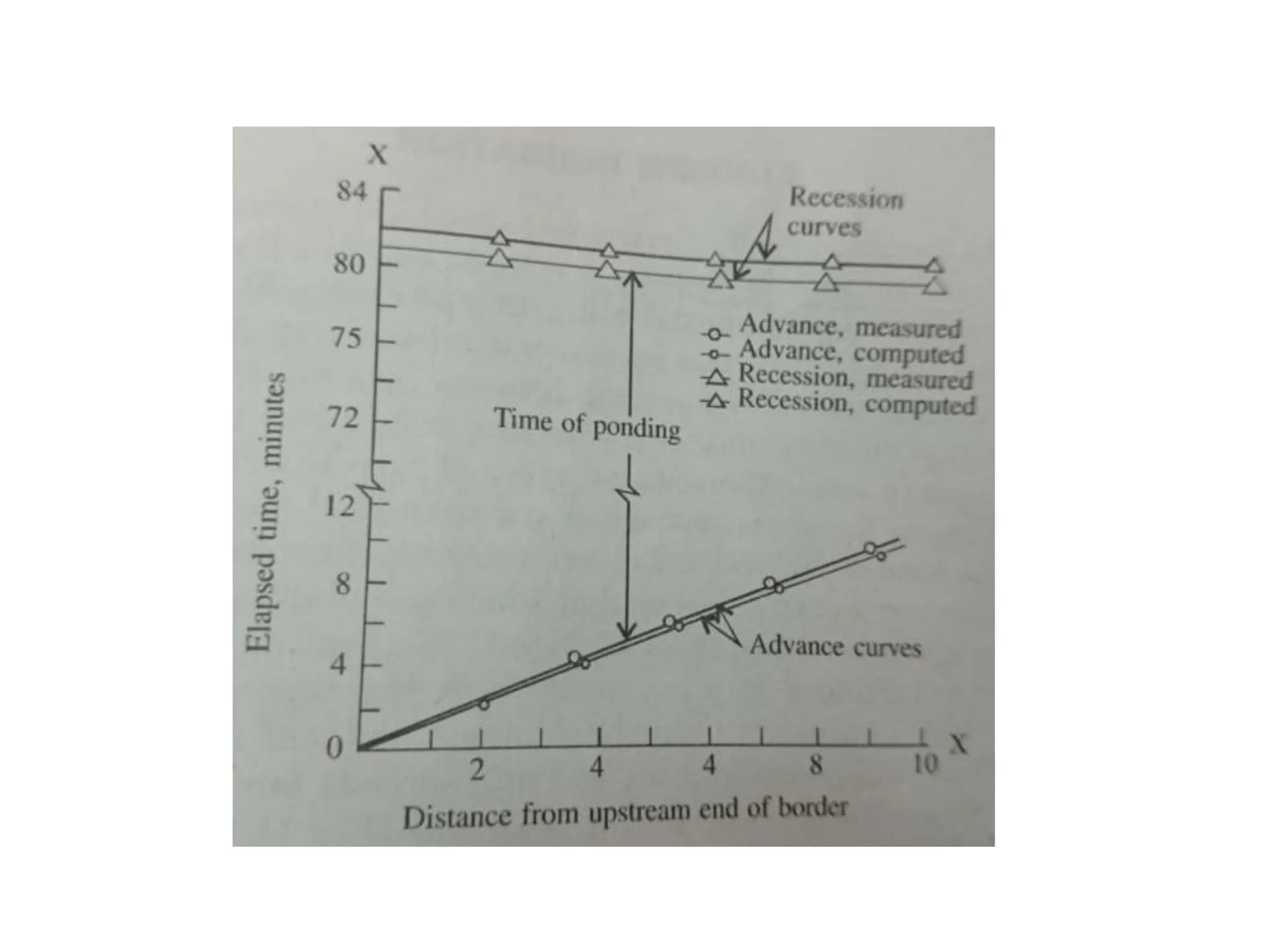
Border irrigation involves dividing land into long, parallel strips called borders separated by low ridges. Water is introduced at the top of each border strip and flows downhill in a shallow sheet confined by the ridges. As the water infiltrates into the soil, it moves down the strip. Proper design of border irrigation considers factors like strip width and length, soil type, irrigation stream size, and slope. Check basin irrigation uses bunds to form basins that hold water for infiltration until the soil is saturated. The size and shape of check basins depends on soil type and crop grown.