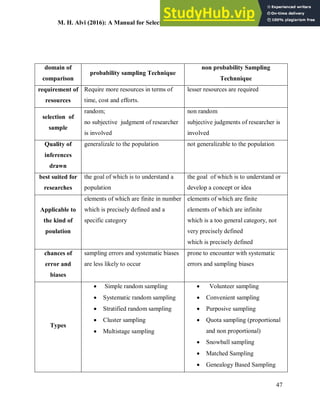
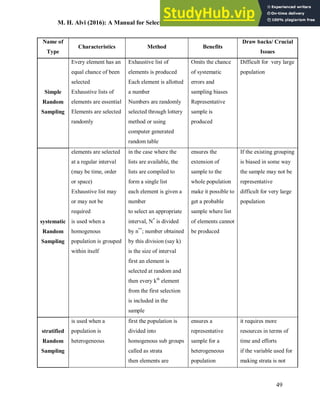
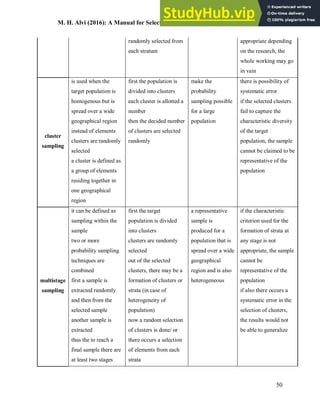
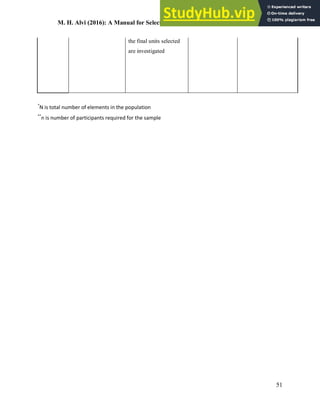
This document provides an overview of key concepts related to sampling in research. It defines a population as all members that meet the criteria for a research study, and a sample as a smaller subset of the population selected for investigation. The purpose of sampling is discussed as drawing inferences about the total population based on information from the sample, with the goal of the sample being representative of the population to obtain generalizable results. Different types of probability and non-probability sampling techniques are then introduced.










































![M. H. Alvi (2016): A Manual for Selecting Sampling Techniques in Research
43
REFERNCES
Alvi, M.H. (2014). A Manual for Basic Techniques of Data Analysis and Distribution. Retrieved
from Munich Personal RePEc Archive: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/60138/
Barreiro, P. .L & Albandoz, J. .P. (2001). Population and sample Sampling
techniques. Management Mathematics for European Schools. Retrieved 5 March, 2016, from:
http://optimierung.mathematik.uni-
kl.de/mamaeusch/veroeffentlichungen/ver_texte/sampling_en.pdf
Stattrekcom. (2016, no-date). Survey Sampling Methods. [Weblog]. Retrieved 5 March
2016, from: http://stattrek.com/survey-research/sampling-methods.aspx?Tutorial=AP
Enotescom. (2016, no-date). What is sampling? What are the different methods of sampling?My
posted question is related with Research Methodology | eNotes.[Weblog]. Retrieved 5 March
2016, from: http://www.enotes.com/homework-help/what-sampling-what-different-methods-
sampling-154057
Sampling Techniques. Retrieved 5 March, 2016, from:
http://cs.fit.edu/~jpmcgee/classes/CSE5800/SamplingTechniques.pdf
McLeod, S. A. (2014). Sampling Methods. Retrieved 5 March, 2016, from:
www.simplypsychology.org/sampling.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amanualforselectingsamplingtechniquesinresearch-230804175940-d33a03f8/85/A-Manual-For-Selecting-Sampling-Techniques-In-Research-43-320.jpg)