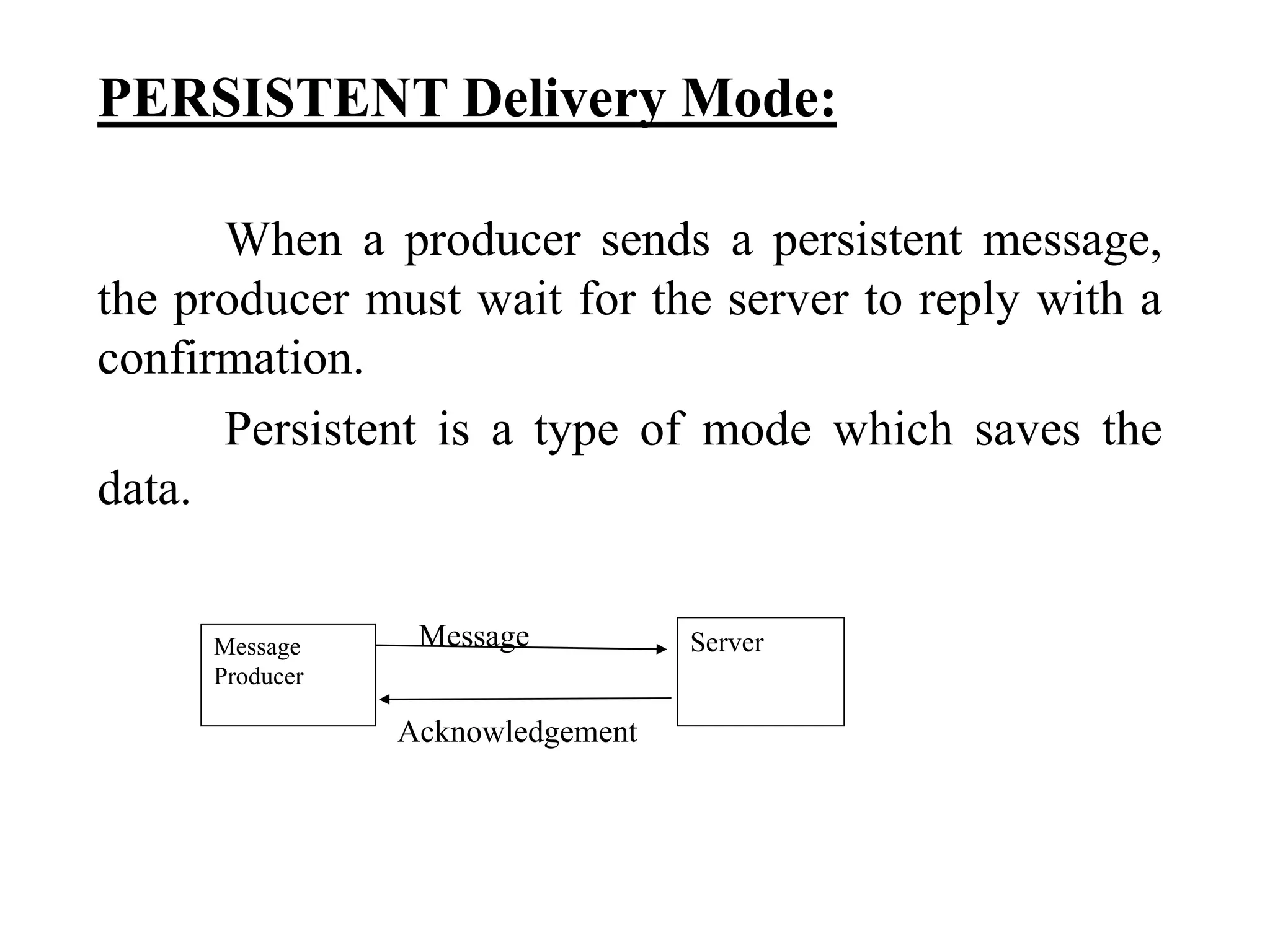
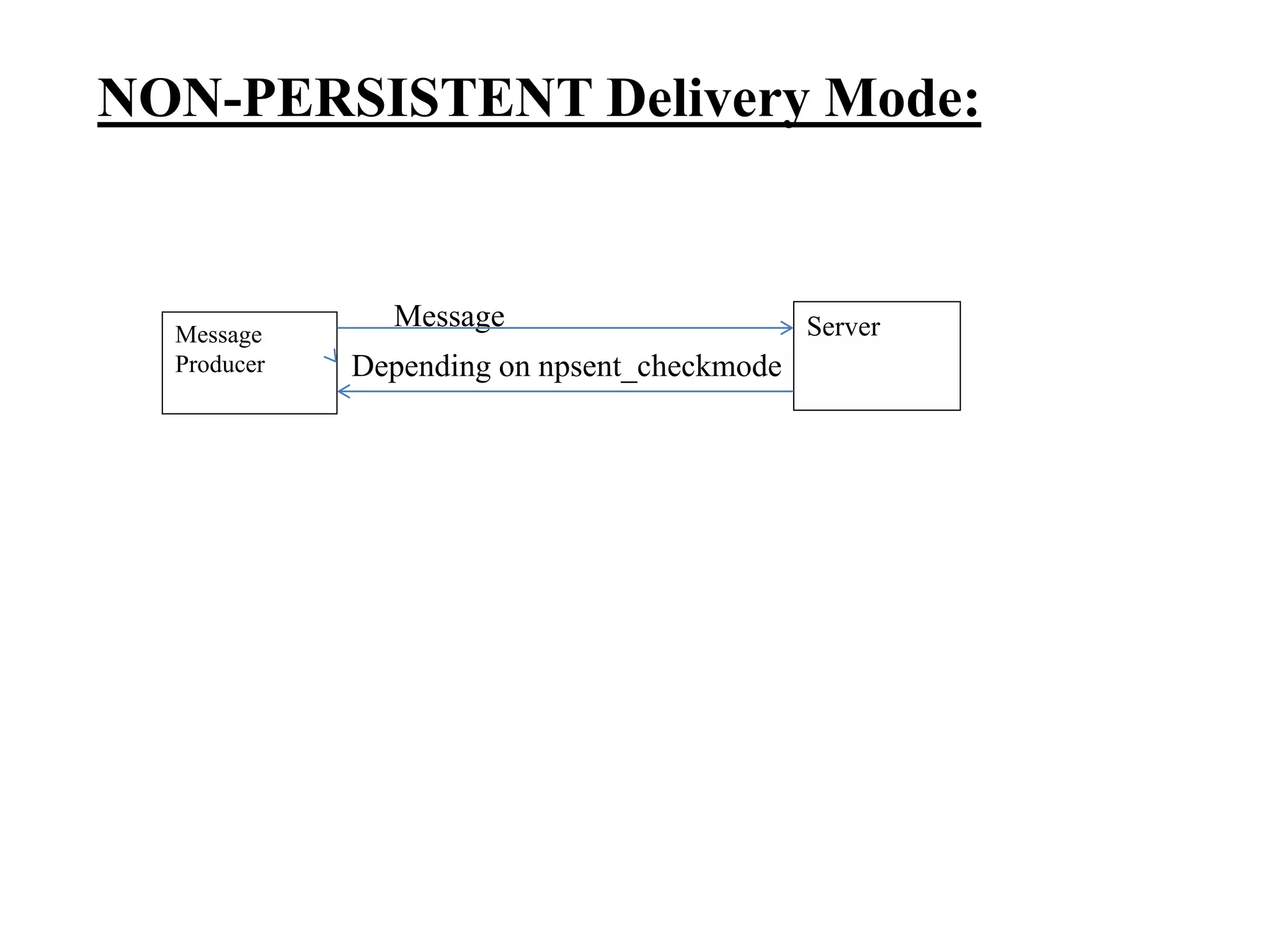
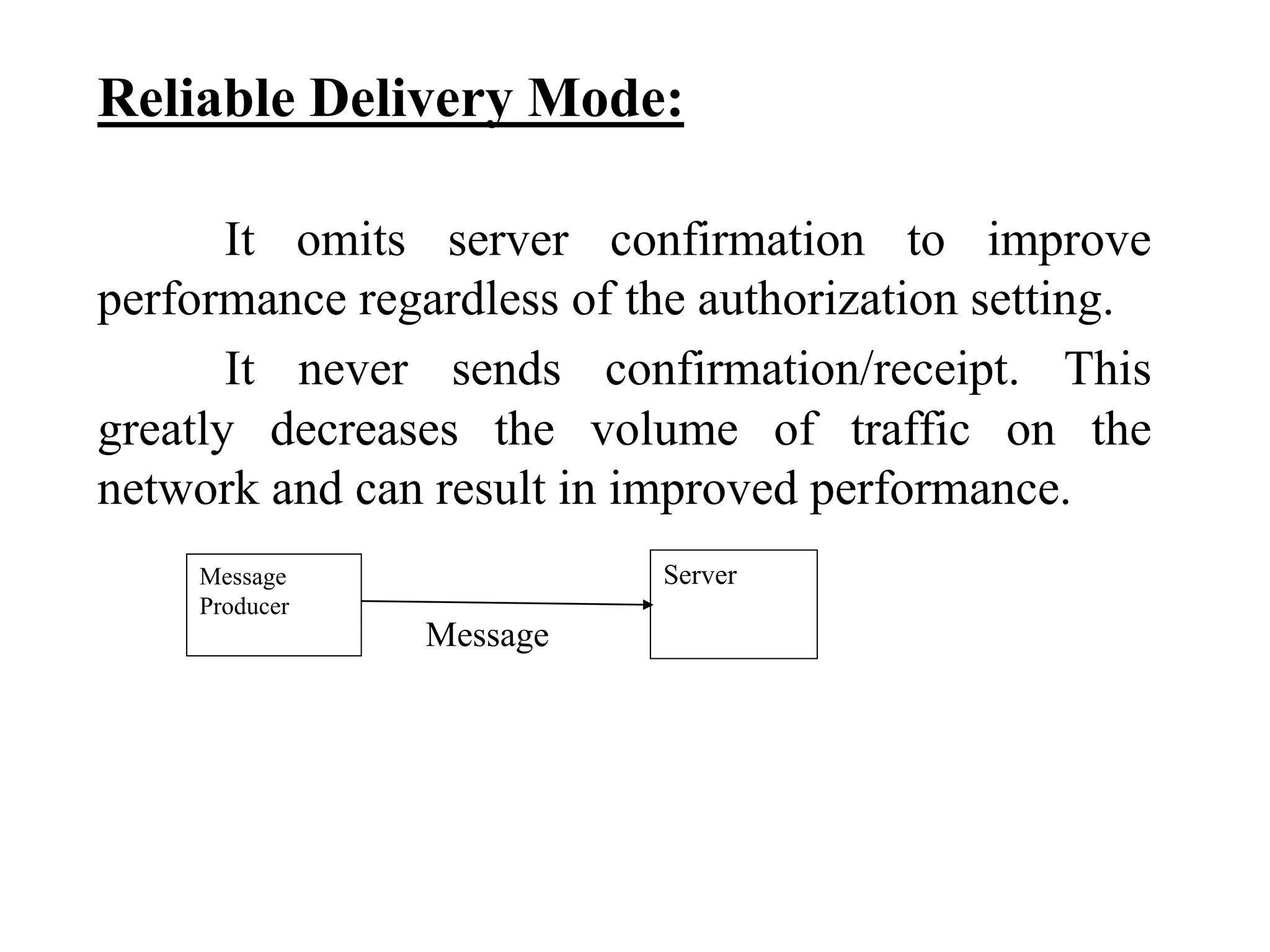
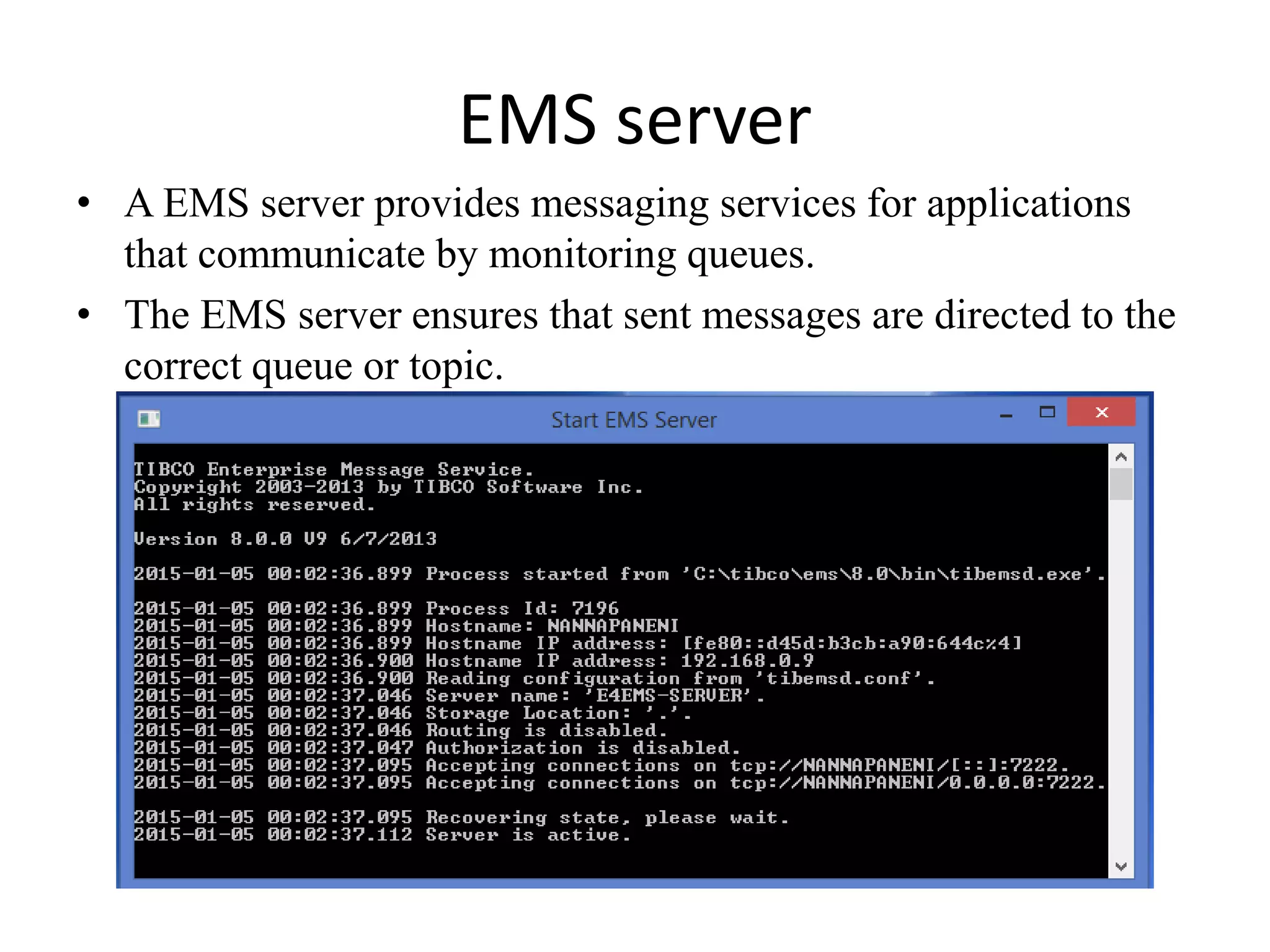
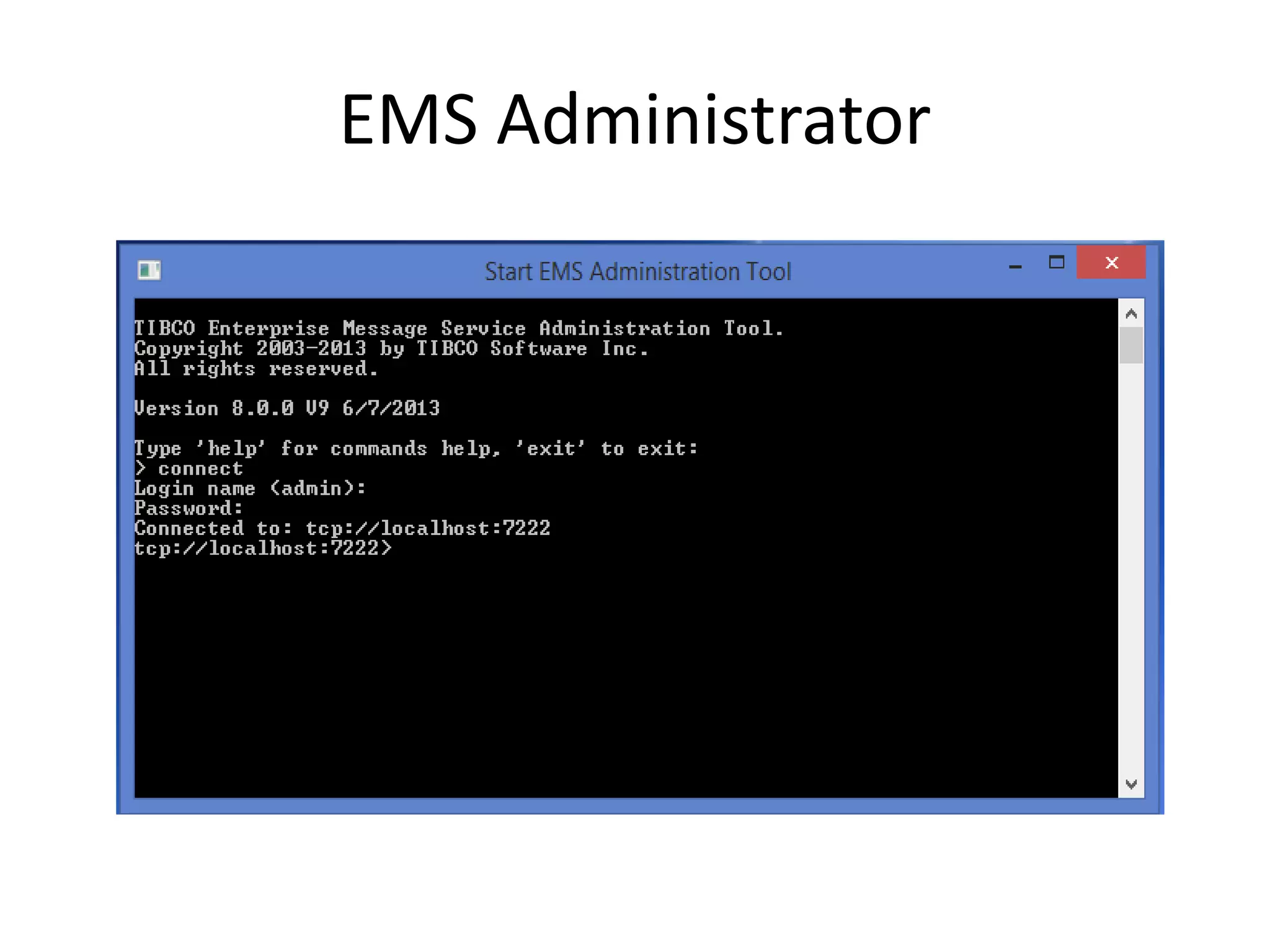
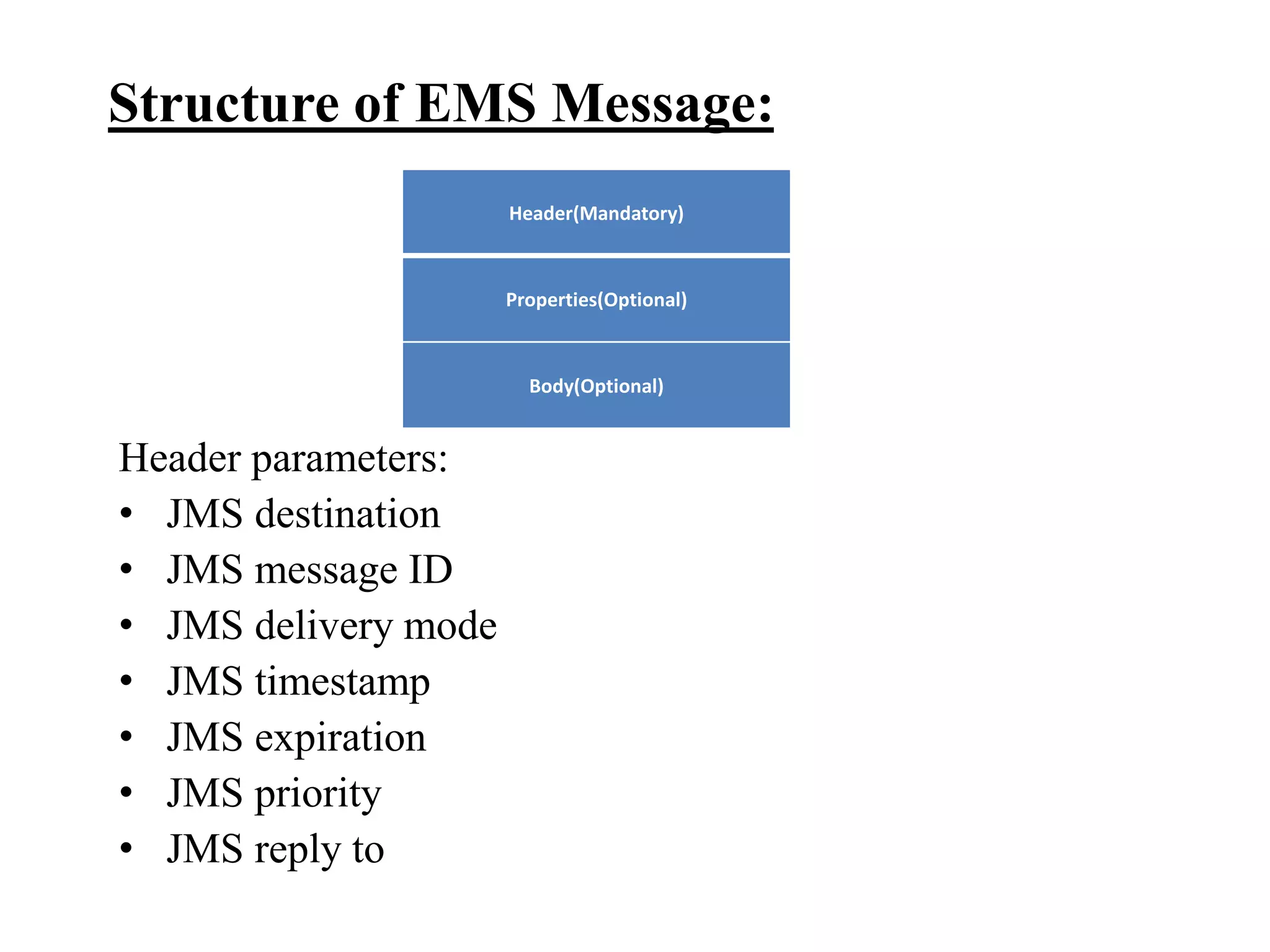
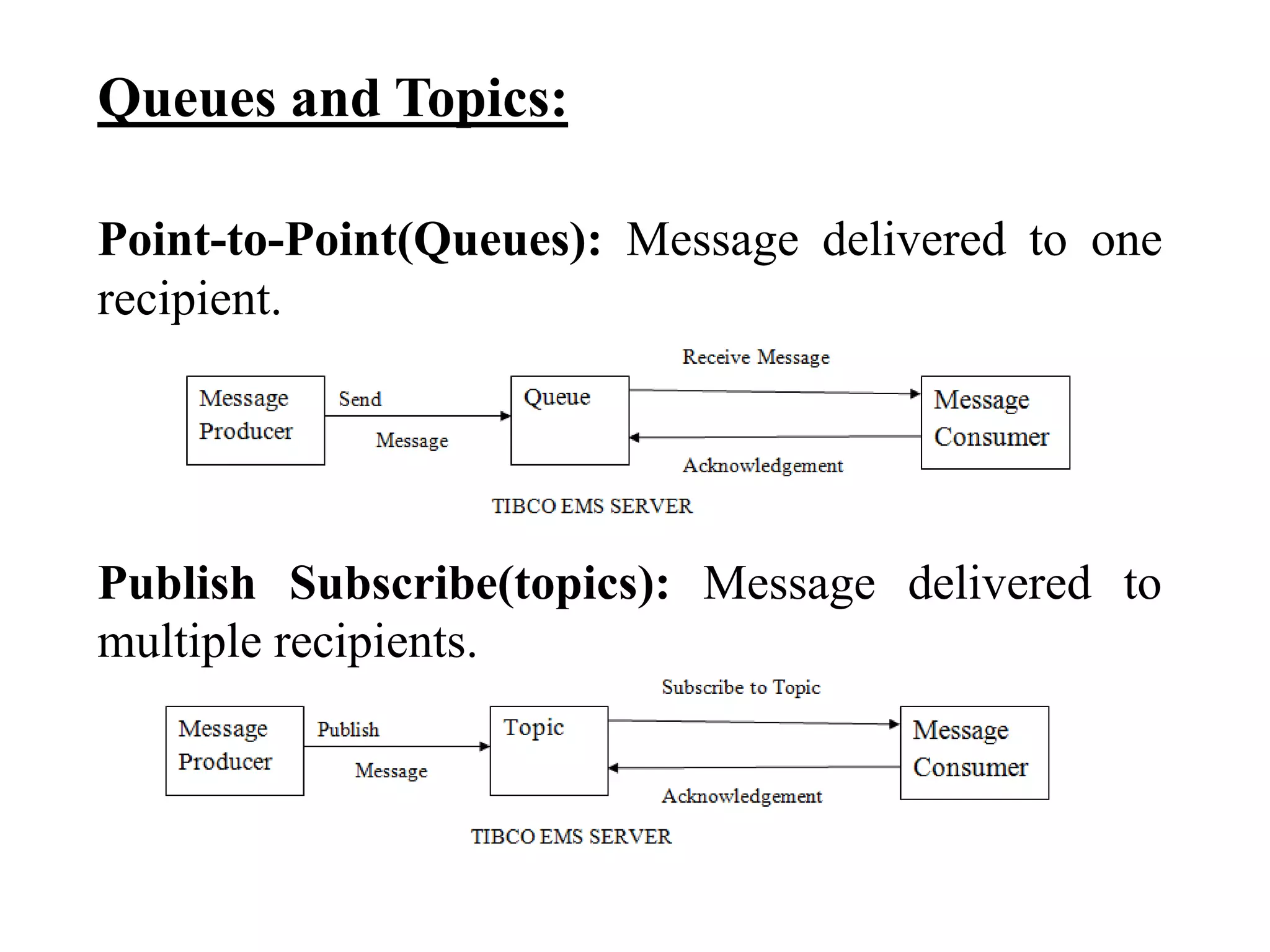
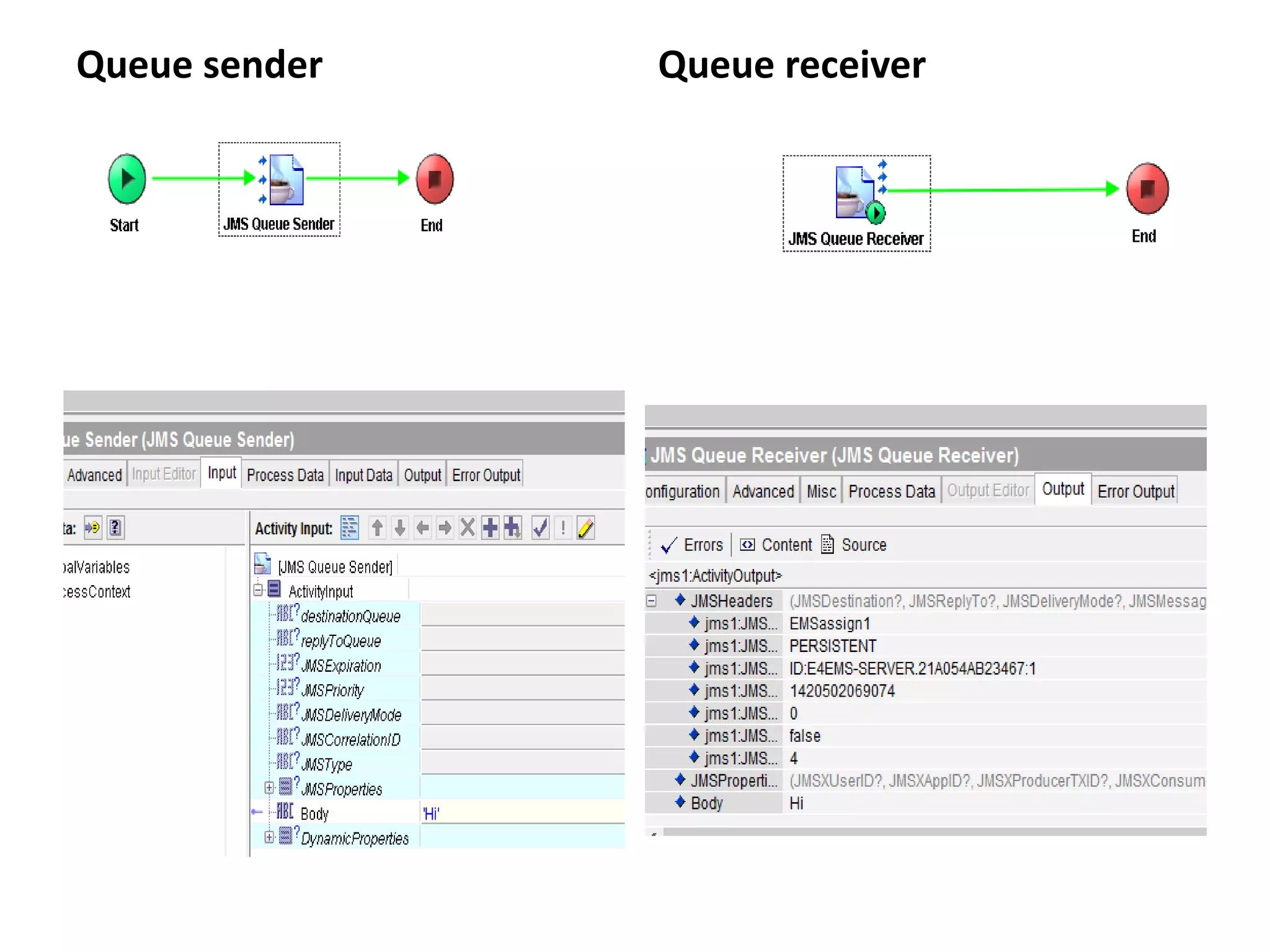
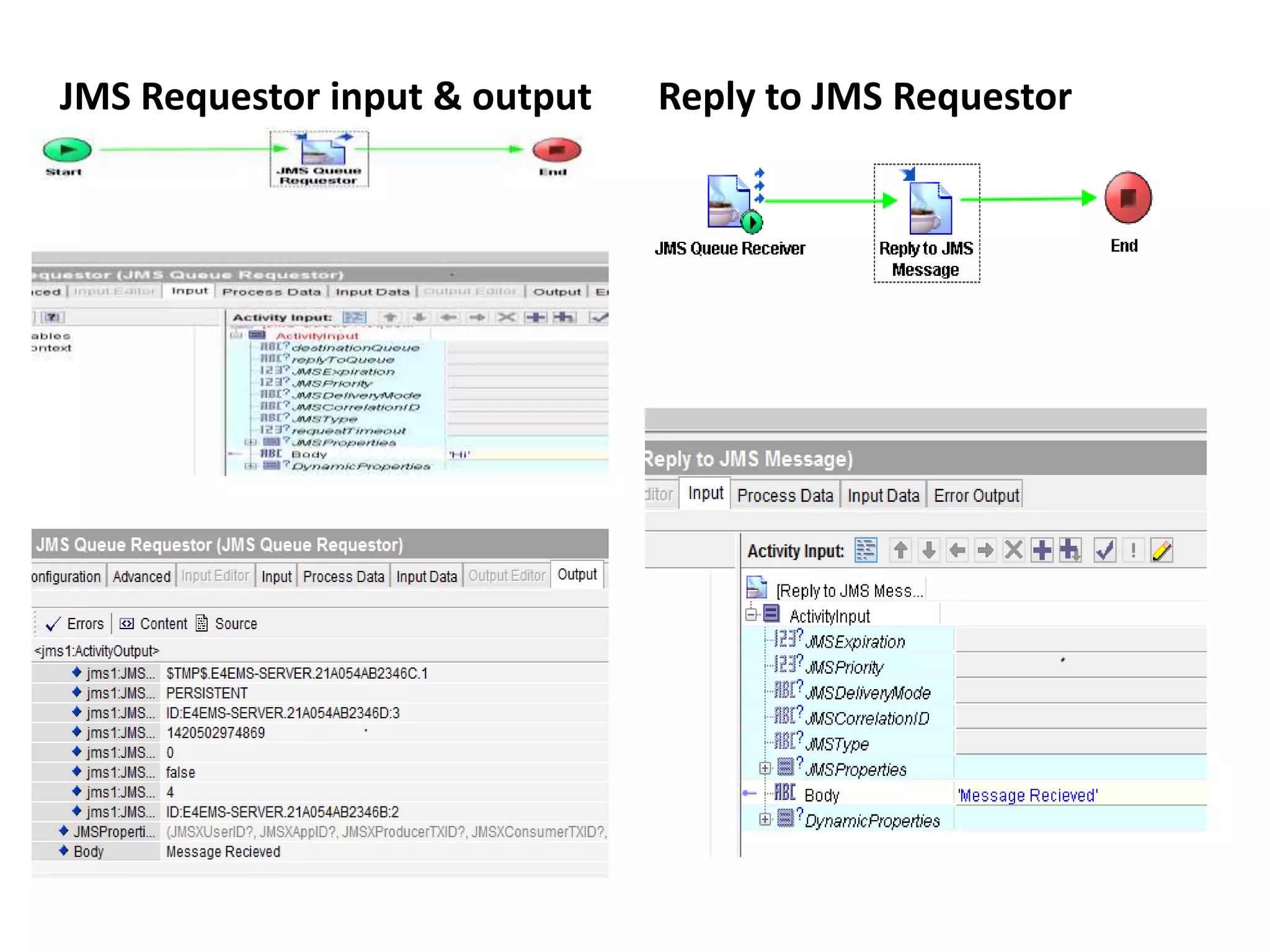
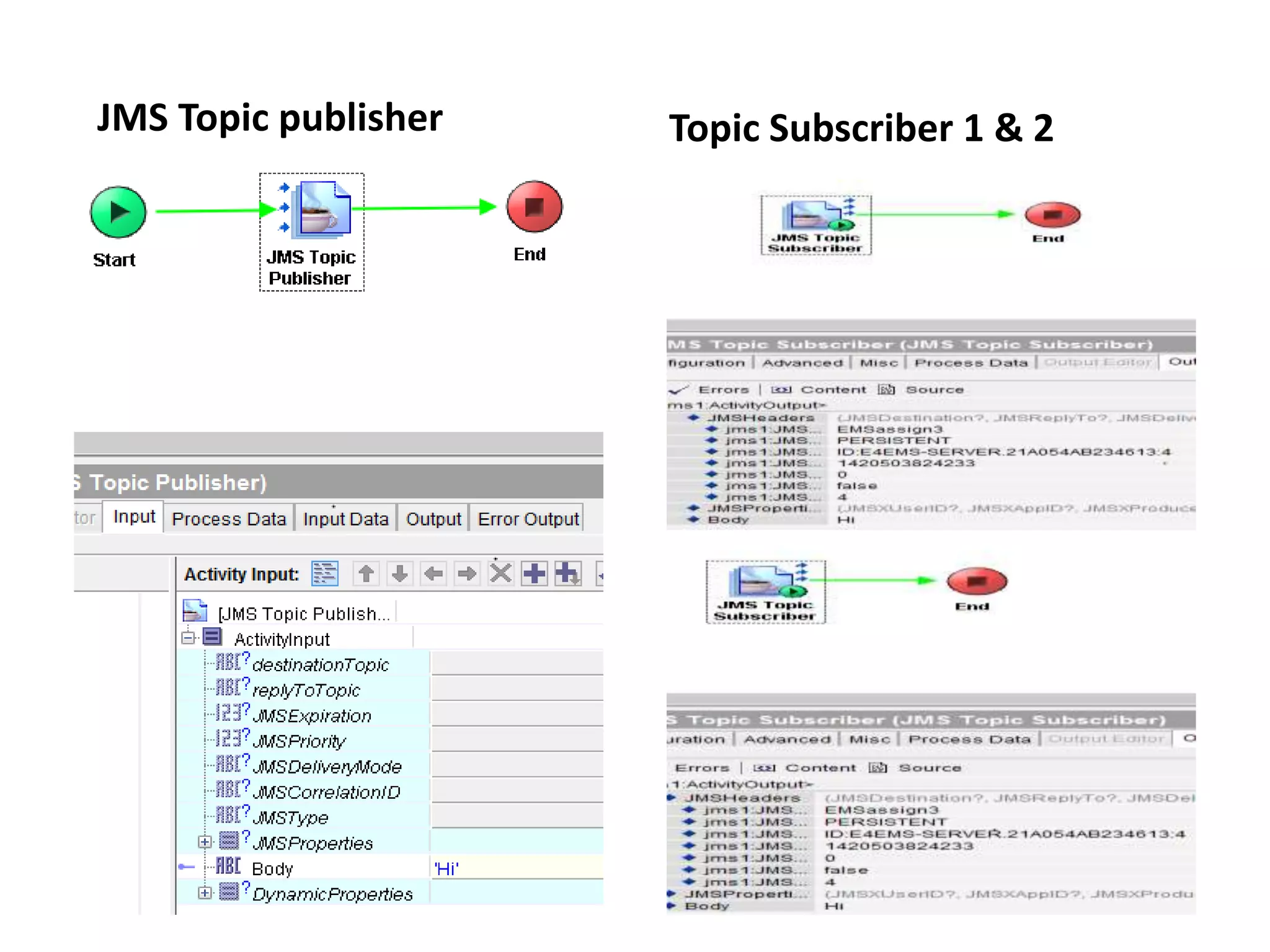
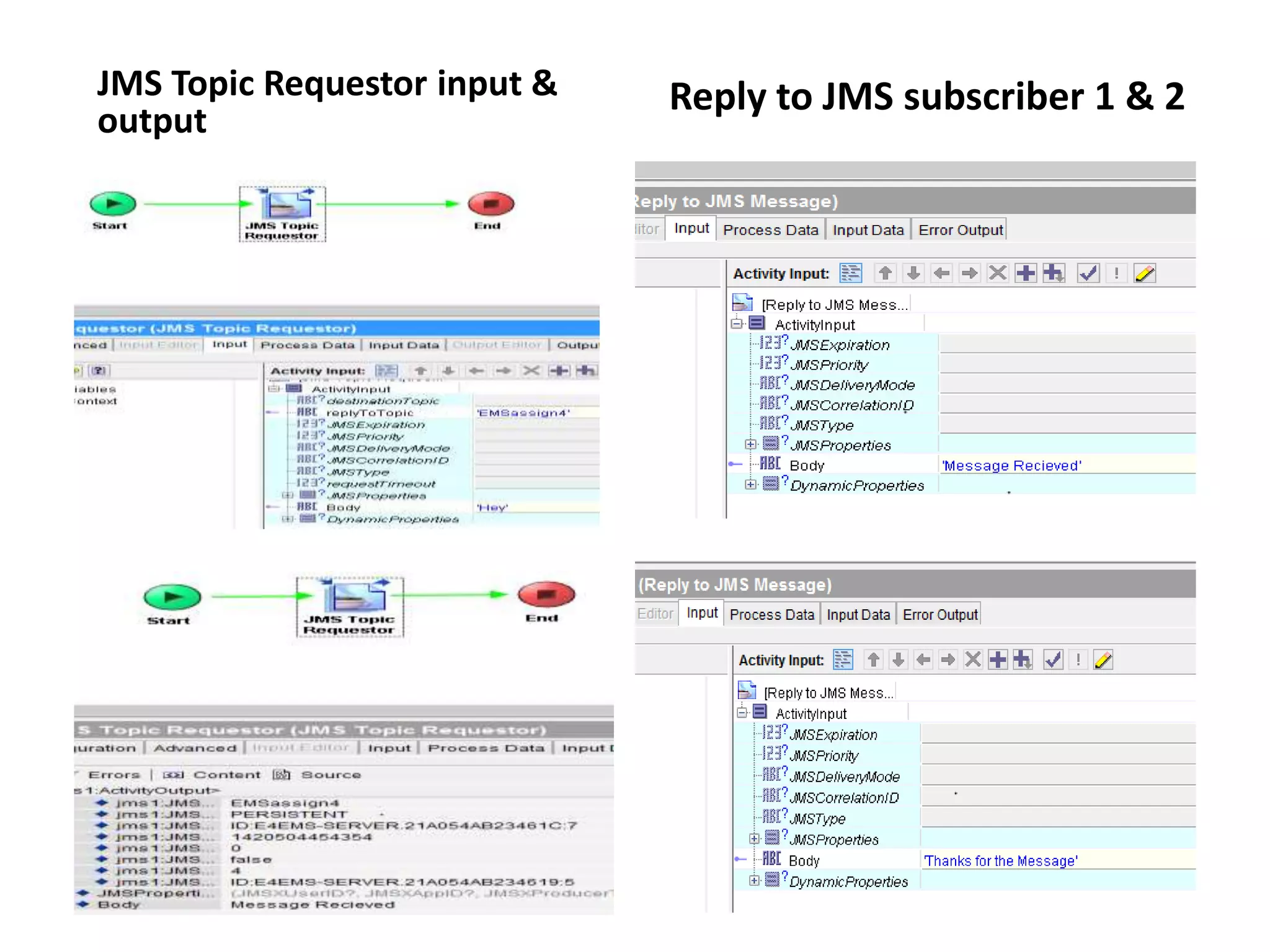
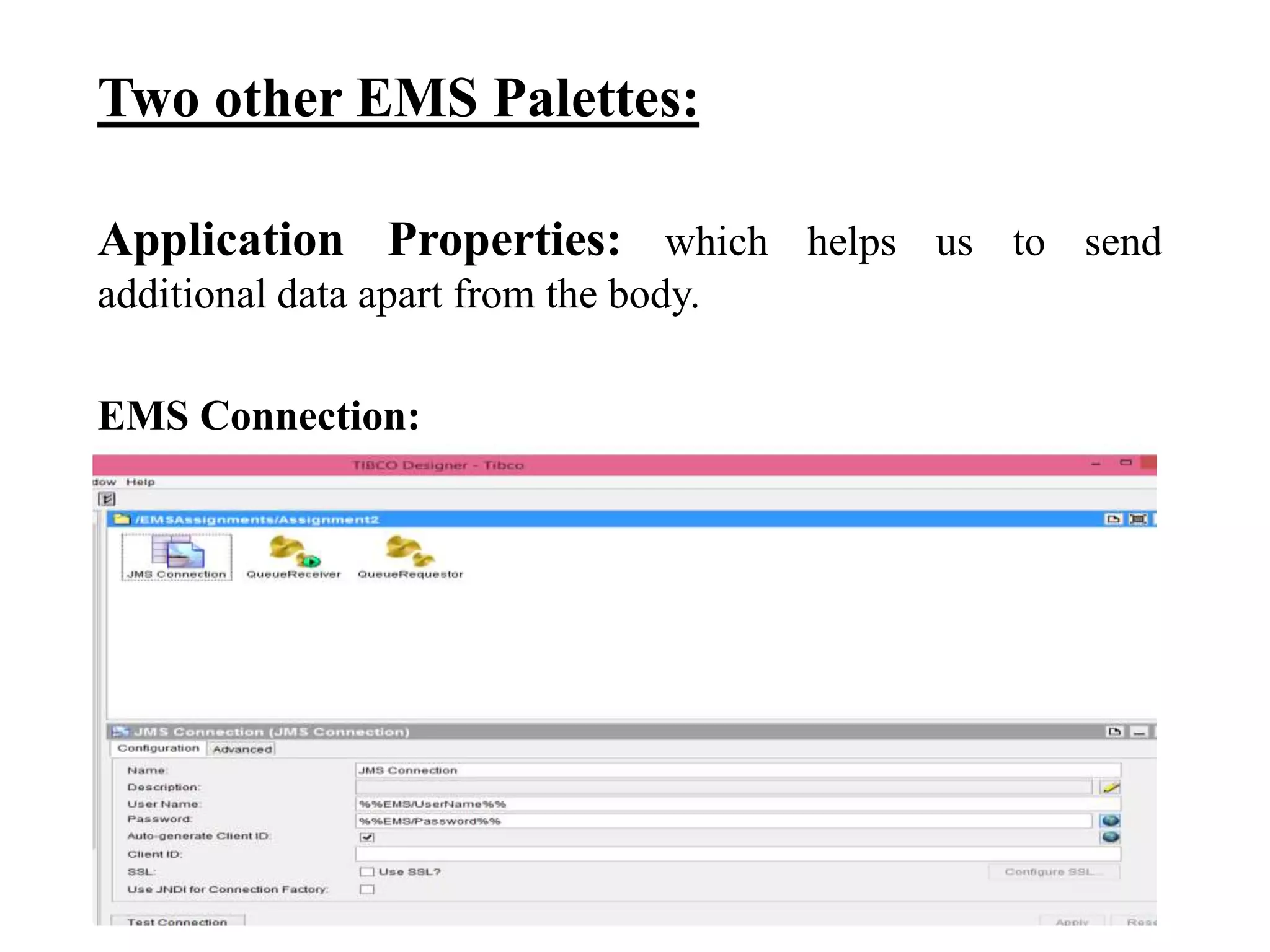
The document provides an overview of Enterprise Message Service (EMS), detailing its message delivery modes: persistent, non-persistent, and reliable delivery, alongside their implications for message performance and reliability. It explains key components such as queues and topics for message delivery, distinguishing between point-to-point and publish-subscribe messaging models. Additional information covers EMS server functions, message structure, and various activities for message sending and receiving.