This document provides an overview of Java Message Service (JMS) including:
- JMS enables loosely coupled, asynchronous messaging between distributed applications.
- The JMS API is used to create, send, receive and read messages.
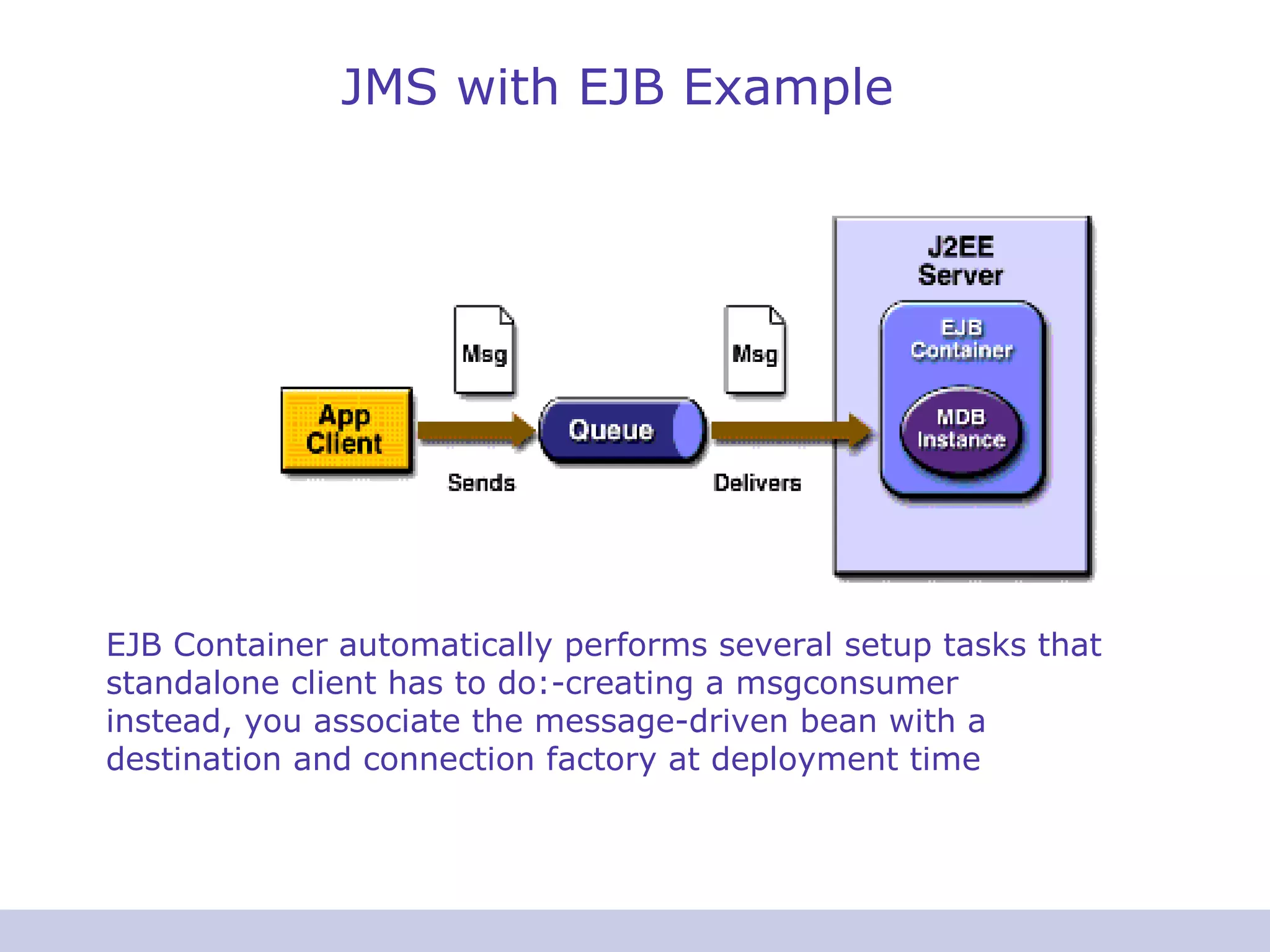
- JMS uses administered objects like connection factories and destinations that clients look up to access the provider.
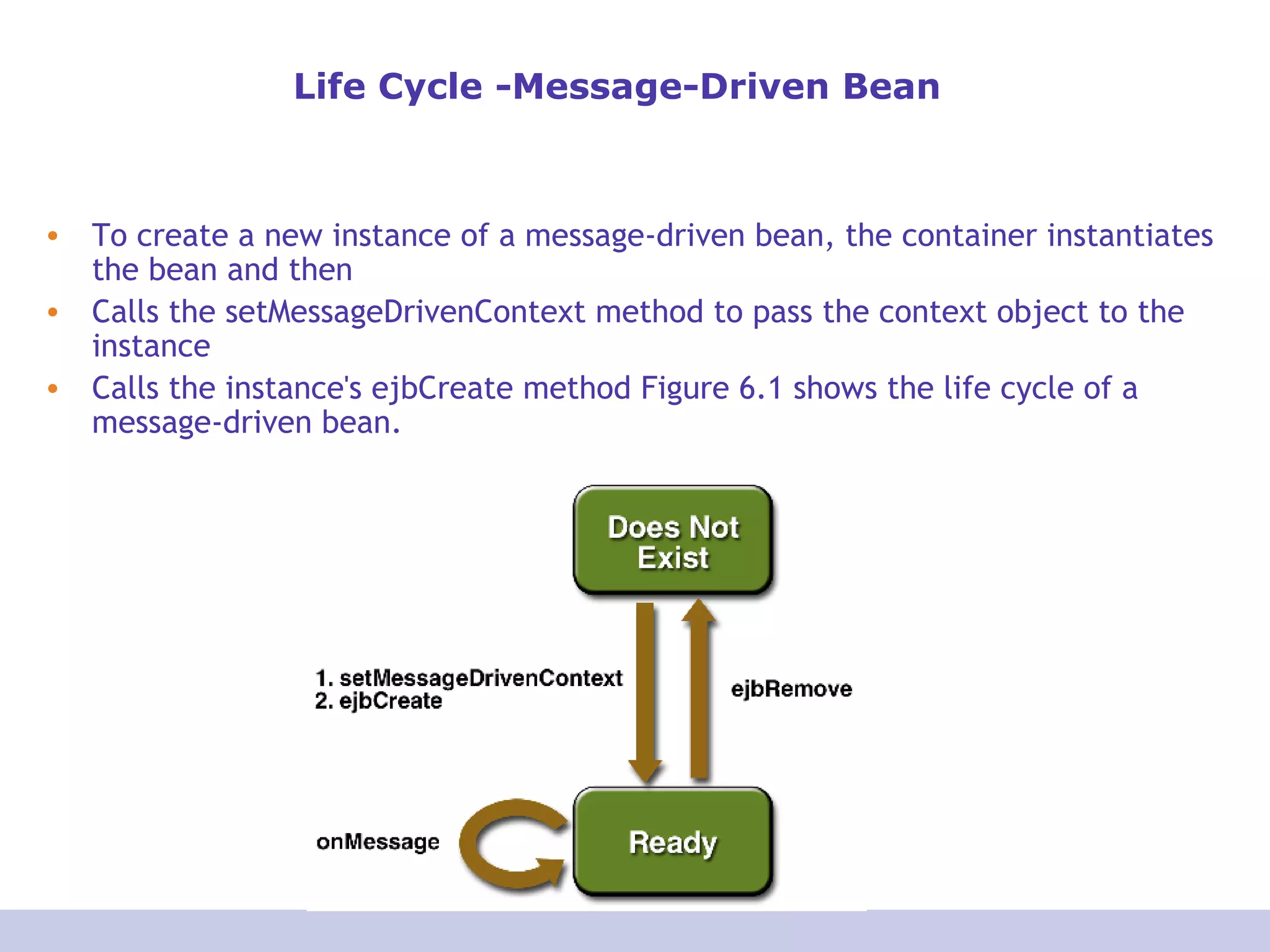
- Messages can be consumed synchronously or asynchronously using message listeners.
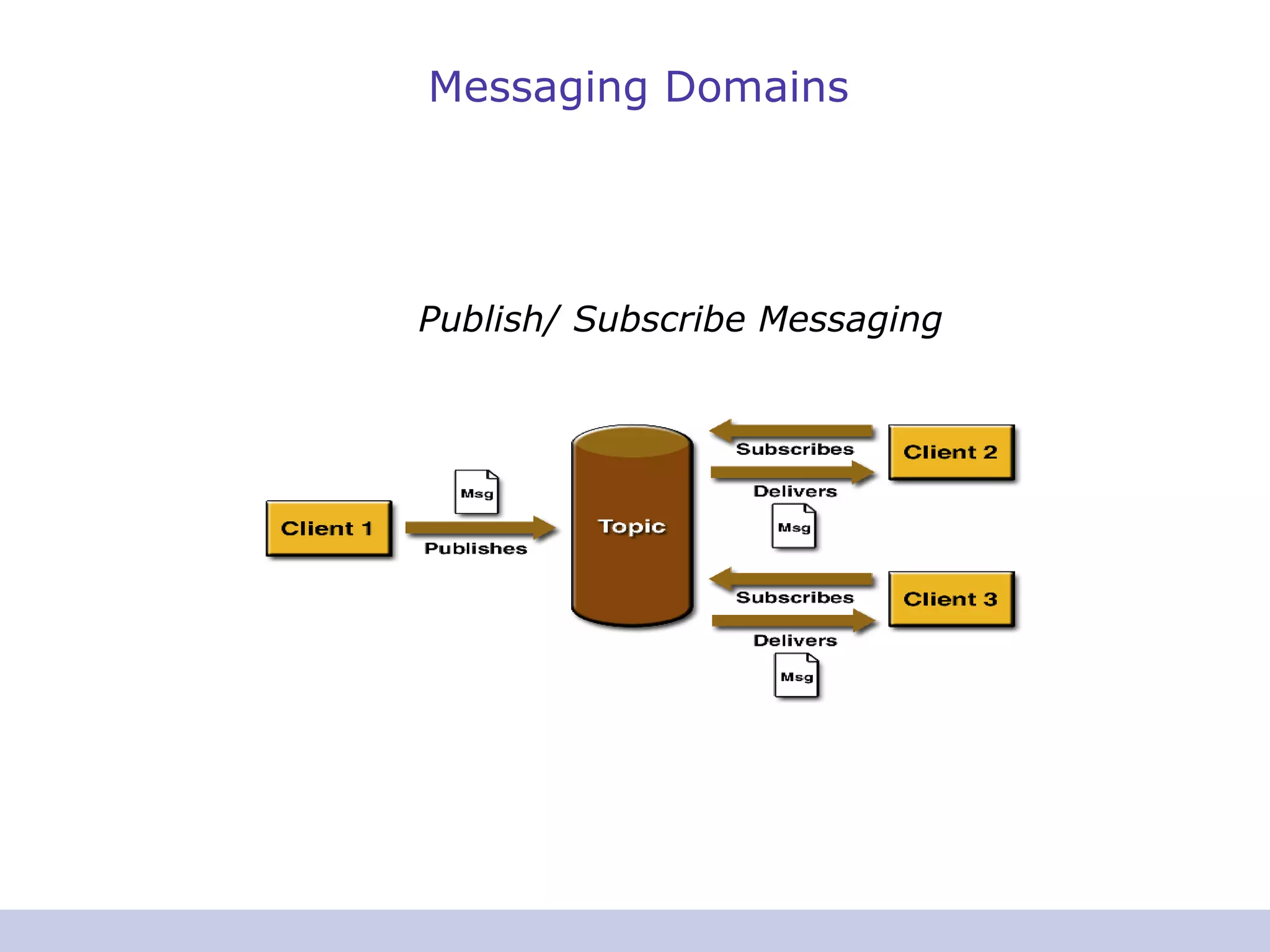
- JMS supports two messaging domains: point-to-point and publish/subscribe.