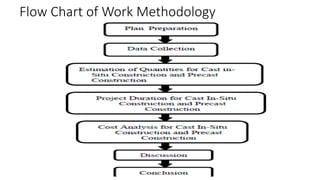
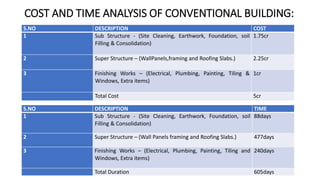
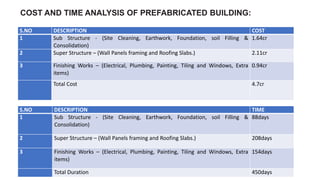
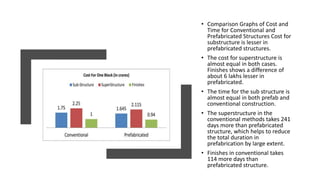
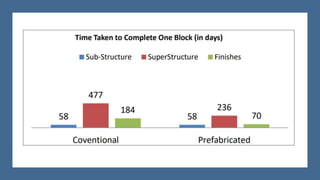
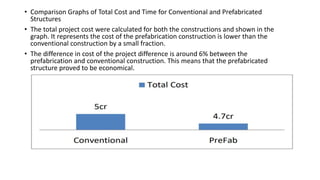
The document presents a comparative study between precast construction and conventional construction for low-cost housing. It analyzes the cost and time required for each type of construction based on a case study of a residential building project in Andhra Pradesh, India. The study found that precast construction has a slightly lower total cost (around 6% less) and significantly shorter completion time (355 days less) compared to conventional construction. It suggests several measures to promote increased use of precast construction in India, such as investment in research, standardization of elements, training more engineers, and government incentives.