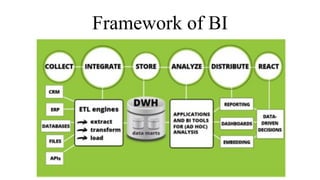
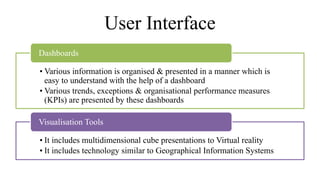
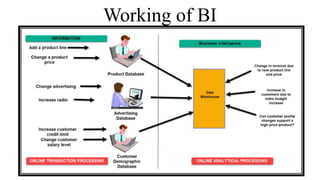
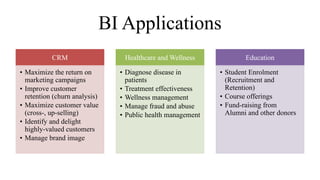
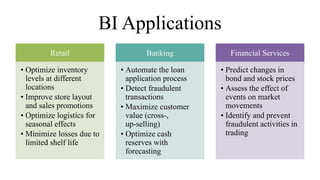
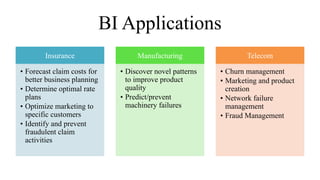
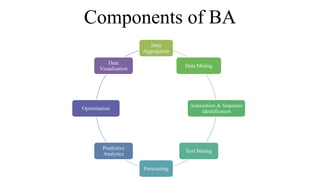
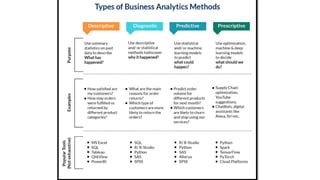
Business intelligence (BI) is a broad set of technologies used to gather, store, analyze and provide access to data to help business users make better decisions. BI technologies include reporting, dashboards, data mining, etc. Business analytics (BA) focuses more on predictive analytics using statistical modeling and machine learning to predict future outcomes and optimize decisions. While BI and BA overlap, BI answers questions about past performance, while BA answers questions about why things are happening, what will happen next, and how to optimize outcomes.