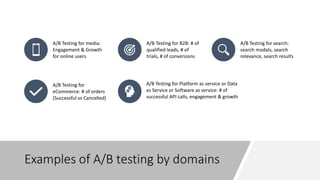
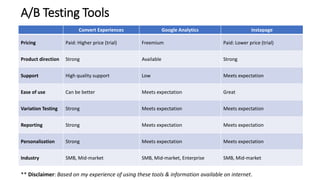
A/B testing involves showing two variants of a digital experience to different user groups and measuring which performs better according to key metrics. It is used to test hypotheses about how to improve user engagement and conversion rates. The process involves researching problems, developing hypotheses, creating alternatives, validating alternatives through testing, and then implementing the best performing version. Some best practices include focusing tests, using statistical analysis, controlling for external factors, and collecting user feedback. Common areas to conduct A/B tests include websites, apps, search, ecommerce, and APIs. Popular A/B testing tools vary in features and pricing.