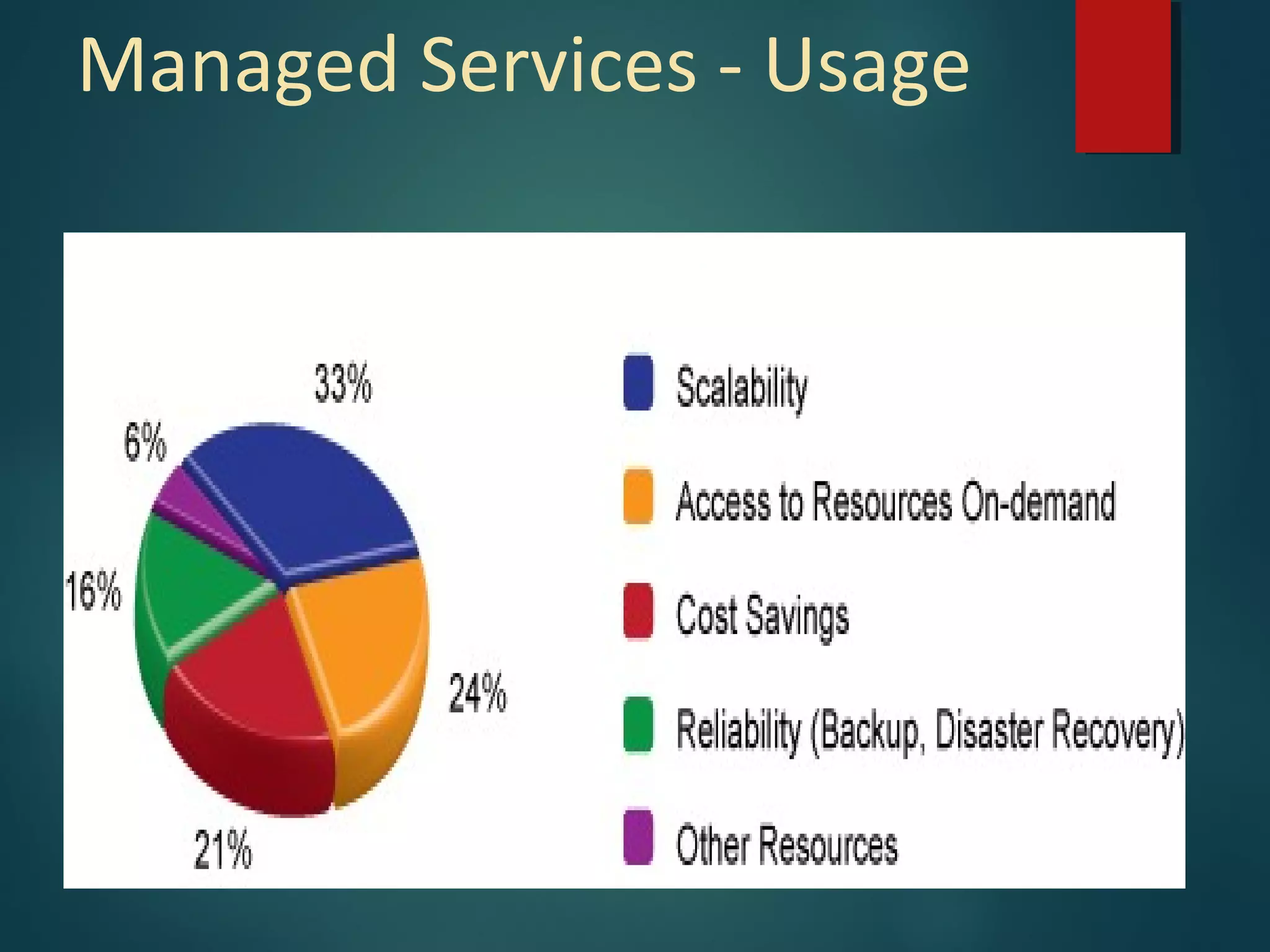
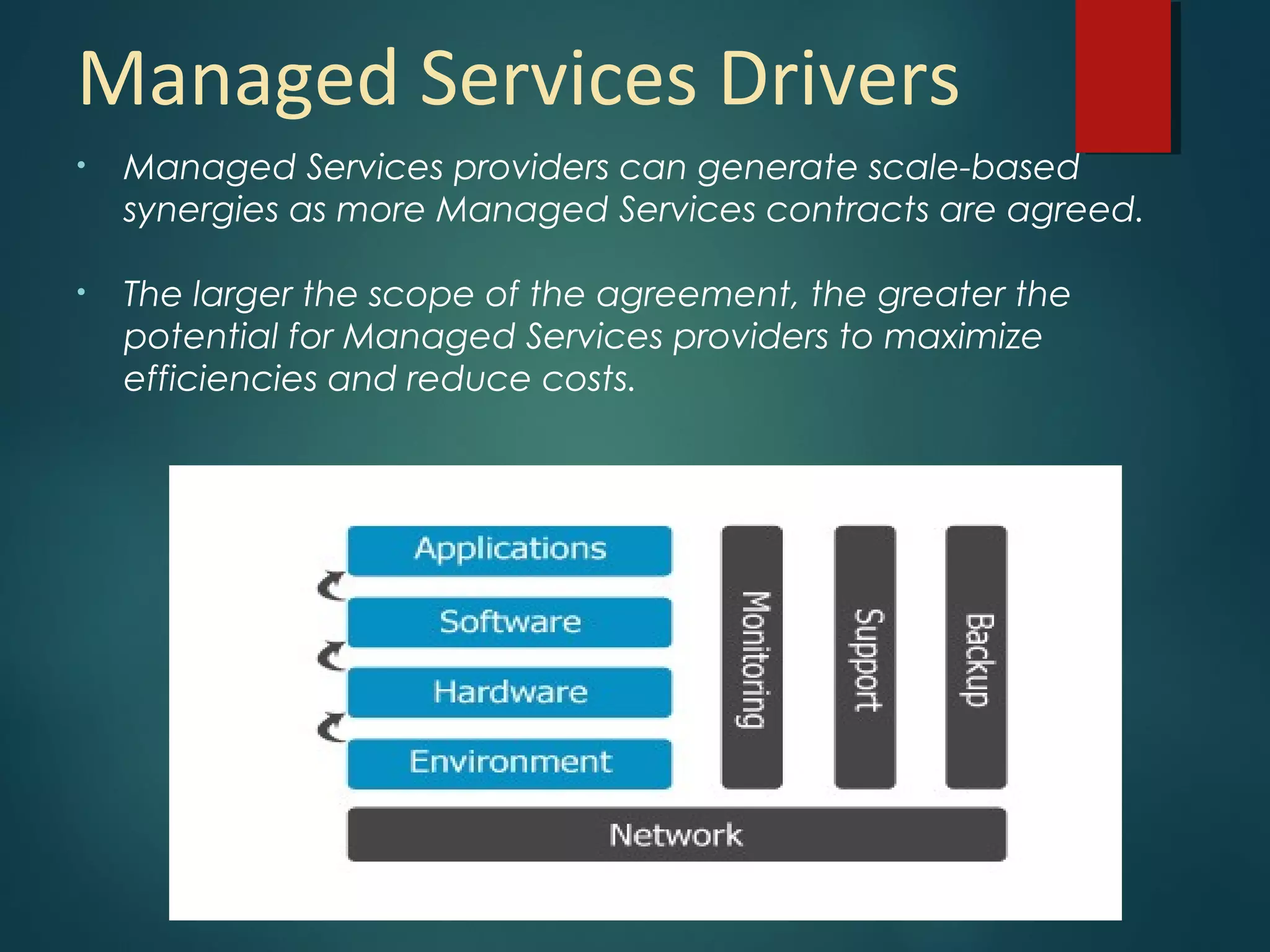
Managed services involve outsourcing management responsibilities to improve operations and reduce costs, especially in organizations with multiple locations or specialized needs. Key benefits include 24/7 monitoring, a single point of contact for issues, and cost efficiencies for both customers and service providers. A successful managed services model requires strategic development, operational planning, and implementation to ensure long-term business effectiveness.