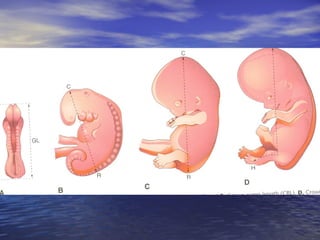
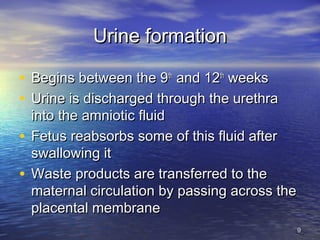
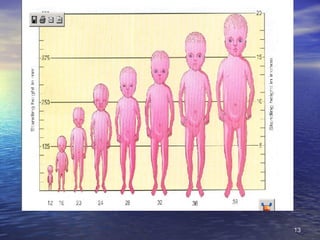
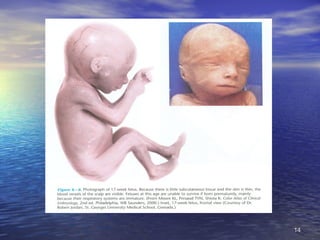
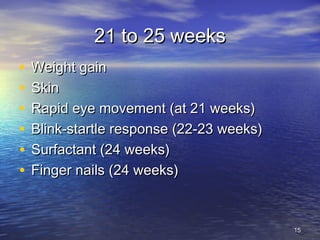
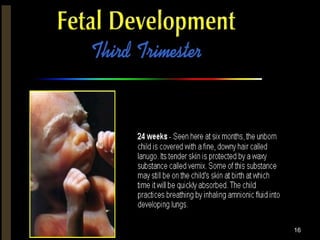
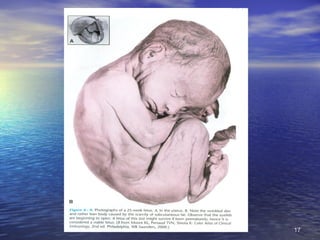
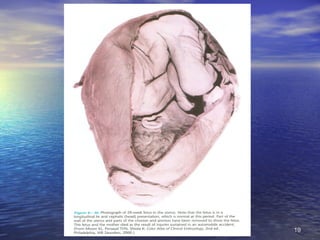
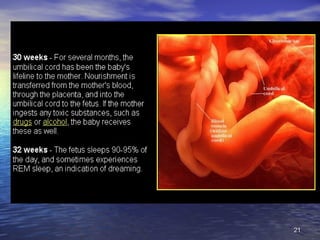
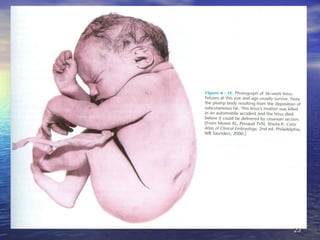
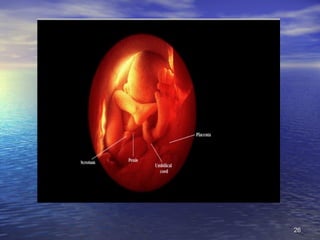
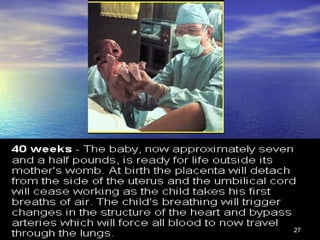
The document outlines the stages of fetal development from 9 weeks to birth, detailing key growth milestones, organ differentiation, and changes occurring in both the fetus and placenta. It covers various periods, emphasizing rapid growth phases, the establishment of vital functions like urine formation and nutrient exchange, and physical developments including limb formation and the differentiation of reproductive organs. Additionally, the document highlights the importance of the placenta and various physiological changes leading to childbirth.