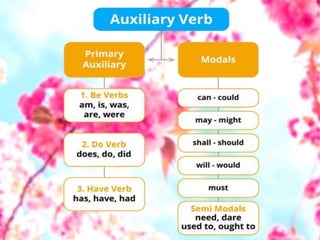
There are two types of auxiliary verbs: primary and modal. Primary auxiliaries like be, have, and do are used to show tense and can function as main verbs. Modal verbs like can, could, may, and must are used to express ideas like possibility, intention, ability or necessity. Semi-modal verbs like dare, need, ought to and used to have characteristics of both modal and main verbs.