9.Seed, Classes of seed and Seed germination.pptx
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
0 likes•56 views
Seed germination
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
Similar to 9.Seed, Classes of seed and Seed germination.pptx
Similar to 9.Seed, Classes of seed and Seed germination.pptx (20)
“ Seed and Fruit development and Seed and Fruit Abortion ”.pptx

“ Seed and Fruit development and Seed and Fruit Abortion ”.pptx
endospermcultureandsomaticembryogenesis-150823084254-lva1-app6891.pdf

endospermcultureandsomaticembryogenesis-150823084254-lva1-app6891.pdf
More from UmeshTimilsina1
More from UmeshTimilsina1 (20)
Plant propagation: Sexual and Asexual propapagation.pptx

Plant propagation: Sexual and Asexual propapagation.pptx
24. Importance and prospects of Organic horticulture in Nepal.pptx

24. Importance and prospects of Organic horticulture in Nepal.pptx
23. Importance and prospect of Indigenous horticulture crops.pptx

23. Importance and prospect of Indigenous horticulture crops.pptx
22. Hyydroponics, aeroponics, verticulture and riverbed farming.pptx

22. Hyydroponics, aeroponics, verticulture and riverbed farming.pptx
21. Highdensity planting, multistoried cropping and multiple cropping.pptx

21. Highdensity planting, multistoried cropping and multiple cropping.pptx
18. Training and prunning of horicultural crops.pptx

18. Training and prunning of horicultural crops.pptx
16. Discovery, function and commercial uses of different PGRS.pptx

16. Discovery, function and commercial uses of different PGRS.pptx
20. Unfruitfullness: its Causes and Control measures pptx

20. Unfruitfullness: its Causes and Control measures pptx
13. Tuber, rhizome and bulb development and Ageing and senescence.pptx

13. Tuber, rhizome and bulb development and Ageing and senescence.pptx
12. Pollination, fertilization ,Fruit set and fruit development.pptx

12. Pollination, fertilization ,Fruit set and fruit development.pptx
11. Reproductive phase: Plant growth and development.pptx

11. Reproductive phase: Plant growth and development.pptx
5. Classification of Fruits according to types.pptx

5. Classification of Fruits according to types.pptx
3. Agro-Ecological zoning and niches form the horticultural perspective.pptx

3. Agro-Ecological zoning and niches form the horticultural perspective.pptx
2. Botanical based classification of horticultural plants (2).pptx

2. Botanical based classification of horticultural plants (2).pptx
1. Horticultural based Classification of Horticultural crops.pptx

1. Horticultural based Classification of Horticultural crops.pptx
2. Importance, Scope, national policies of horticulture and constraints [Auto...

2. Importance, Scope, national policies of horticulture and constraints [Auto...
Recently uploaded
God is a creative God Gen 1:1. All that He created was “good”, could also be translated “beautiful”. God created man in His own image Gen 1:27. Maths helps us discover the beauty that God has created in His world and, in turn, create beautiful designs to serve and enrich the lives of others.
Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...

Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...christianmathematics
Mehran University Newsletter is a Quarterly Publication from Public Relations OfficeMehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024

Mehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024Mehran University of Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro
APM Welcome
Tuesday 30 April 2024
APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across Sectors
Presented by:
Professor Adam Boddison OBE, Chief Executive Officer, APM
Conference overview:
https://www.apm.org.uk/community/apm-north-west-branch-conference/
Content description:
APM welcome from CEO
The main conference objective was to promote the Project Management profession with interaction between project practitioners, APM Corporate members, current project management students, academia and all who have an interest in projects.APM Welcome, APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across Sectors

APM Welcome, APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across SectorsAssociation for Project Management
Recently uploaded (20)
Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx

Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx
ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx

ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx
Beyond the EU: DORA and NIS 2 Directive's Global Impact

Beyond the EU: DORA and NIS 2 Directive's Global Impact
Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...

Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...
Presentation by Andreas Schleicher Tackling the School Absenteeism Crisis 30 ...

Presentation by Andreas Schleicher Tackling the School Absenteeism Crisis 30 ...
This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.

This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.
APM Welcome, APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across Sectors

APM Welcome, APM North West Network Conference, Synergies Across Sectors
9.Seed, Classes of seed and Seed germination.pptx
- 6. Jamun Durian
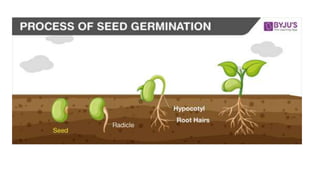
- 9. SEED GERMINATION •Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or similar structure. •The most common example of germination is the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm. • In addition, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of hyphae from fungal spores, is also germination.
- 10. • The part of the plant that first emerges from the seed is the embryonic root, termed the radicle or primary root. • It allows the seedling to become anchored in the ground and start absorbing water. • After the root absorbs water, an embryonic shoot emerges from the seed. • This shoot comprises three main parts: the cotyledons (seed leaves), the section of shoot below the cotyledons (hypocotyl), and the section of shoot above the cotyledons (epicotyl). • The way the shoot emerges differs among plant groups.
- 11. Video on Seed Germination
- 12. Seed germination : Mechanisms • Seed germination represents a dynamic period in life cycle of plants as a seed makes the transition from a metabolically quiescent to an active and growing entity. • The sequence of germination in its simplest form: 1. Water imbibition 2. Enzyme activation 3. Hydrolysis and catabolism of storage materials 4. Initiation of growth 5. Formation of new cells 6. Rupture of seed coat and 7. Emergence of seedling
- 14. Types of germination 1. Dicot germination Hypogeal germination Epigeal germination 2. Monocot germination Hypogeal germination
- 15. Video on Epigeal and hypogeal germination
- 16. a. Epigeal germination • In epigeal germination (or epigeous germination), the hypocotyl elongates and forms a hook, pulling rather than pushing the cotyledons and apical meristem through the soil. • Once it reaches the surface, it straightens and pulls the cotyledons and shoot tip of the growing seedlings into the air. • Beans, most of the vegetables, tamarind and papaya are examples of plants that germinate this way.
- 17. b. Hypogeal • In this type of germination, the epicotyl elongates and forms the hook. • In this type of germination, the cotyledons stay underground where they eventually decompose. • Peas, gram, groundnut and mango, for example, germinate this way.
- 18. 2.Monocot germination • In monocot seeds, the embryo's radicle and cotyledon are covered by a coleorhiza and coleoptile, respectively. • The coleorhiza is the first part to grow out of the seed, followed by the radicle. • The coleoptile is then pushed up through the ground until it reaches the surface. • There, it stops elongating and the first leaves emerge.