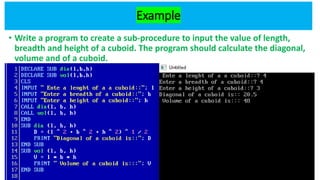
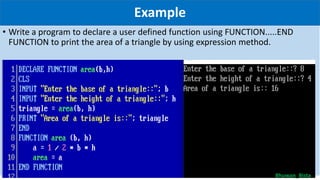
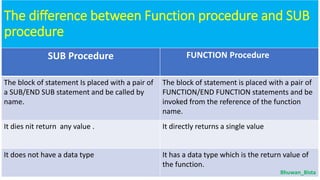
Modular programming involves dividing a program into smaller, manageable modules. The main module contains the program entry and exit points, while sub-modules perform specific tasks controlled by the main module. There are two types of procedures in modular programming - SUB procedures, which do not return values, and FUNCTION procedures, which return a single value. Parameters allow data to be passed into procedures to perform operations and return results. Modular programming offers benefits like reduced code, improved readability and maintainability, and ability to test modules independently.


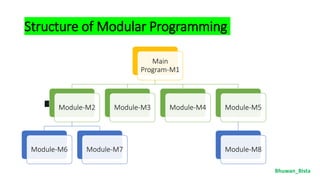





![Defining a SUB Procedure
oThe SUB....END SUB statement is a procedure
statement that marks the beginning and ending of a
subprogram. The syntax is:
SUB Procedure name [parameter, list]
[Statement]
END SUB
Bhuwan_Bista](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modularprogramming-210211052229/85/Modular-programming-9-320.jpg)