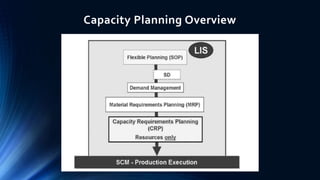
This document provides an overview of capacity planning in SAP PP. It discusses key capacity planning elements like available capacity, capacity requirements, capacity evaluation, and capacity leveling. Available capacity represents the work a resource can perform per day, while capacity requirements are calculated from planned order dates and quantities. Capacity evaluation compares requirements to available capacity. Capacity leveling aims to address shortfalls or overloads by dispatching operations to resources with sufficient capacity and achieving optimal loading. The document outlines how capacities and requirements are maintained and calculated in SAP PP.