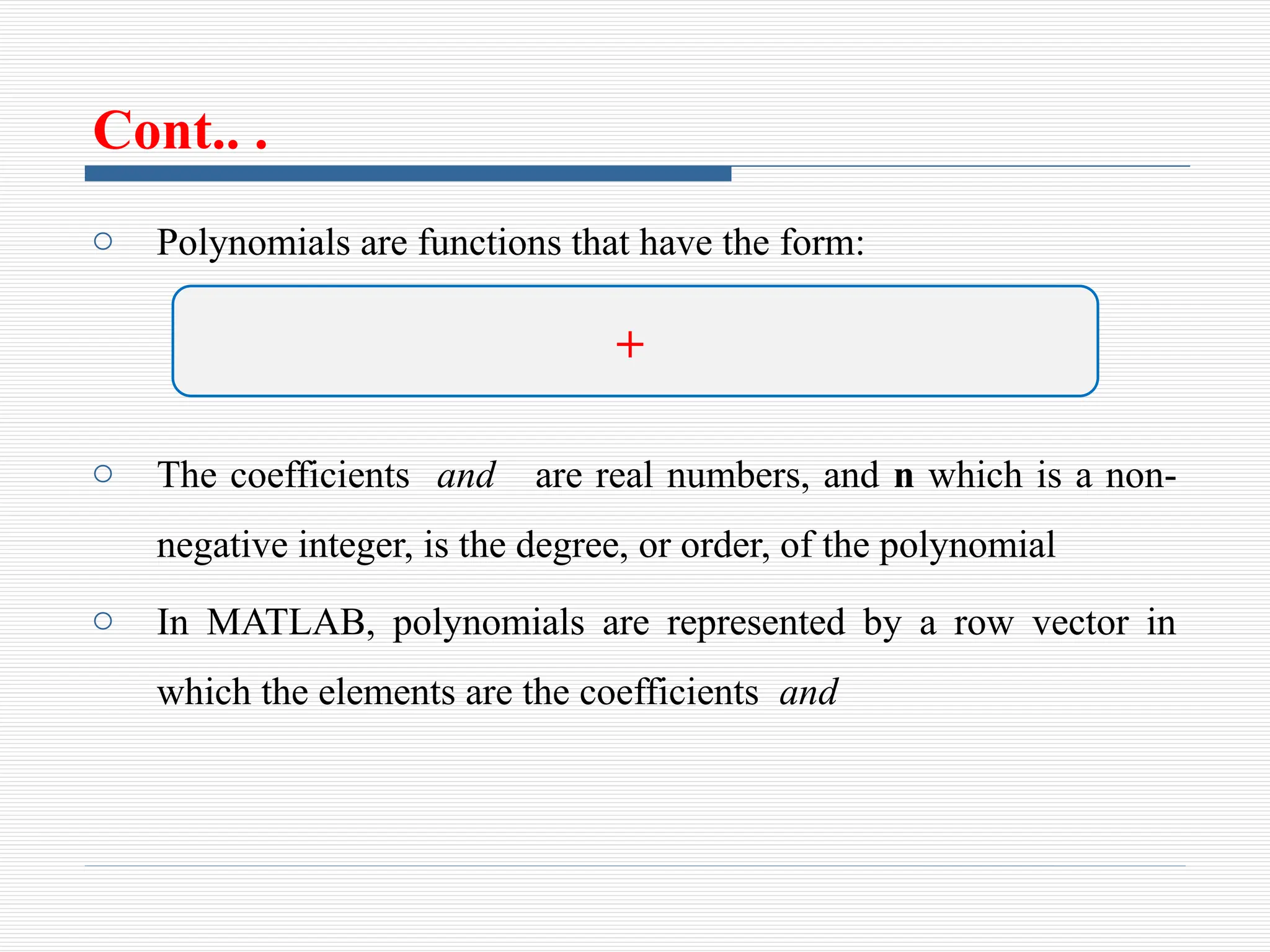
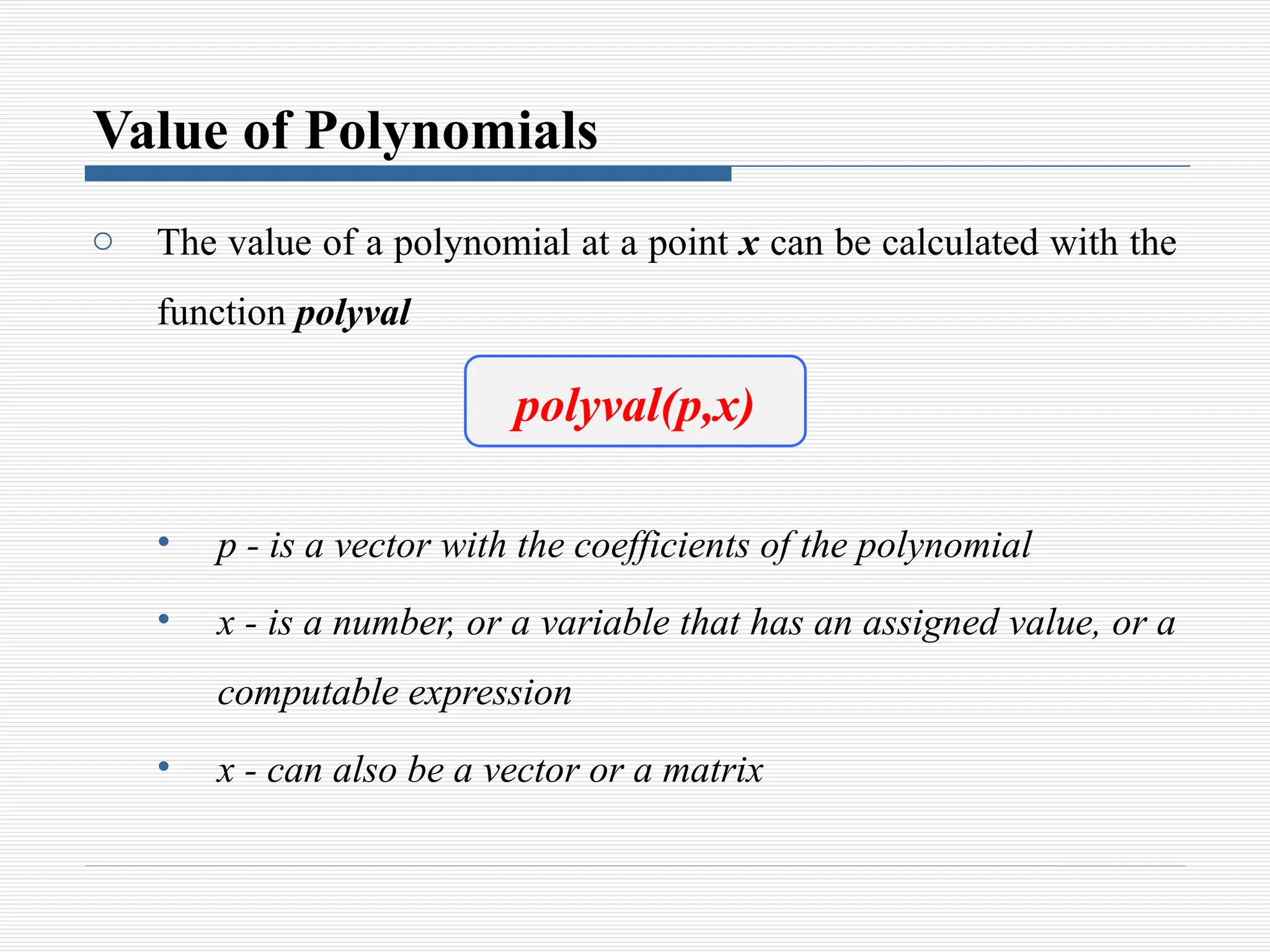
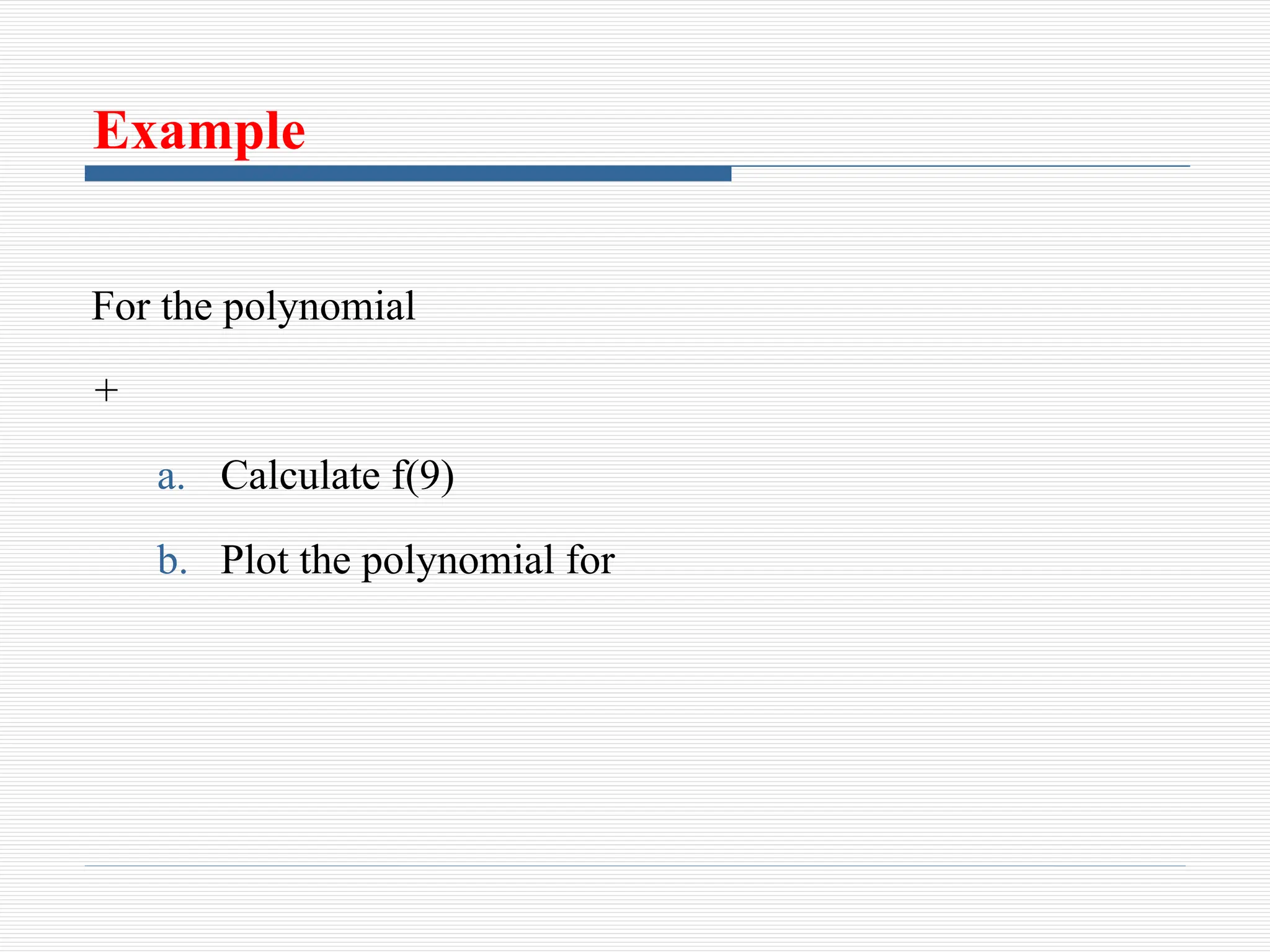
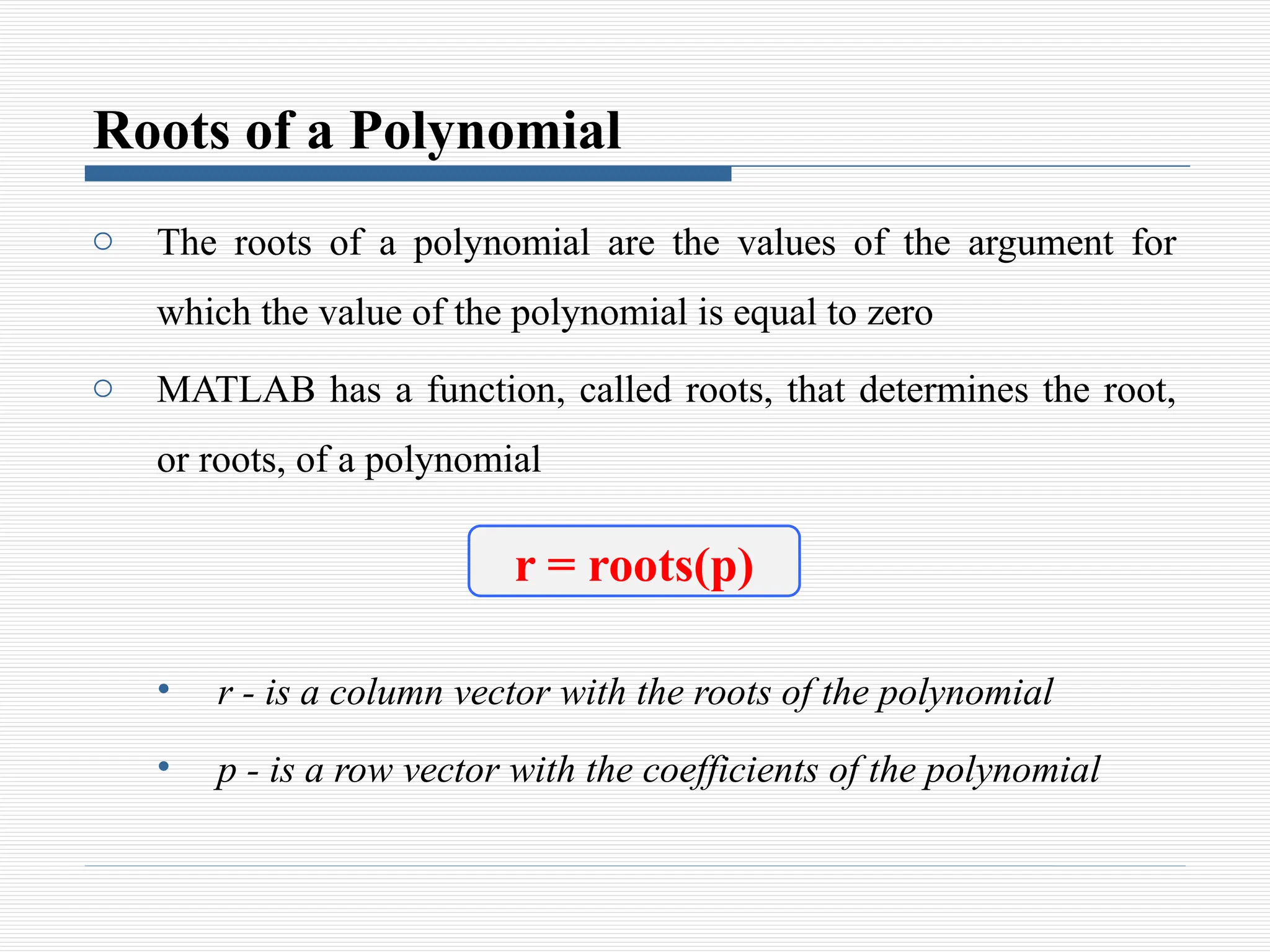
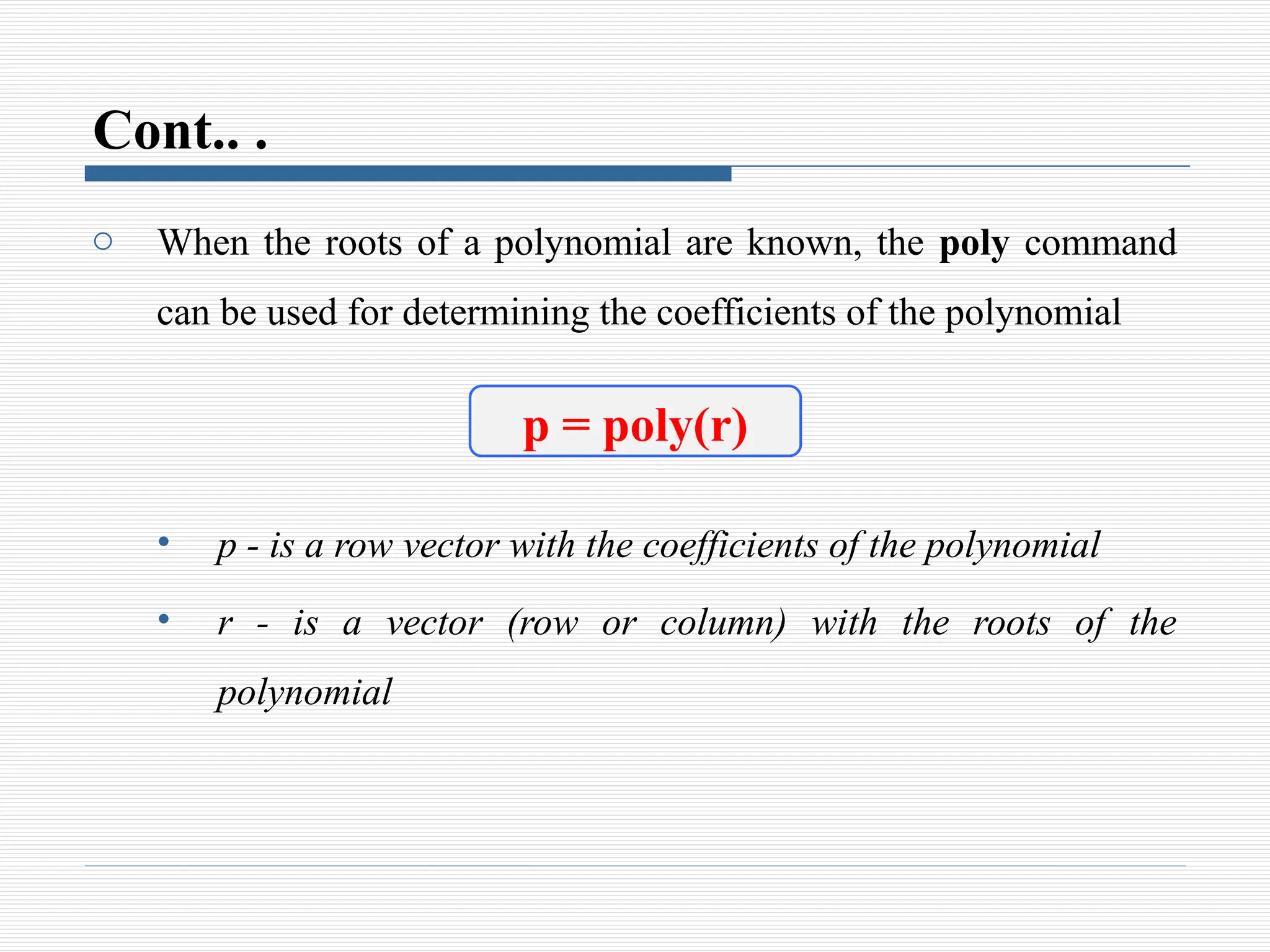
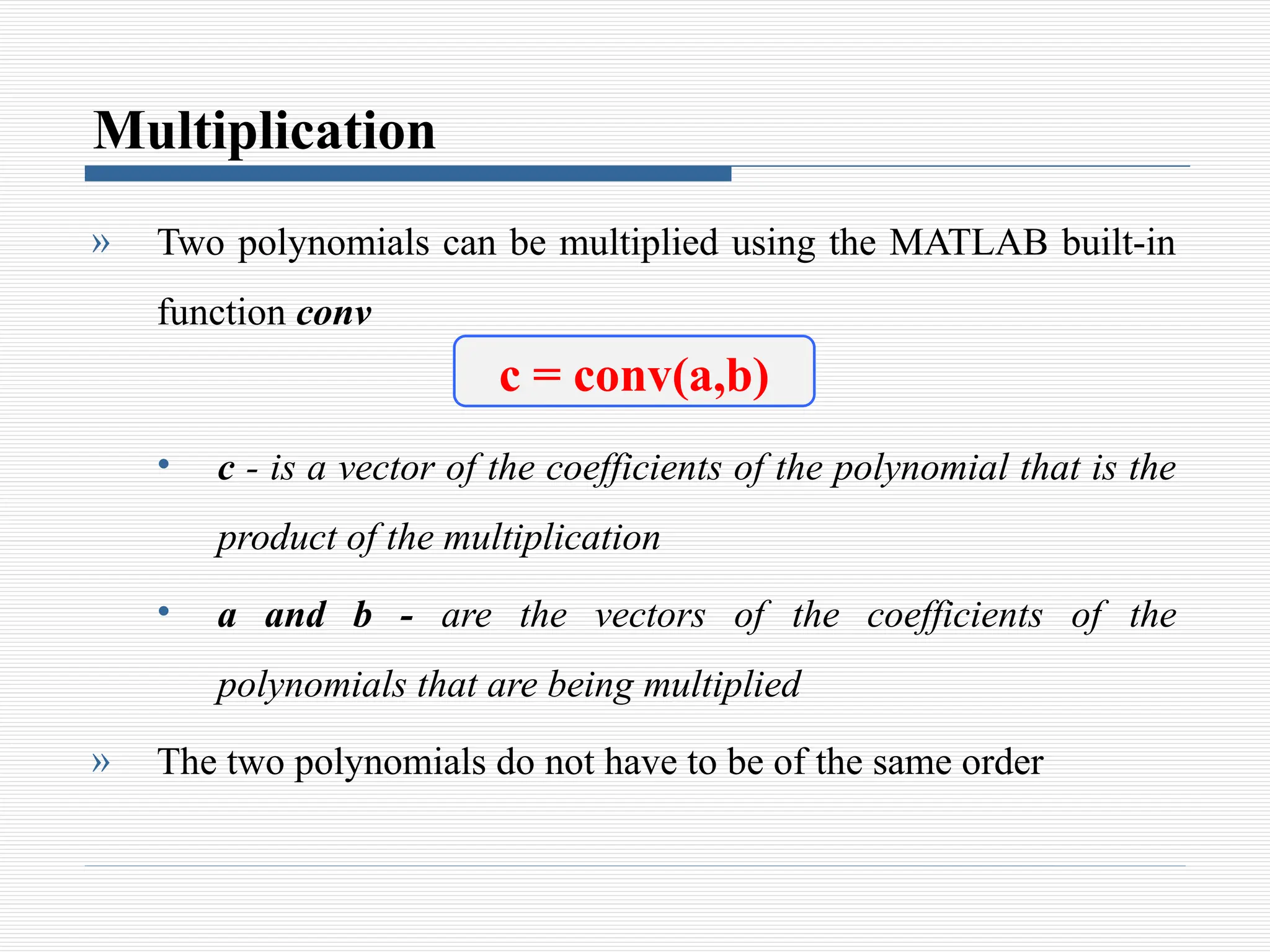
The document discusses the use of polynomials in problem solving and modeling within science and engineering, detailing their representation in MATLAB. It provides information on evaluating polynomials, finding roots, performing operations like addition, multiplication, and division, as well as calculating derivatives using MATLAB functions. Examples illustrate how to manipulate polynomials effectively within the software.

![Cont.. .
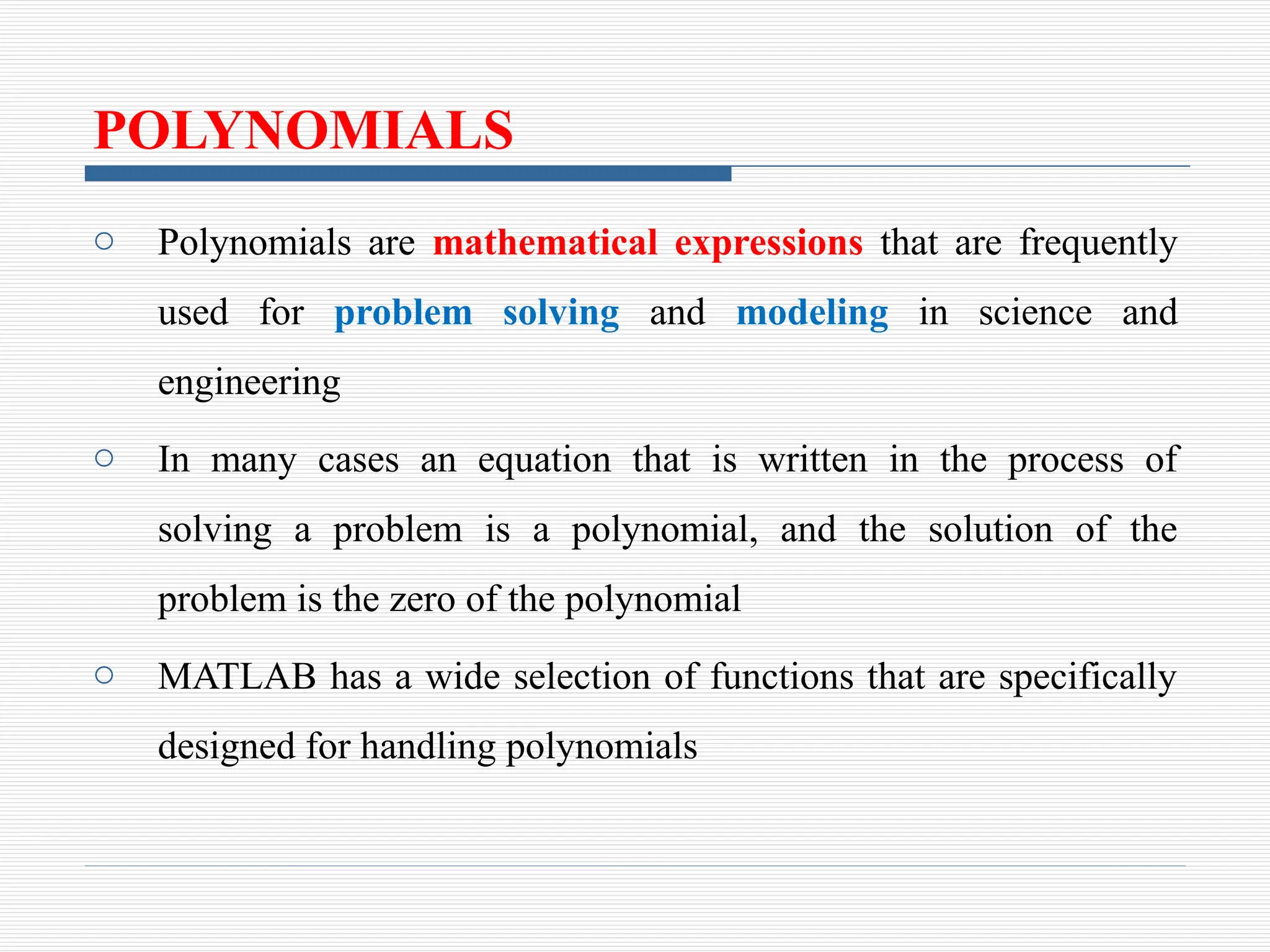
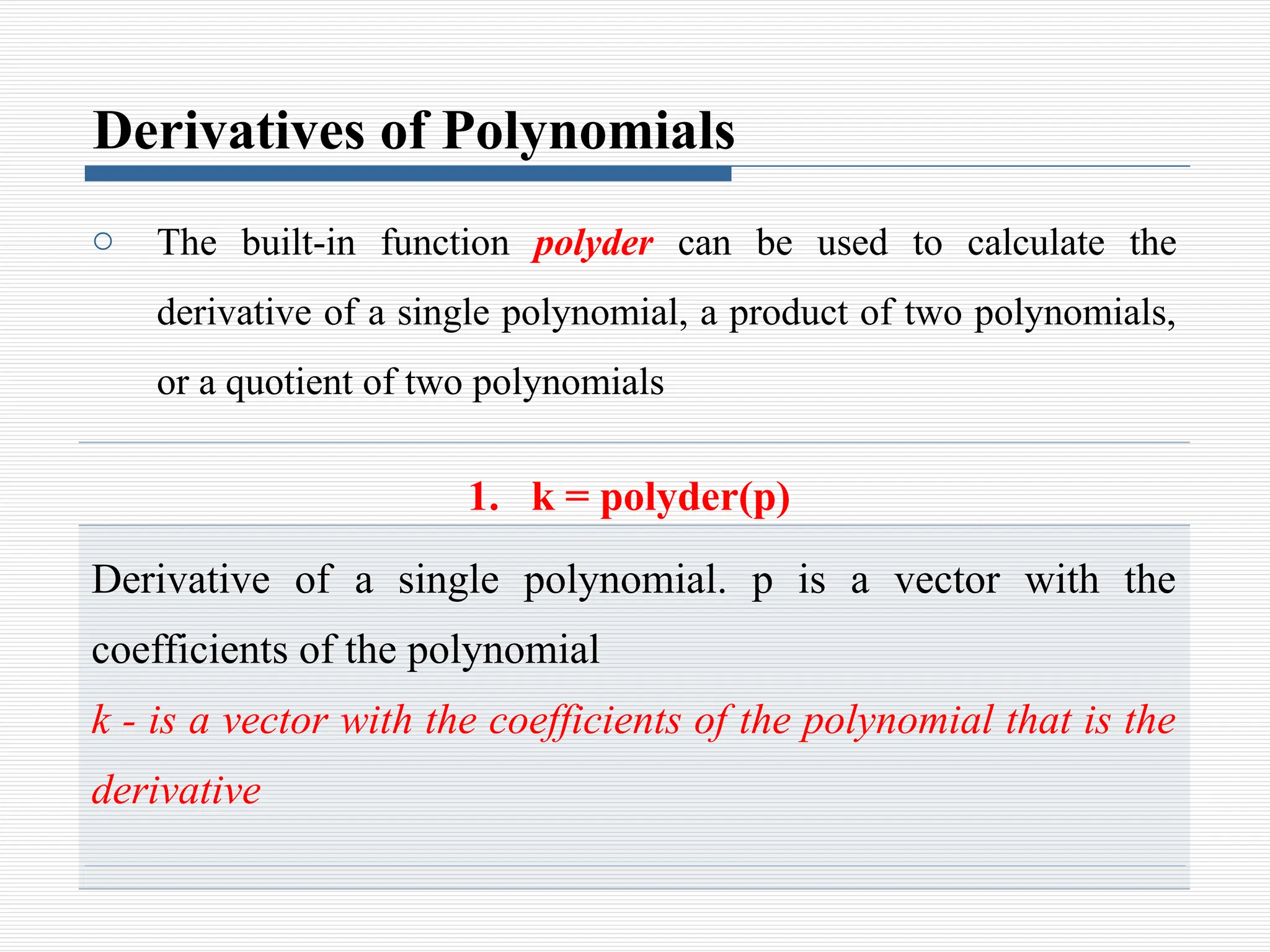
o The first element is the coefficient of the x with the highest
power
o The vector has to include all the coefficients, including the ones
that are equal to 0
Example:
Equation MATLAB Form
MATLAB Representation [ 5,0,0,6,7,0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8polynomialscurvefittinginterpolation-241107073648-366794e8/75/8_Polynomials-Curve-Fitting-Interpolation-pptx-4-2048.jpg)

![Division
» A polynomial can be divided by another polynomial with the
MATLAB built-in function deconv
• q - vector with the coefficients of the quotient polynomial.
• r - vector with the coefficients of the remainder polynomial
• u - vector with the coefficients of the numerator polynomial
• v - vector with the coefficients of the denominator polynomial
[q,r] = deconv(a,b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8polynomialscurvefittinginterpolation-241107073648-366794e8/75/8_Polynomials-Curve-Fitting-Interpolation-pptx-12-2048.jpg)

![Cont.. .
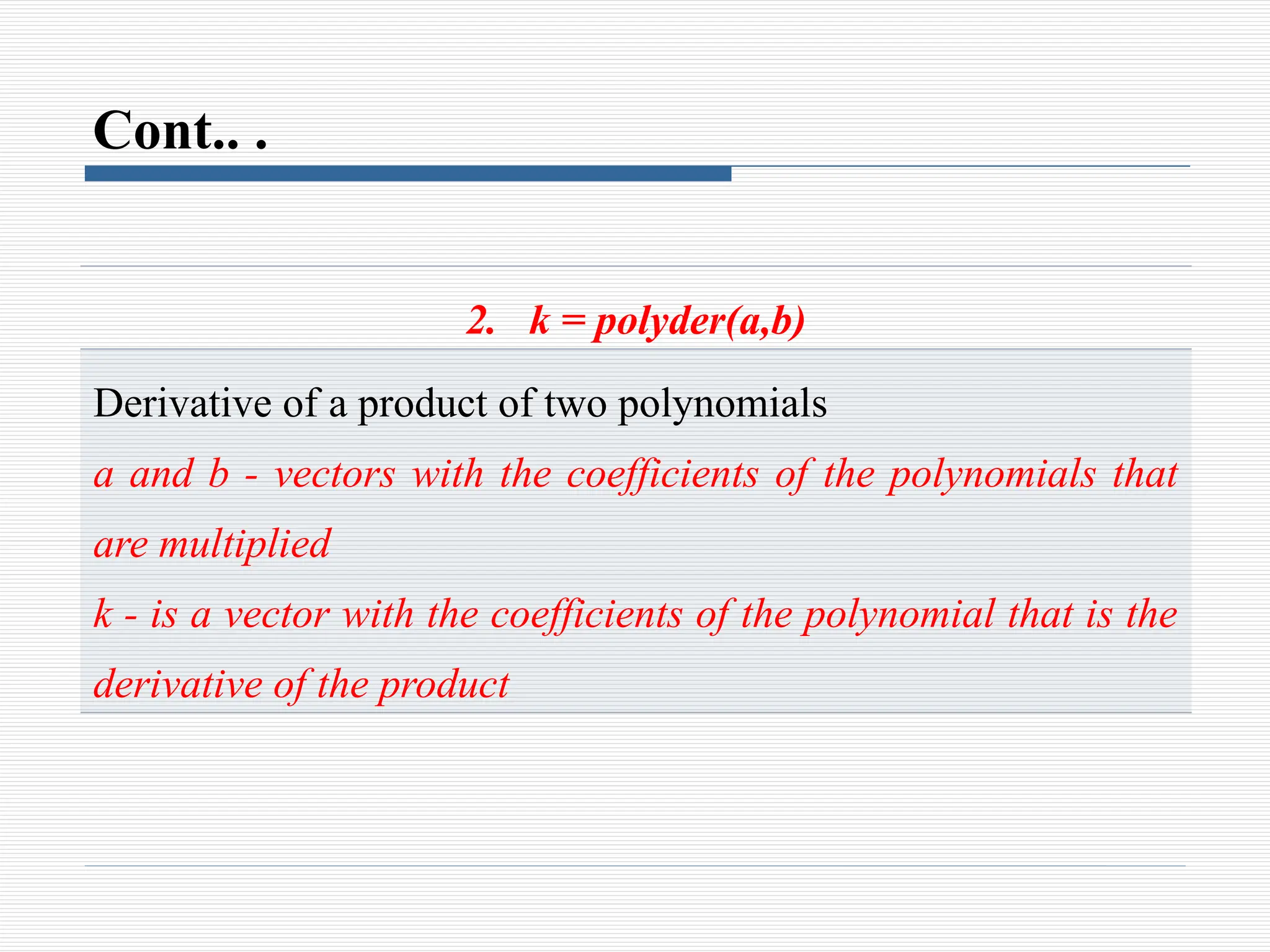
3. [n d]= polyder(u,v)
Derivative of a quotient of two polynomials
u and v - vectors with the coefficients of the numerator and
denominator polynomials
n and d - vectors with the coefficients of the numerator and
denominator polynomials in the quotient that is the derivative](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8polynomialscurvefittinginterpolation-241107073648-366794e8/75/8_Polynomials-Curve-Fitting-Interpolation-pptx-16-2048.jpg)

