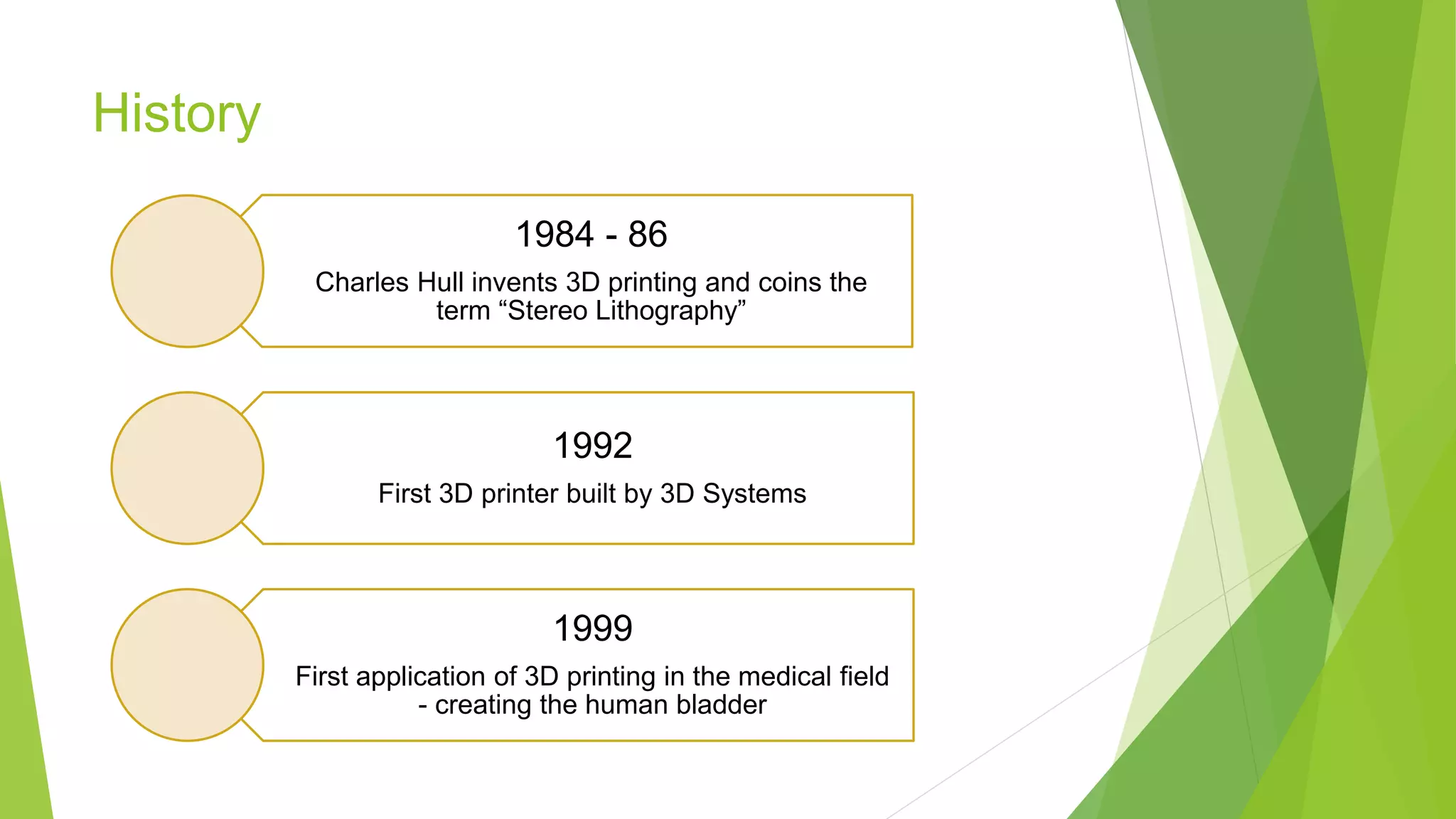
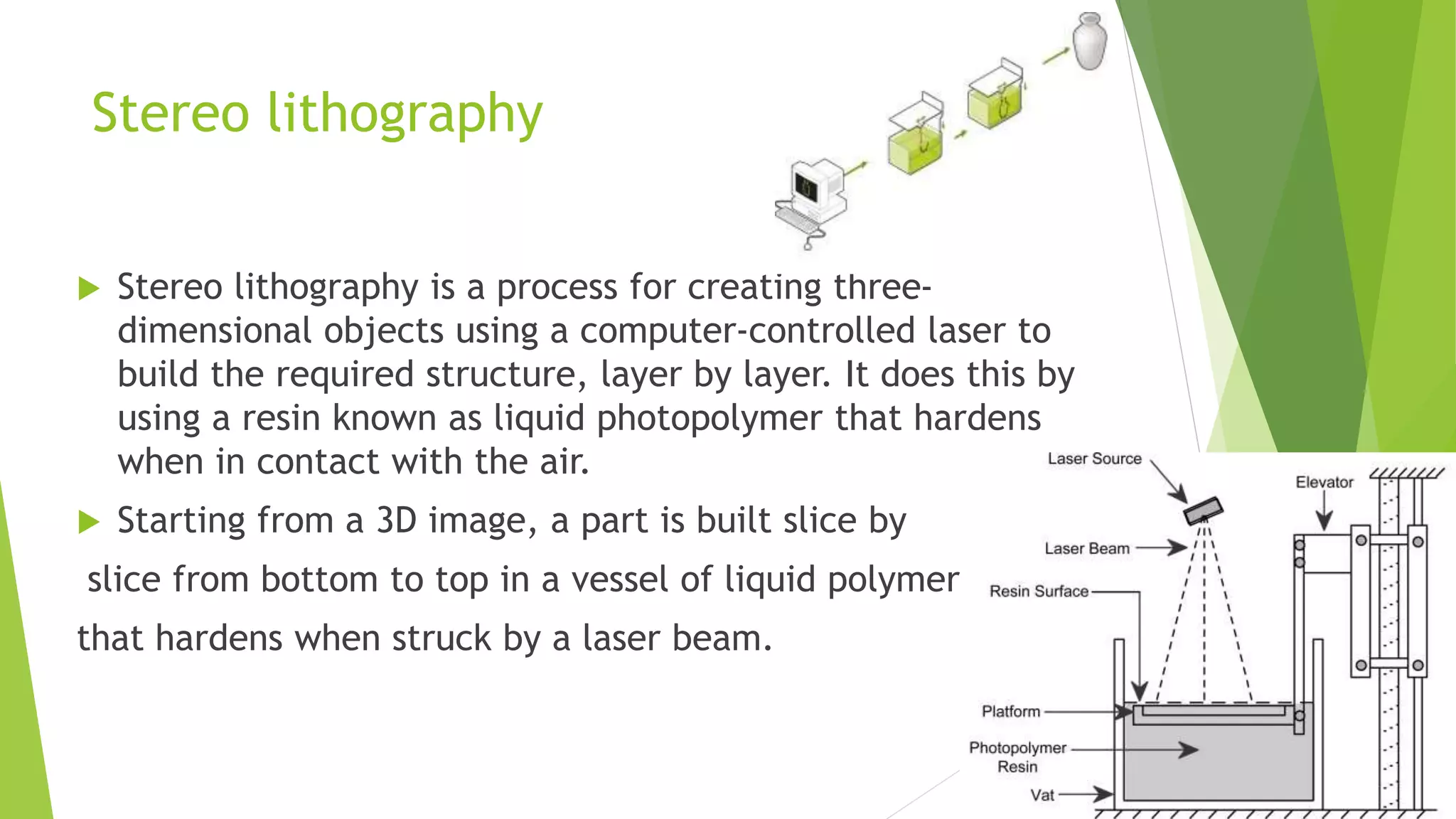
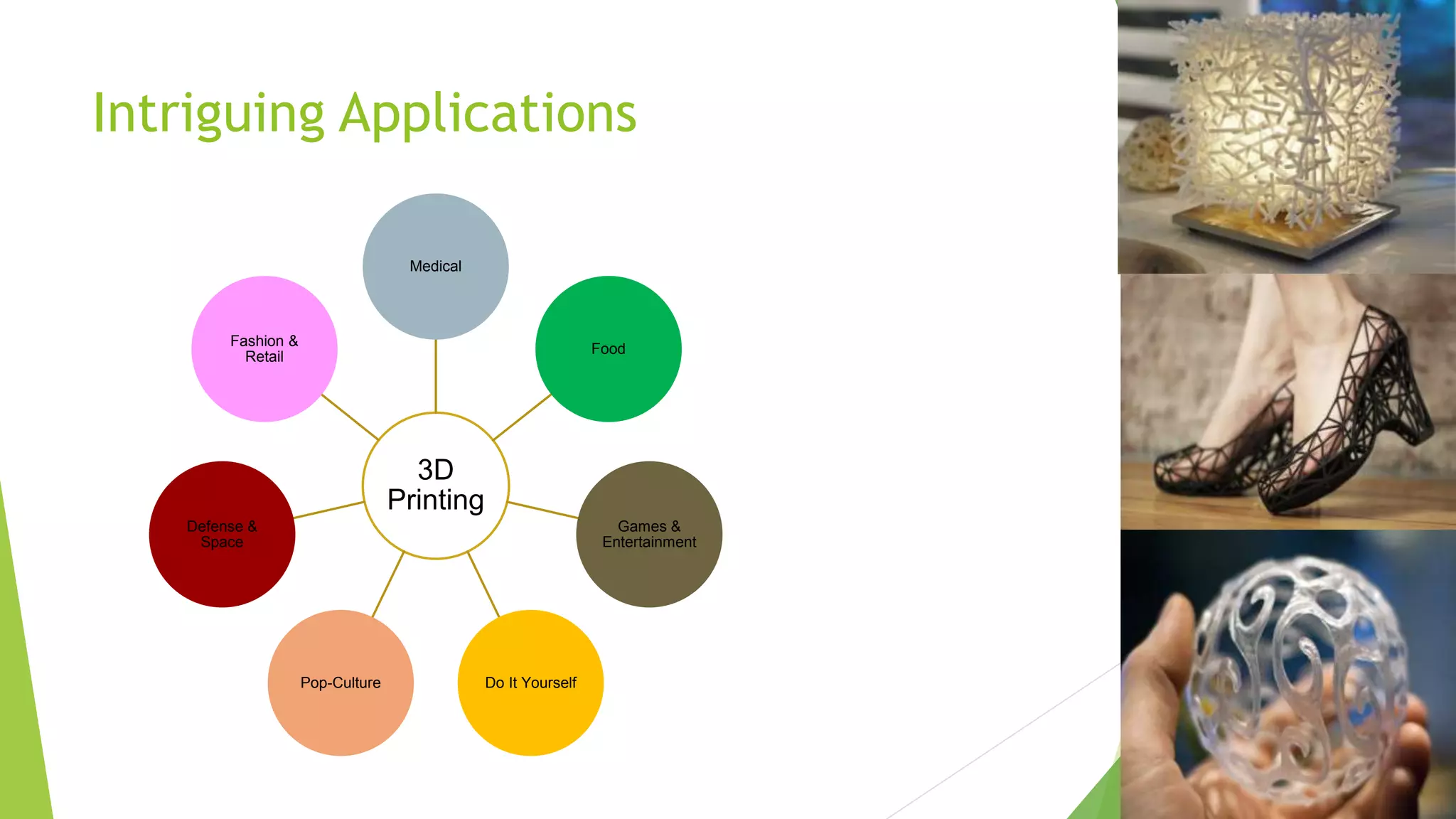
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of making 3D objects from a digital file by successively depositing material layer by layer. A 3D model is first designed using CAD software and sliced into thin layers. The 3D printer then deposits the material to build the object layer by layer, fusing materials such as plastic, metal, ceramic, or glass powder. Common 3D printing methods include selective laser sintering (SLS), fused deposition modeling (FDM), and stereolithography (SLA). 3D printing enables the creation of complex geometries and customized products with applications in fields like engineering, fashion, healthcare, and space exploration.