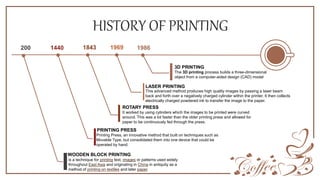
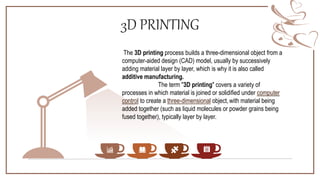
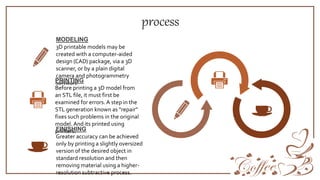
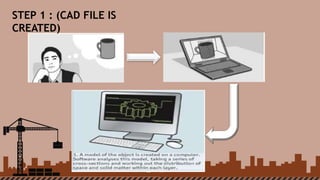
3D printing is an advanced form of printing that builds three-dimensional objects from a digital file. The document outlines the history of printing from wooden block printing to modern techniques like laser printing. It then discusses the evolution of 3D printing from its early concepts in the 1970s to recent advancements. The document explains the 3D printing process and common methods like selective laser sintering and stereolithography. It discusses applications of 3D printing in industries like automotive, medical, and food as well as the role of 3D printing in Industry 4.0. The document also covers the size, cost and impacts of 3D printers as well as advantages, disadvantages, and future scope.



![1984
Chuck Hull of 3D Systems Corporation filed
his own patent for a stereolithography
fabrication system, in which layers are added
by curing photopolymers with ultraviolet light
lasers.
2005
Z corporation launched first
high definition color 3D
printer.
2014
Benjamin S. Cook demonstrate the first multi-
material, vertically integrated printed electronics
additive manufacturing platform which enabled
3D printing of functional electronics operating
up to 40 GHz.
1974
David E. H. Jones laid out the concept of 3D
printing in his regular column Ariadne in the
journal New Scientist.
1993
A company called Solidscape, introducing a
high-precision polymer jet fabrication system
with soluble support structures,
2012
Filabot developed a system for closing the loop[30]
with plastic and allows for any FDM or FFF 3D
printer to be able to print with a wider range of
plastics.
Evolution of 3d printing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3dprinting-200415132139/85/3d-printing-6-320.jpg)



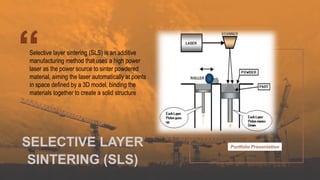




![FOOD INDUSTRY
Additive manufacturing of
food is being developed by
squeezing out food, layer by
layer, into three-dimensional
objects.
A large variety of foods are
appropriate candidates, such
as chocolate and candy, and
flat foods such as crackers,
pasta,[28] and pizza.[
NASA has considered the versatility of
the concept, awarding a contract to the
Systems and Materials Research
Consultancy to study the feasibility of
printing food in space.[
One of the problems with food printing
is the nature of the texture of a food.
For example, foods that are not strong
enough to be filed are not appropriate
for 3D printing.
A food-tech startup Novameat from
Barcelona 3D-printed a steak from
peas, rice, seaweed, and some
other ingredients that were laid
down criss-cross, imitating the
intracellular proteins.
NASA is also looking into the
technology in order to create 3D
printed food to limit food waste and to
make food that are designed to fit an
astronaut's dietary needs.[
1
2
3 4
1
5
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3dprinting-200415132139/85/3d-printing-24-320.jpg)