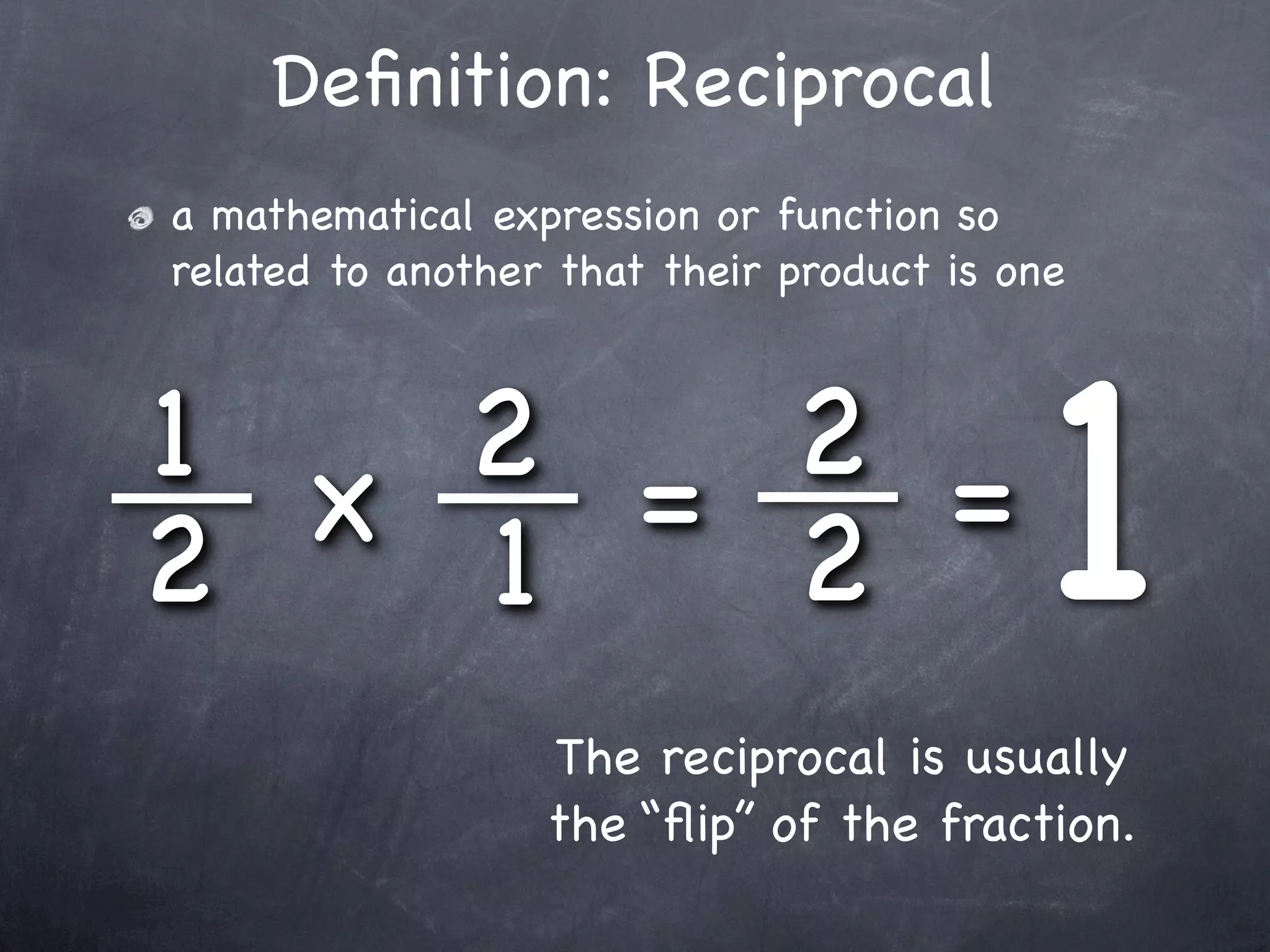
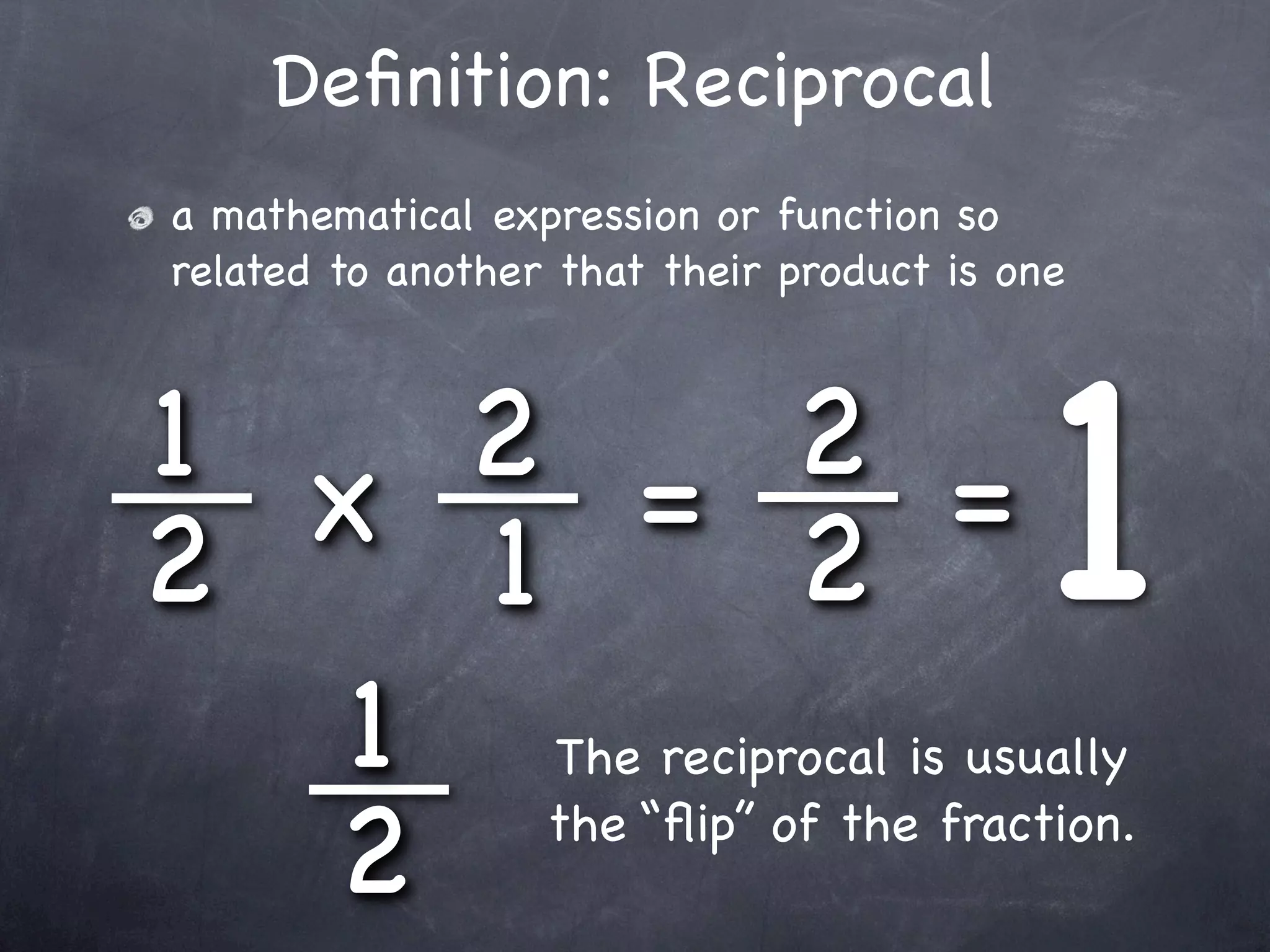
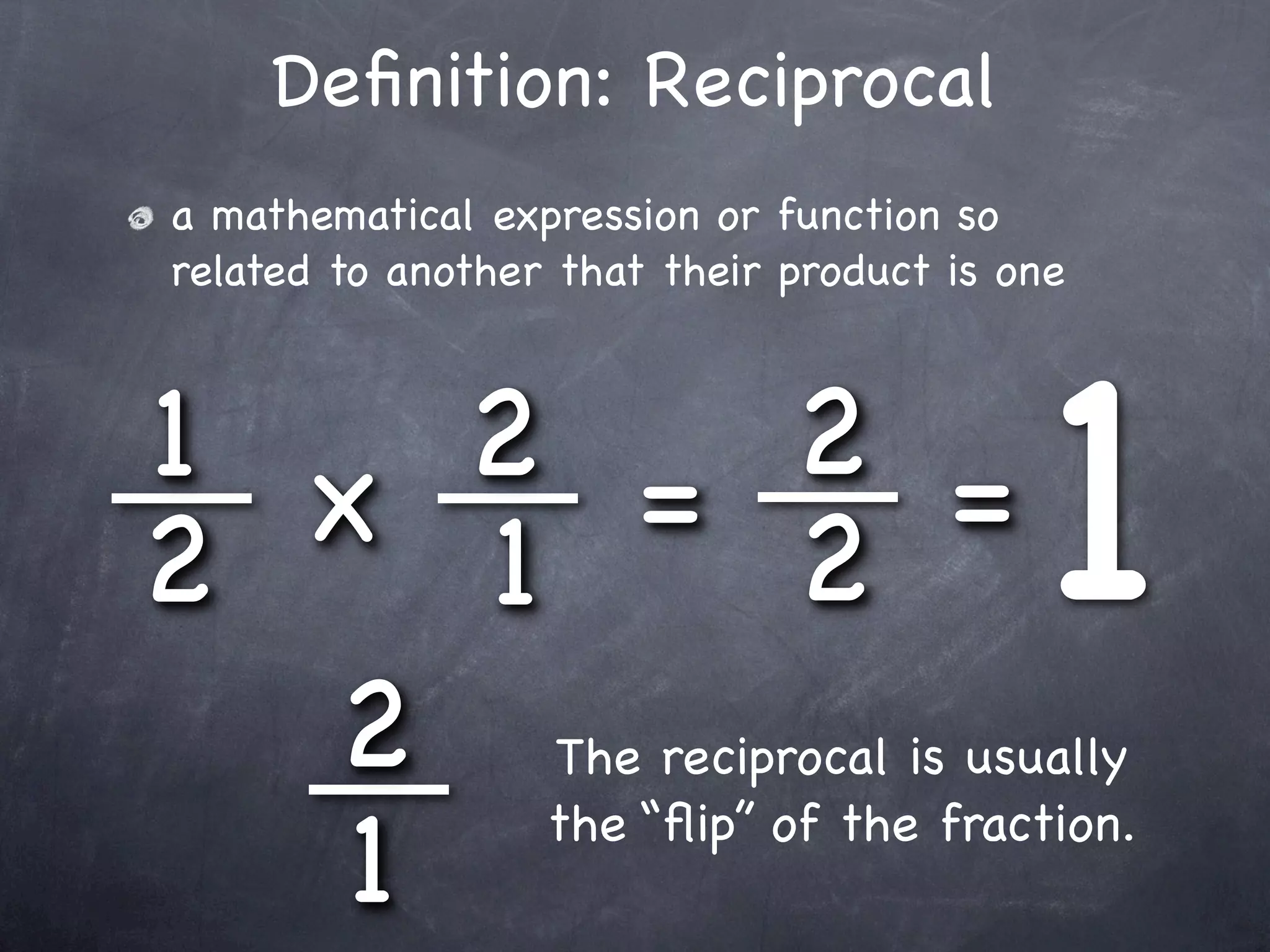
The document provides examples for dividing fractions by using the reciprocal method. It first defines a reciprocal as the "flip" of a fraction. It then shows two examples of dividing fractions step-by-step: 1) find the reciprocal of the divisor, 2) multiply instead of divide, and 3) multiply the numerators and denominators. This allows dividing fractions to become multiplying fractions.