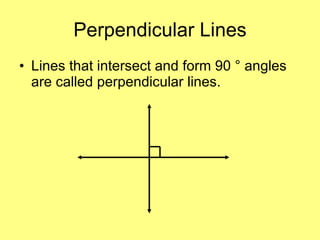
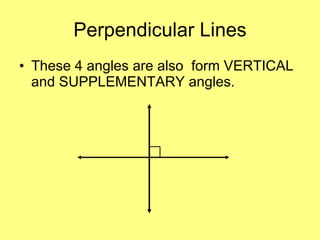
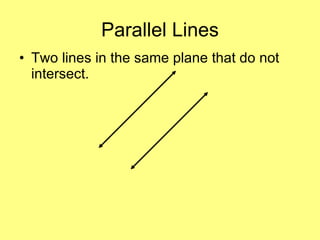
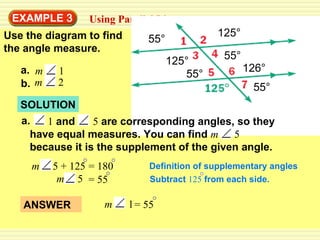
This document contains lesson materials on lines and angles including:
- Solving two equations involving variables w and v
- Vocabulary terms related to lines and angles
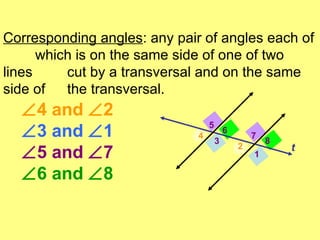
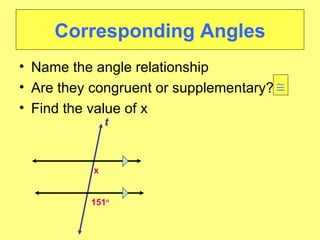
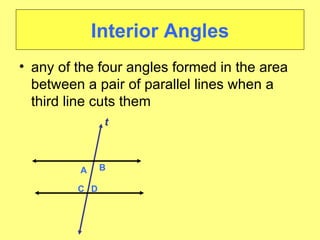
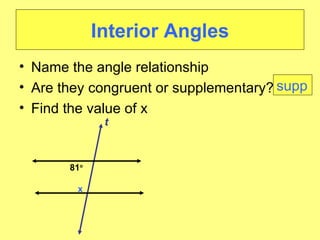
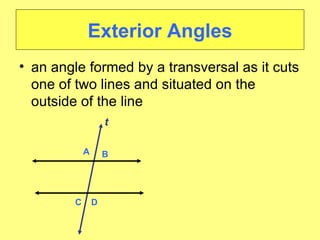
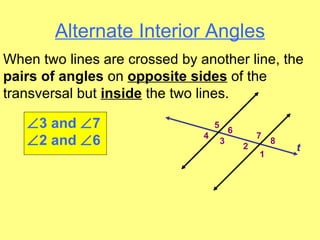
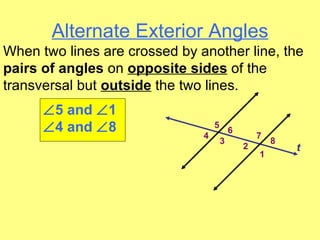
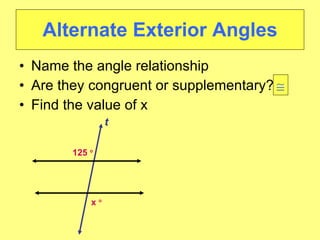
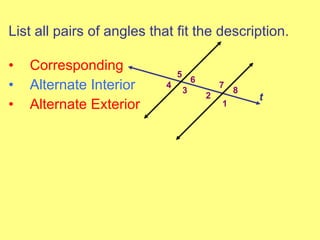
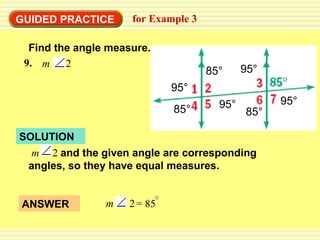
- Identifying different angle relationships (corresponding angles, interior angles, etc.) when lines are cut by a transversal
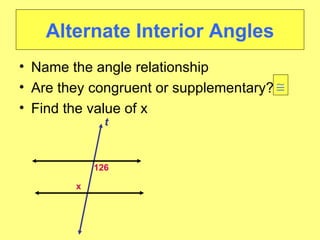
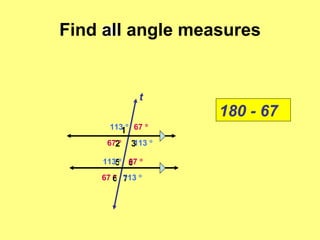
- Worked examples of finding missing angle measures using properties of parallel lines