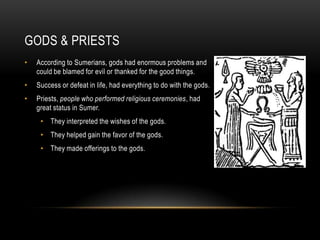
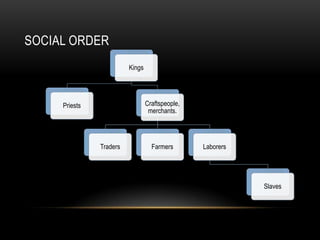
The Sumerians established advanced city-states in Mesopotamia around 3000 BC, where rulers claimed divine approval and religion played a major role. Sargon later conquered the region to form the first empire, though it did not last after his death as rival city-states regained power. The Sumerians developed new technologies, built walled cities like Ur for protection, and practiced polytheism with gods influencing all aspects of life.