1) The document discusses representing real-life situations using rational functions. It reviews polynomials and rational functions, and provides examples of expressing velocity and travel time as rational functions of variables like time and speed.
2) One example expresses the velocity of an object traveling 10 meters as a rational function of time. Another finds the time to travel 250 km from Manila to Baguio as a rational function of speed.
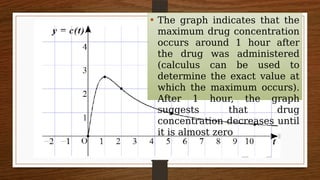
3) Real-world contexts like drug concentration, organ pipe vibration, and travel time-speed relationships are used to demonstrate how rational functions can model real-life situations.