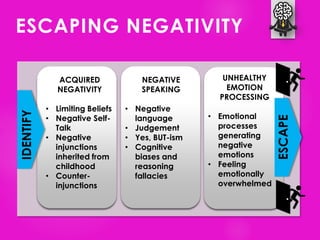
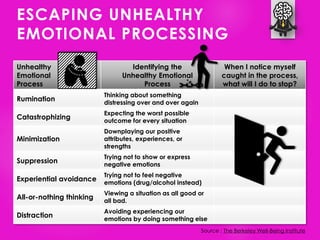
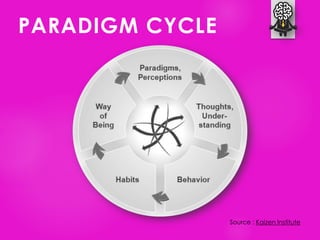
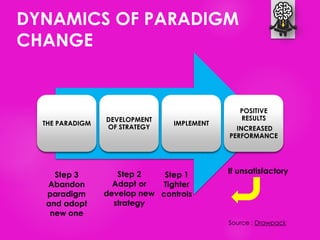
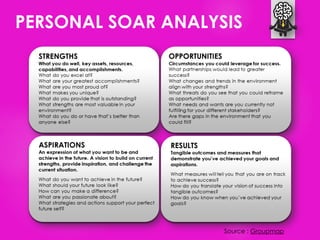
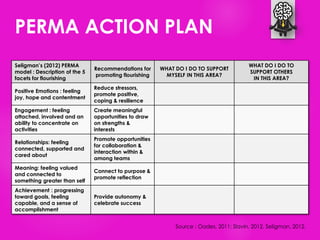
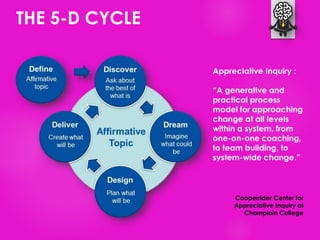
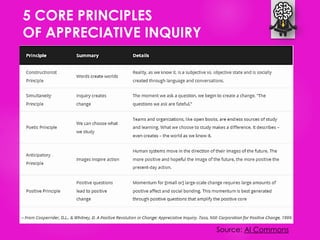
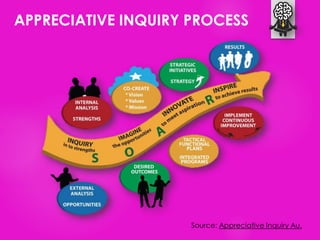
The document outlines seven tools for fostering a positive mindset, emphasizing the importance of mindset in achieving personal and professional goals. It discusses various methods like the performance loop, PERMA model, gratitude practices, and appreciative inquiry to overcome negative beliefs and emotional barriers. Overall, it offers strategies for developing a positive outlook, enhancing well-being, and realizing one's potential.