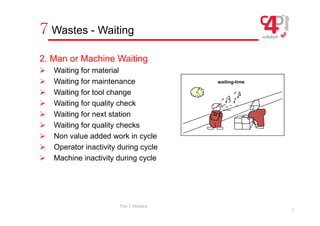
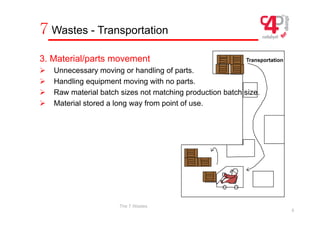
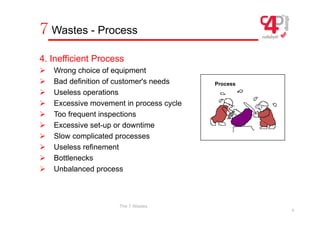
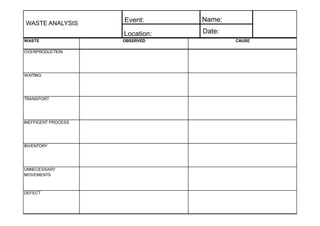
The document defines three types of waste in operations: value added work that customers are willing to pay for, non-value added or "hidden" waste that is necessary under current conditions, and obvious waste that is unnecessary. It identifies the seven most common types of obvious waste as overproduction, waiting, transportation, inefficient processes, large inventories, unnecessary operator movements, and defects. The document provides examples and explanations of each type of waste.