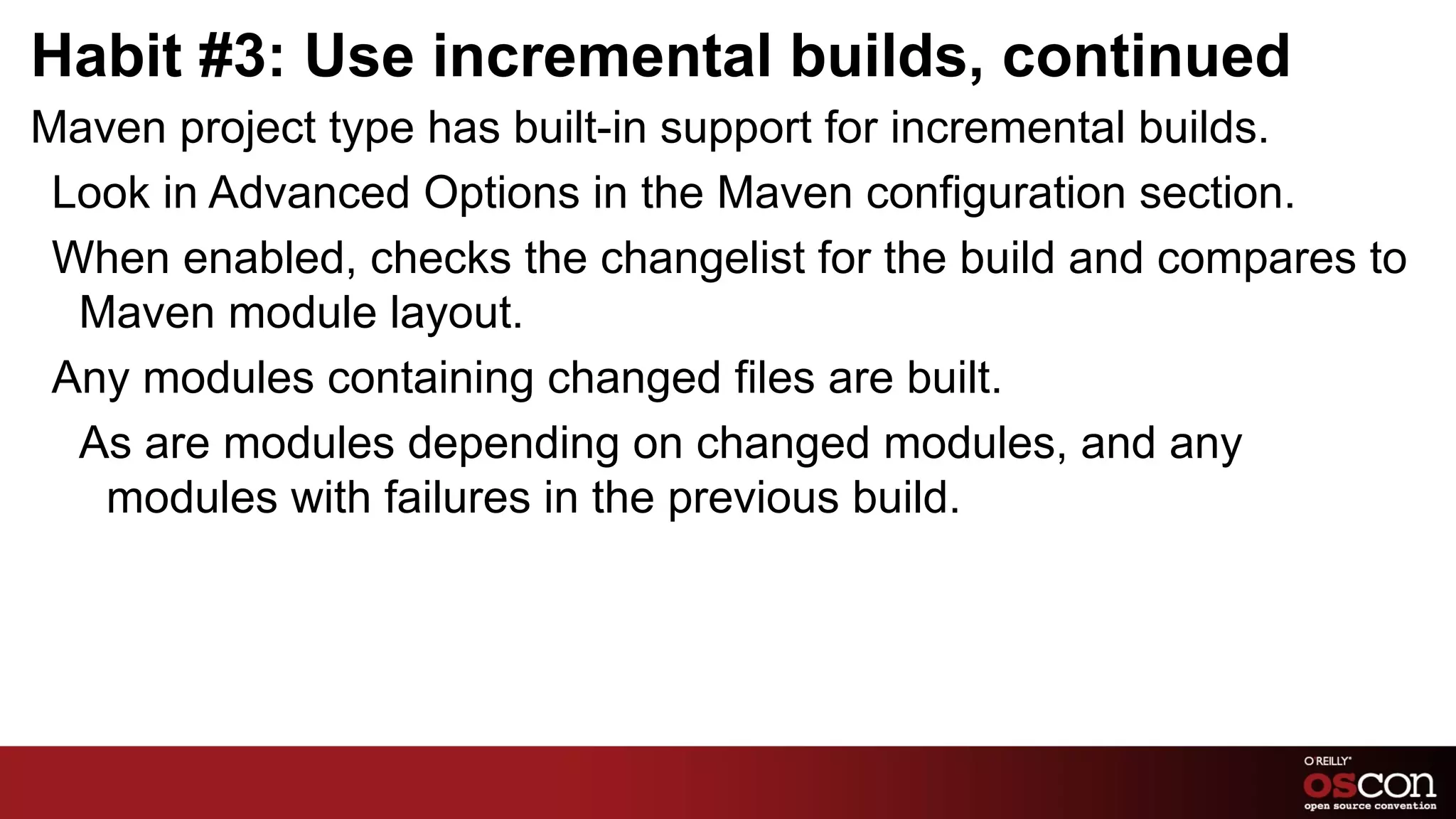
The document outlines seven habits of highly effective Jenkins users, emphasizing the importance of using plugins productively, standardizing build environments, and integrating with other tools. It also advises on managing builds efficiently by breaking up bloat, sticking with stable releases, and engaging with the Jenkins community. The author draws from personal experience and highlights that there is no single 'right way' to utilize Jenkins, encouraging adaptation to organizational needs.