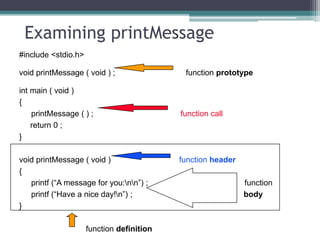
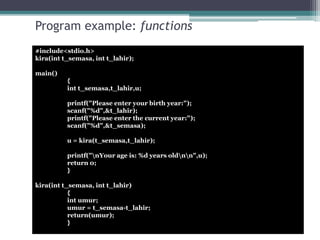
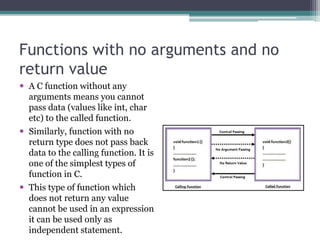
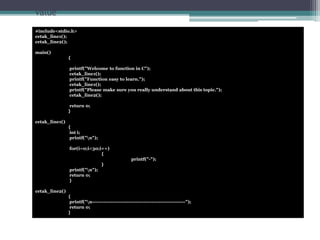
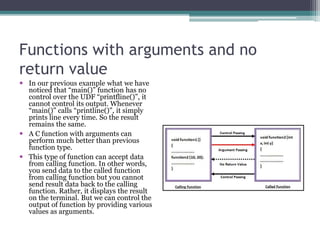
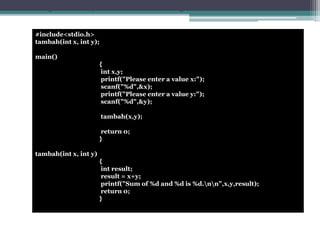
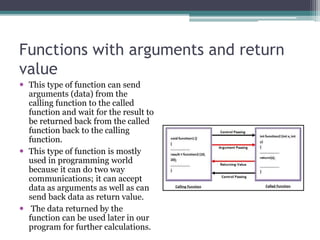
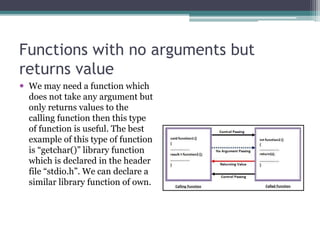
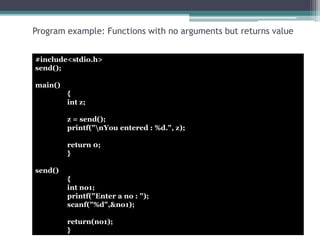
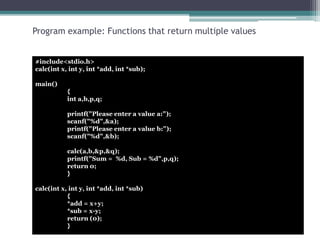
This document discusses different types of functions in C programming. It provides examples of functions with no arguments and no return value, functions with arguments and no return value, functions with arguments and return value, functions with no arguments but return value, and functions that return multiple values. The examples demonstrate how to define and call each type of function.