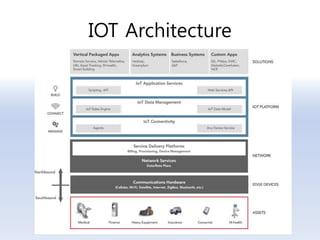
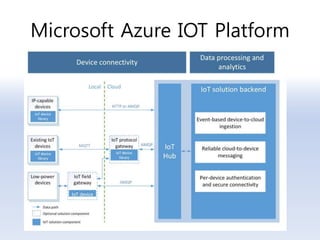
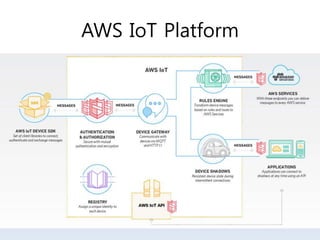
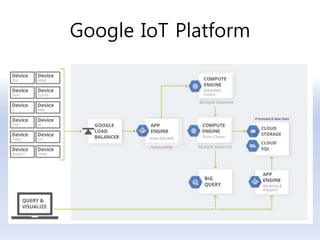
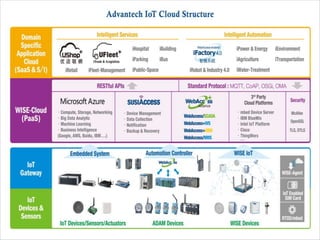
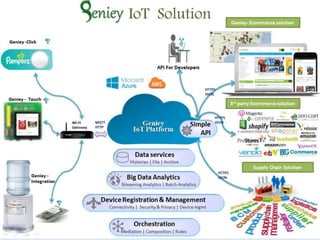
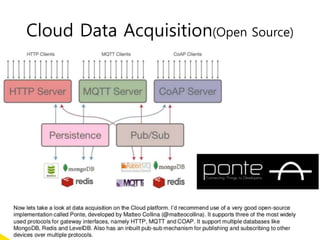
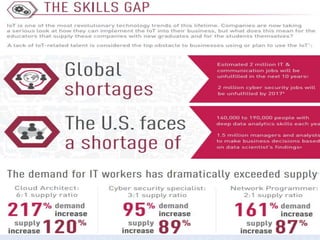
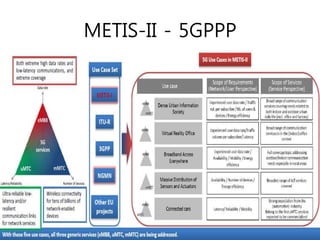
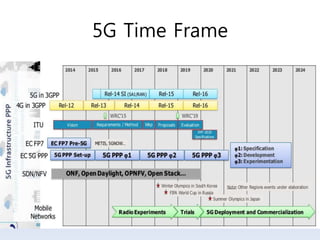
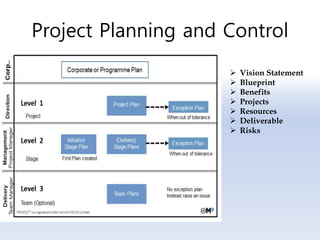
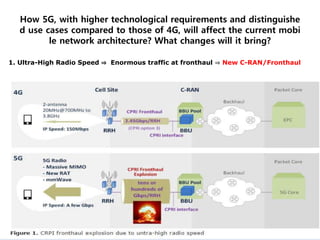
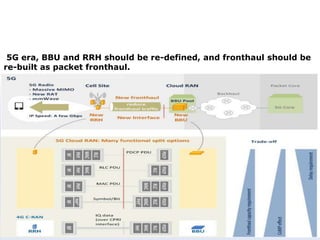
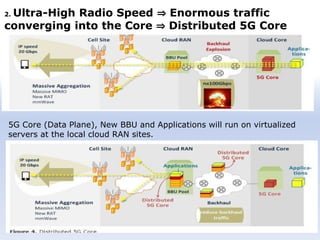
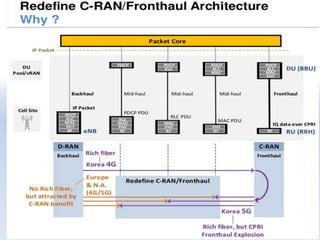
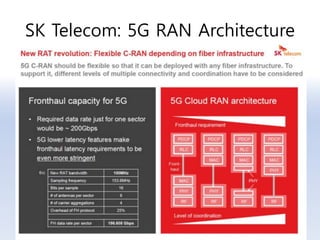
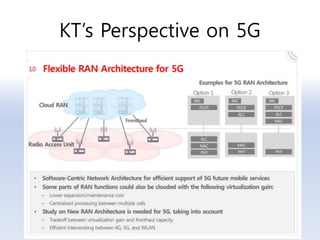
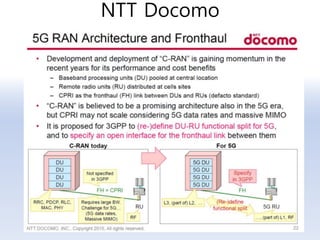
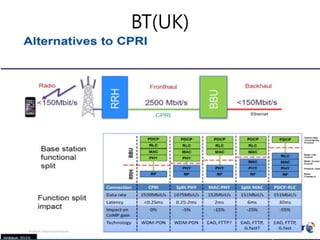
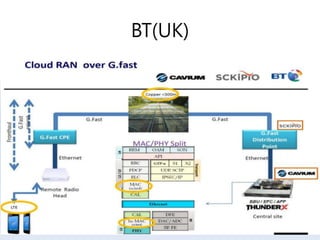
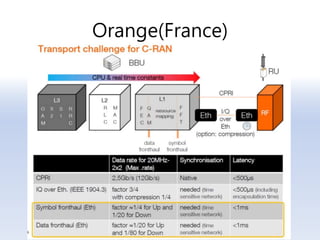
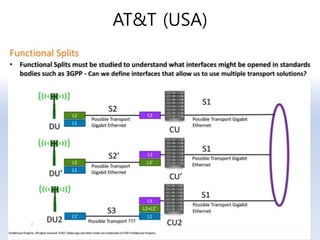
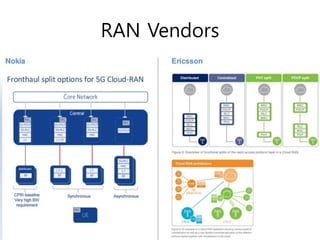
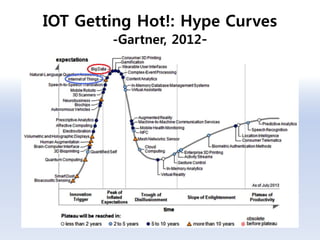
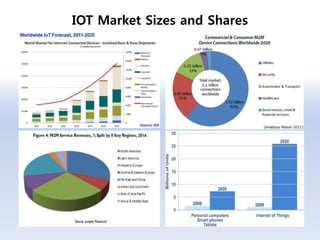
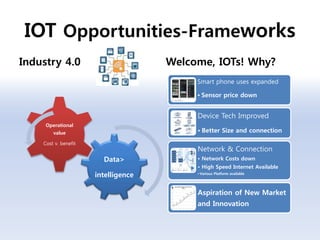
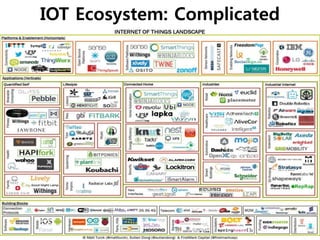
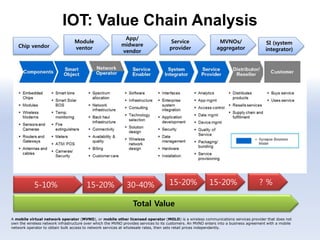
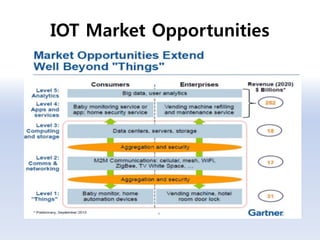
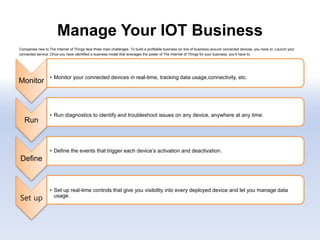
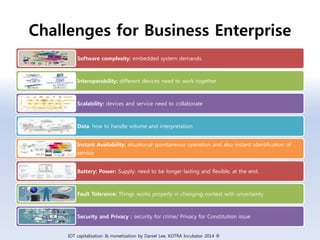
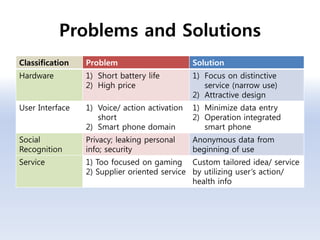
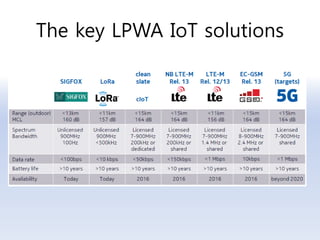
The document discusses 5G networks and Internet of Things (IoT) architecture. For 5G, it describes the key requirements of ultra-high radio speed, ultra-low latency, and massive connectivity. This will require redefining cloud-RAN/fronthaul architecture with distributed 5G cores and packet-based fronthaul to handle high traffic loads. For IoT, it discusses the growth of the market and challenges around standards, security and privacy, and monetization. It provides an overview of key platform architectures from Microsoft, AWS, and Google for IoT. The biggest challenge remains developing solutions that can scale to handle the massive number of IoT devices connecting to 5G networks.
















![3GPP - SMARTER – NexGen(5G)
From SMARTER spec (TR 22.891),there are 14 use cases Related to IoT:
• Massive Internet of Things M2M and device identification
– Should be able to identify and address large number of devices
• Light weight device communication
– Provide Simple light-weight messaging for user to control IoT devices
• Telemedicine
– Method for prioritize critical data transmission
• Light weight device
– Support light weight device which may not equip IMS.
– Support light weight signalling for device configuration.
• wide area sensor
– critical triggering for event
• IoT initialization
– remote provide 3GPP subscription
• Wearable device communication
– connection switch between direct network connection and smartphone connection
• Industrial Factory Automation
– Communication between controller and sensors located in small area
– very low fail rate (< 10-9)
– support cycle times of [1ms to 2ms.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e1ff3953-9906-43b3-837e-dd64f22273f2-160202073536/85/5G-Cloud-RAN-IoT-Architecture-44-320.jpg)