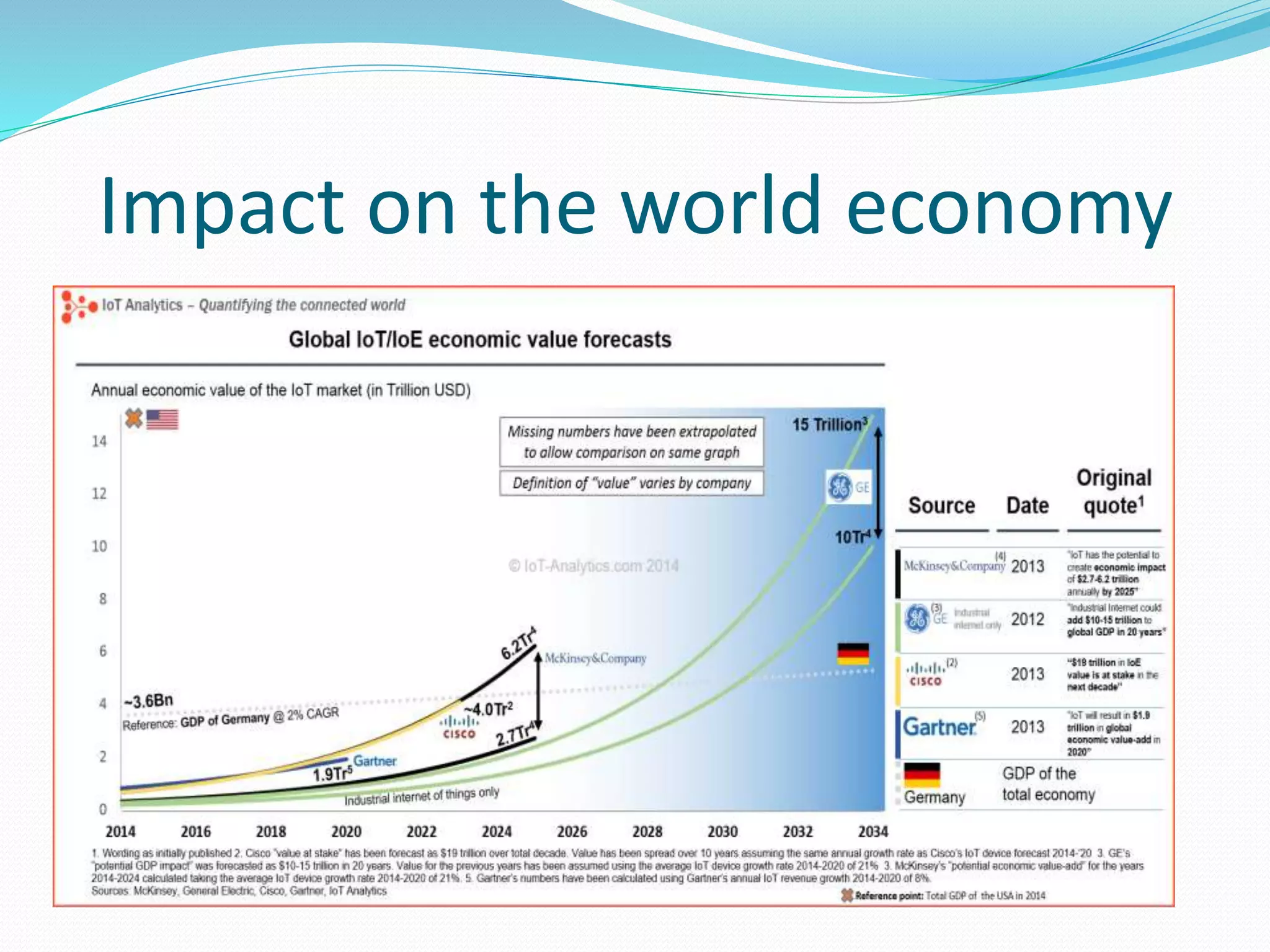
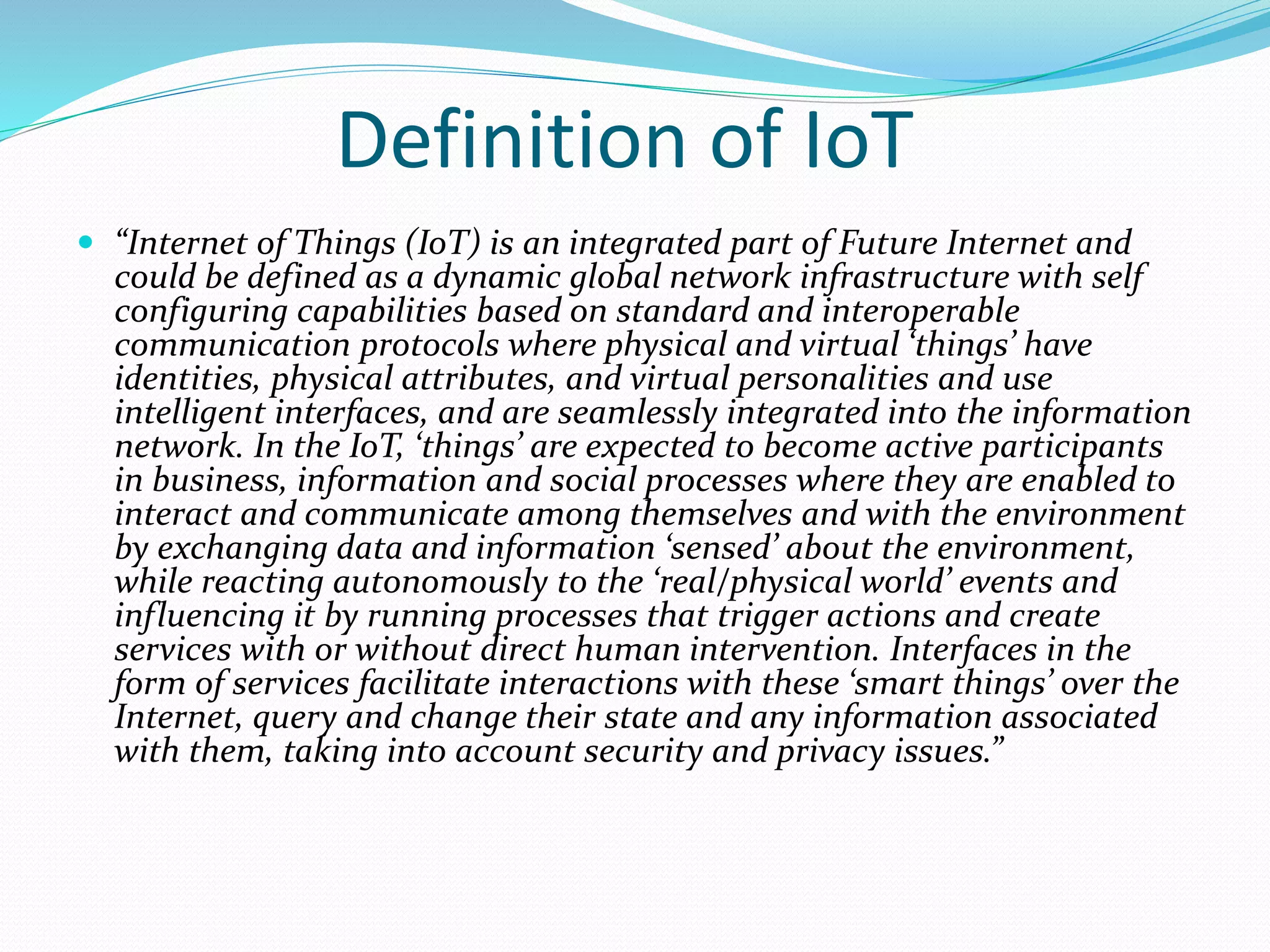
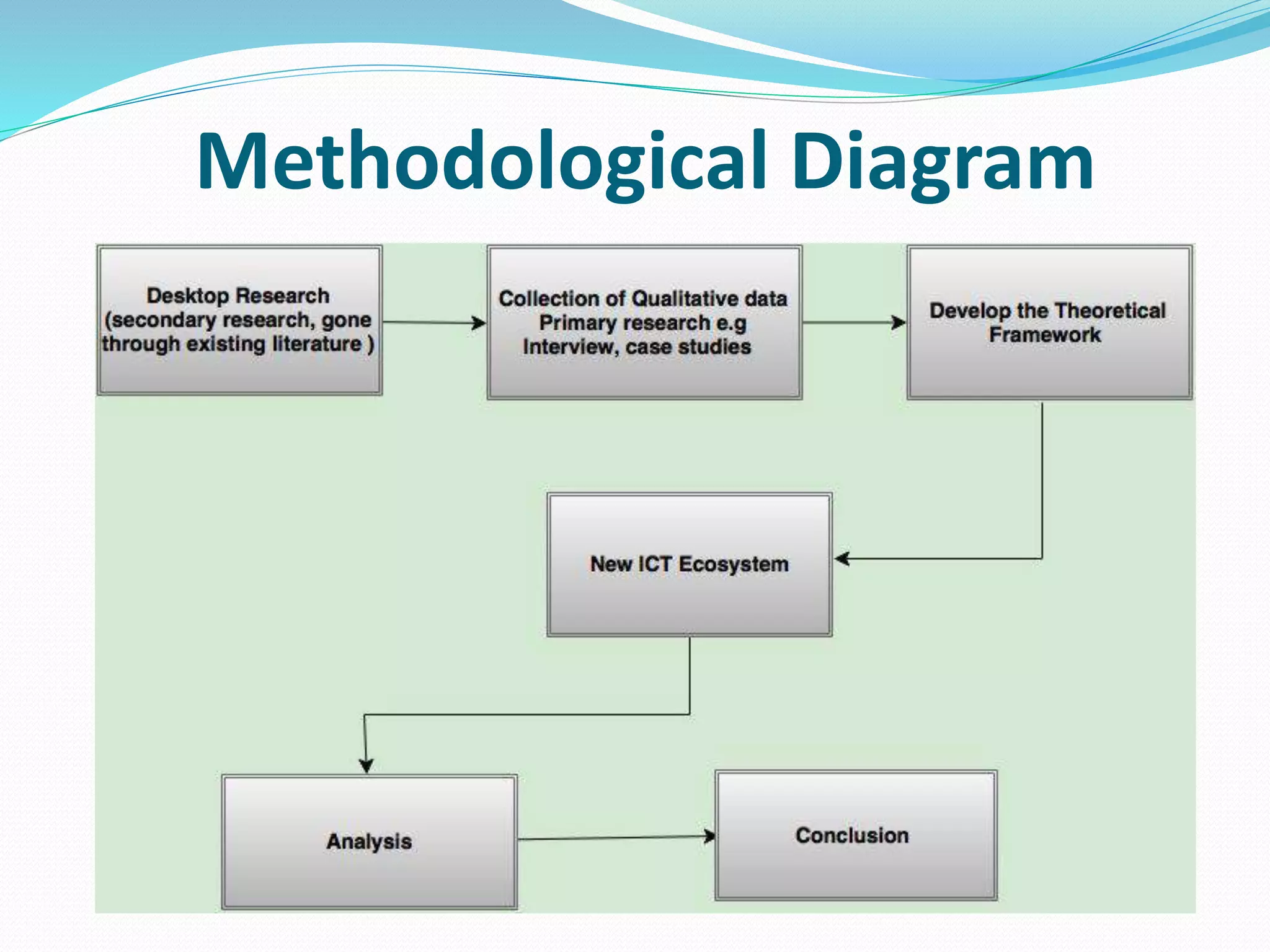
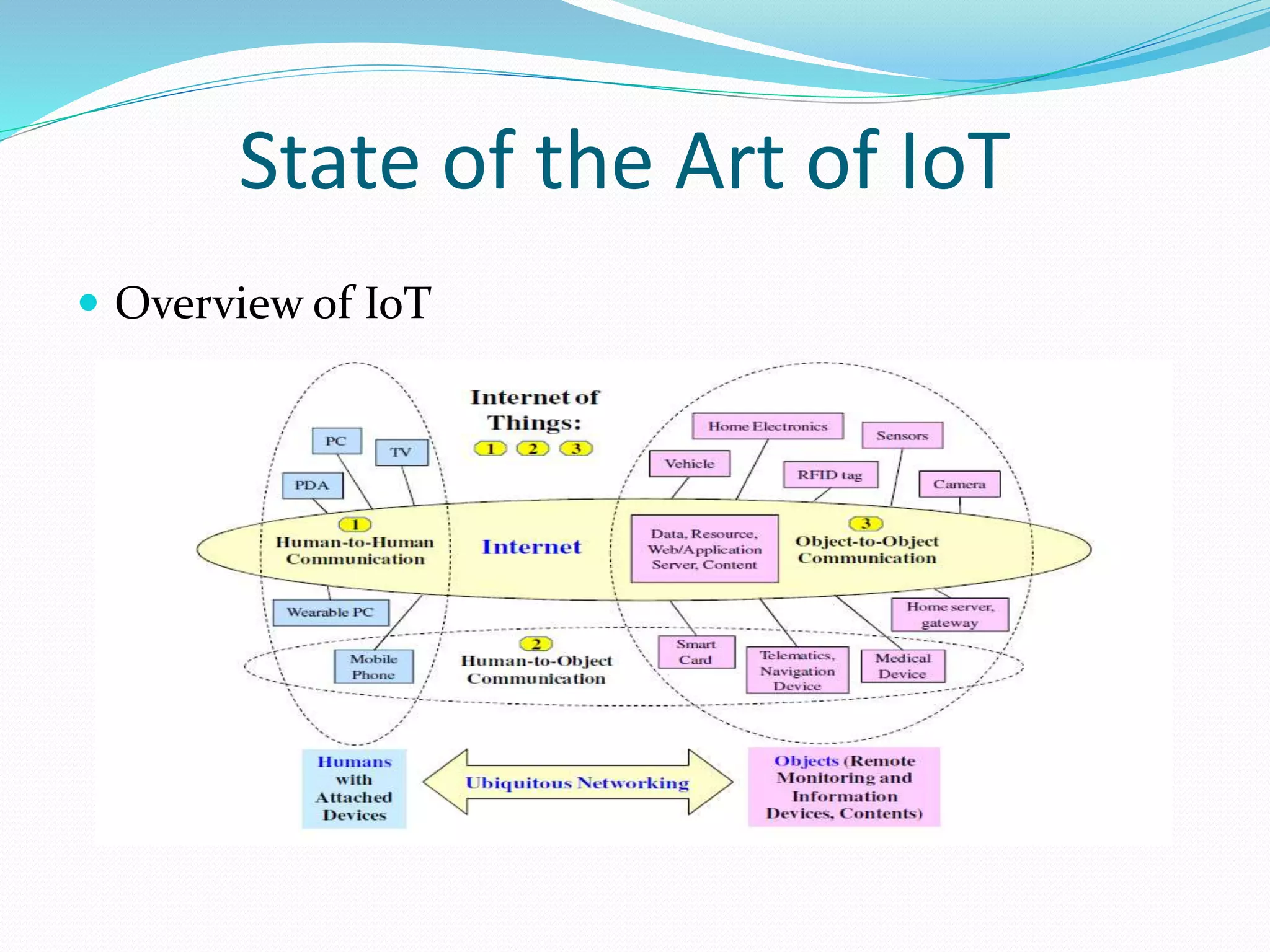
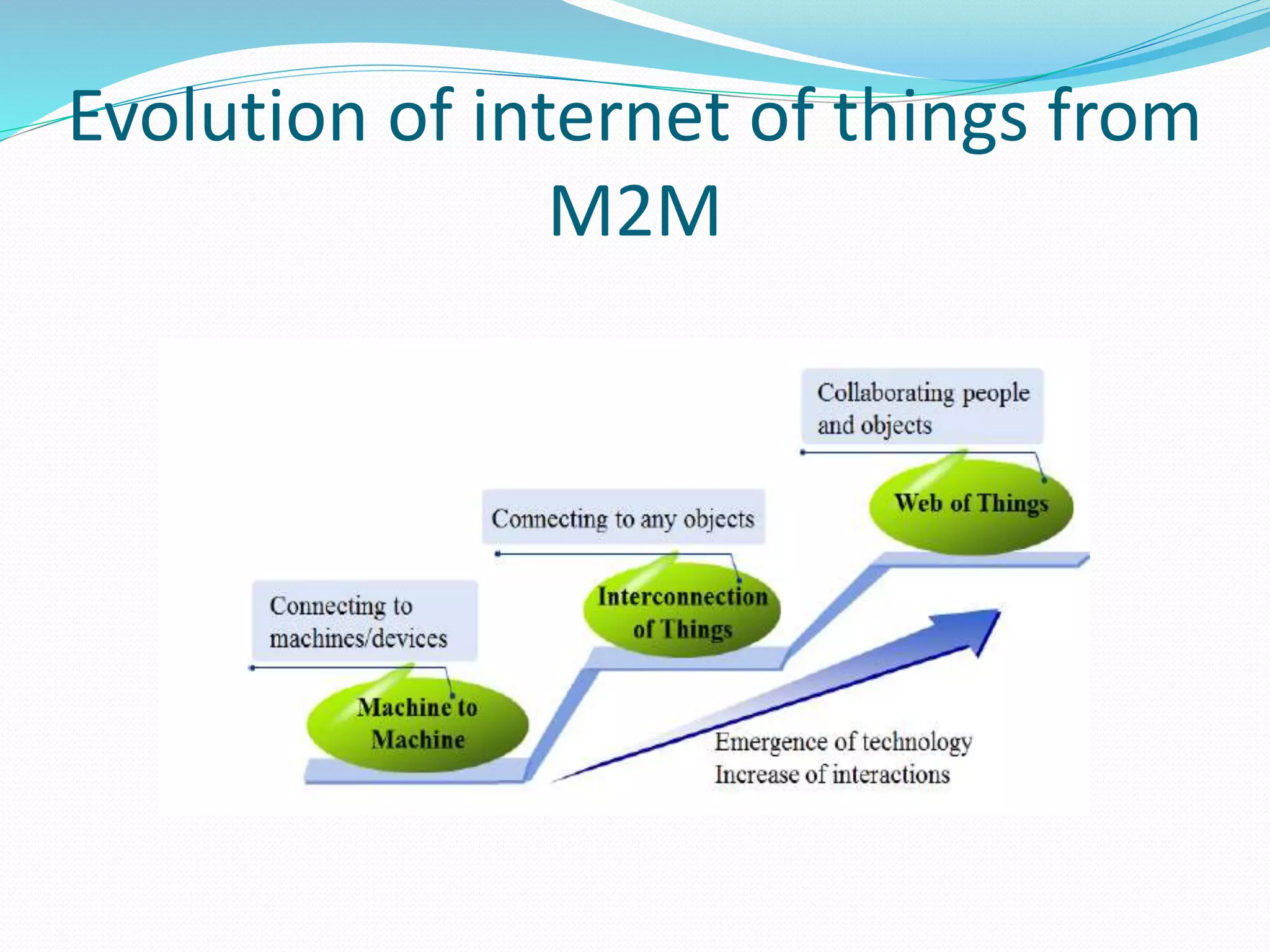
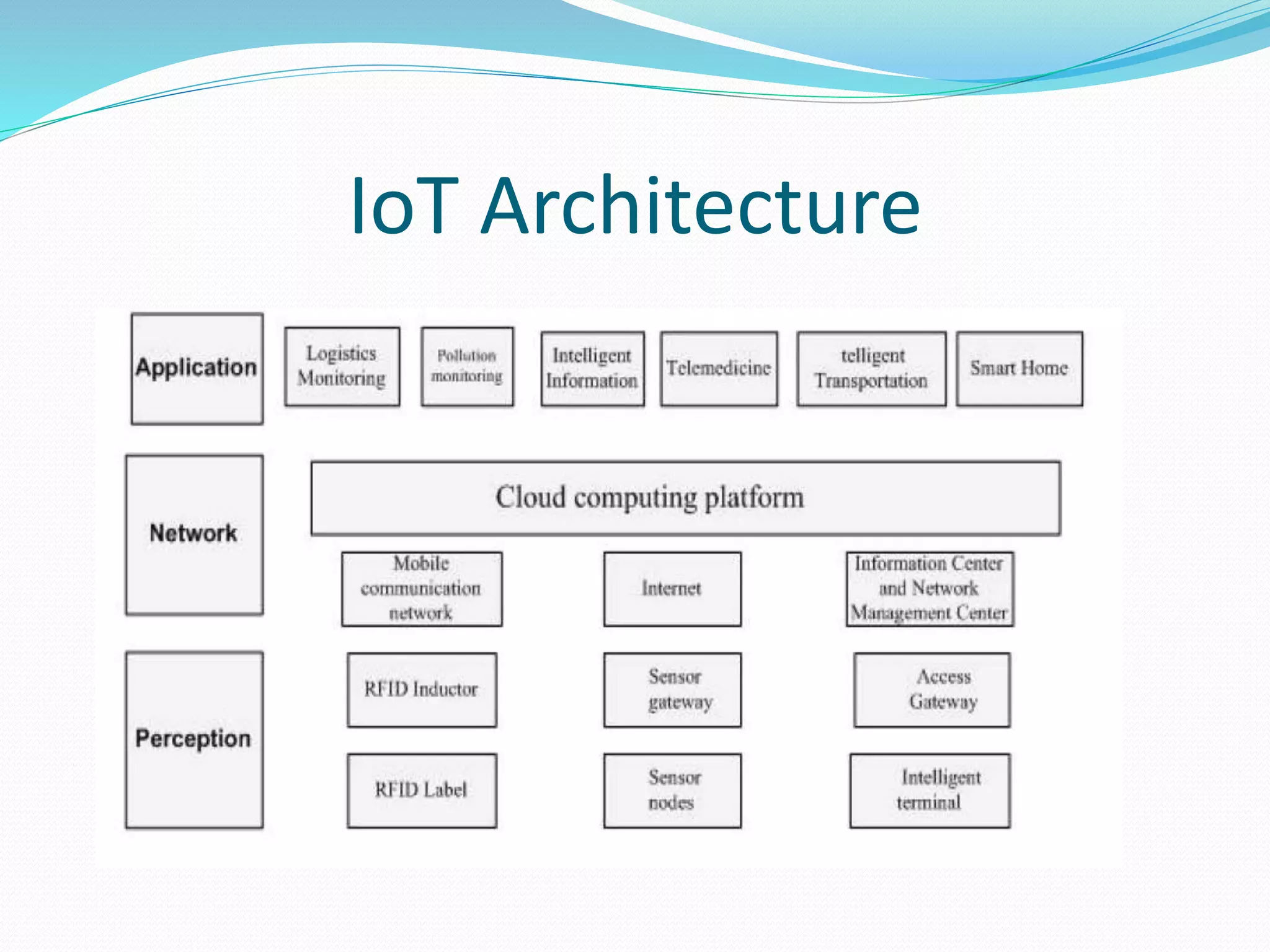
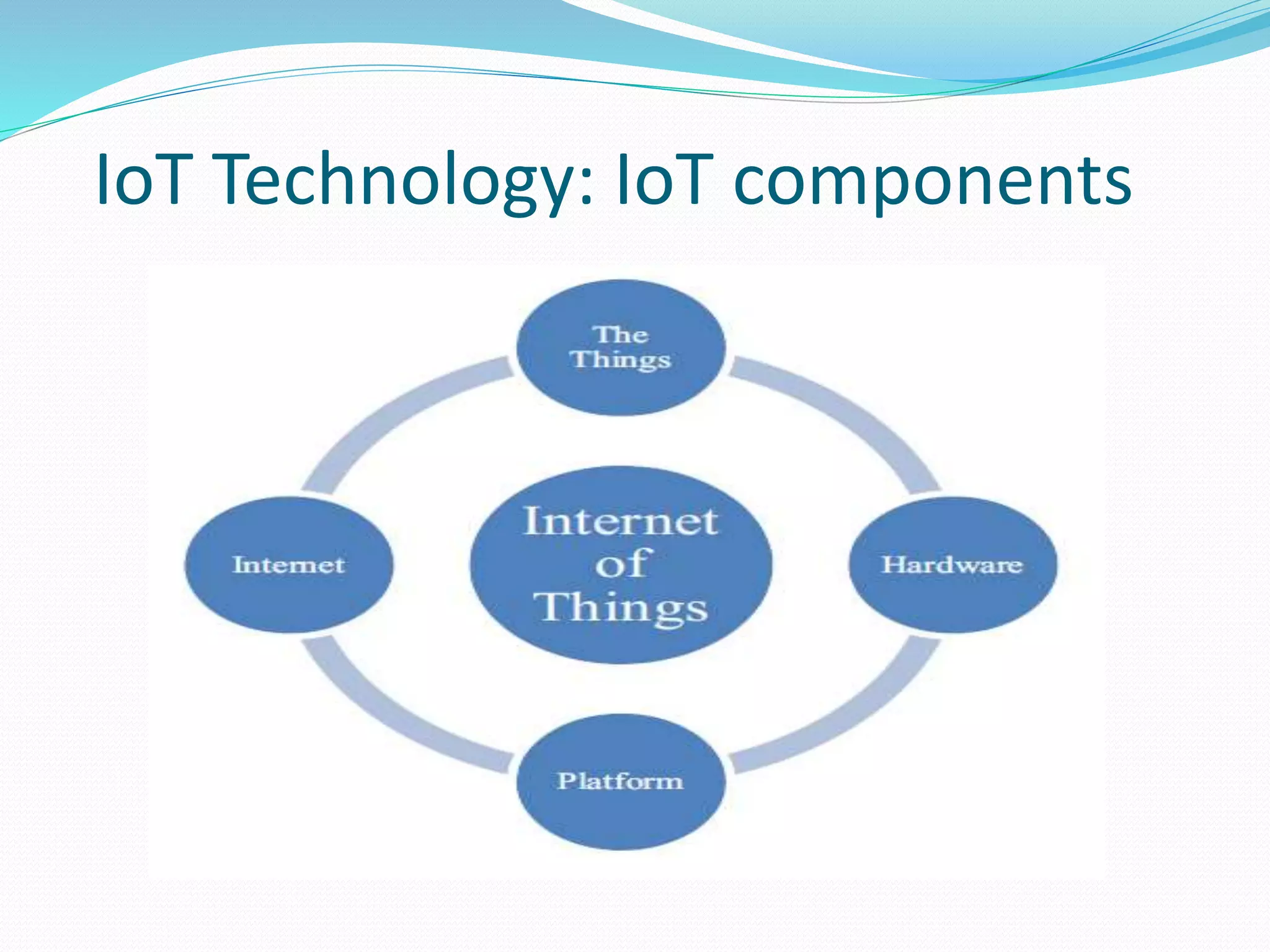
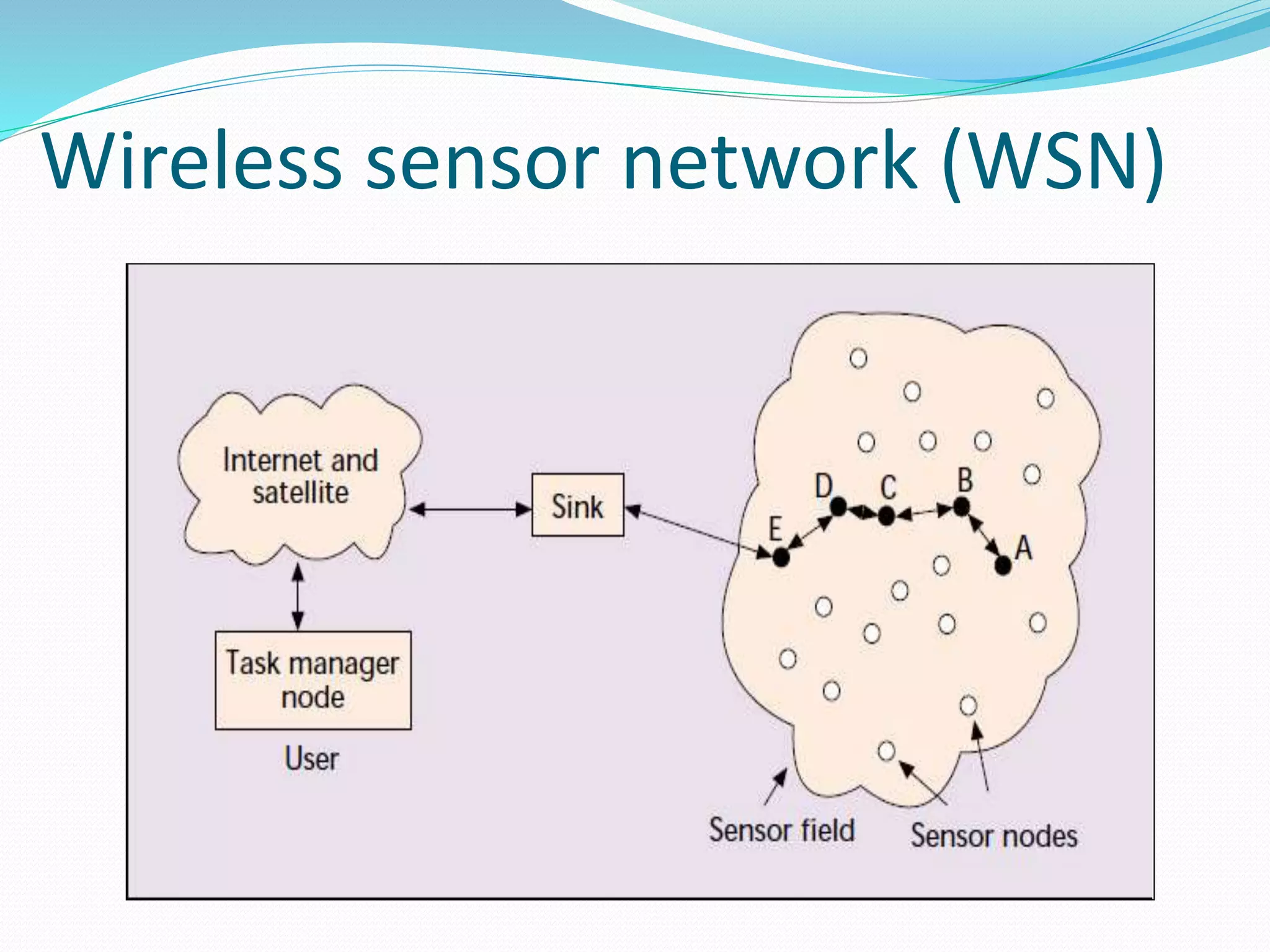
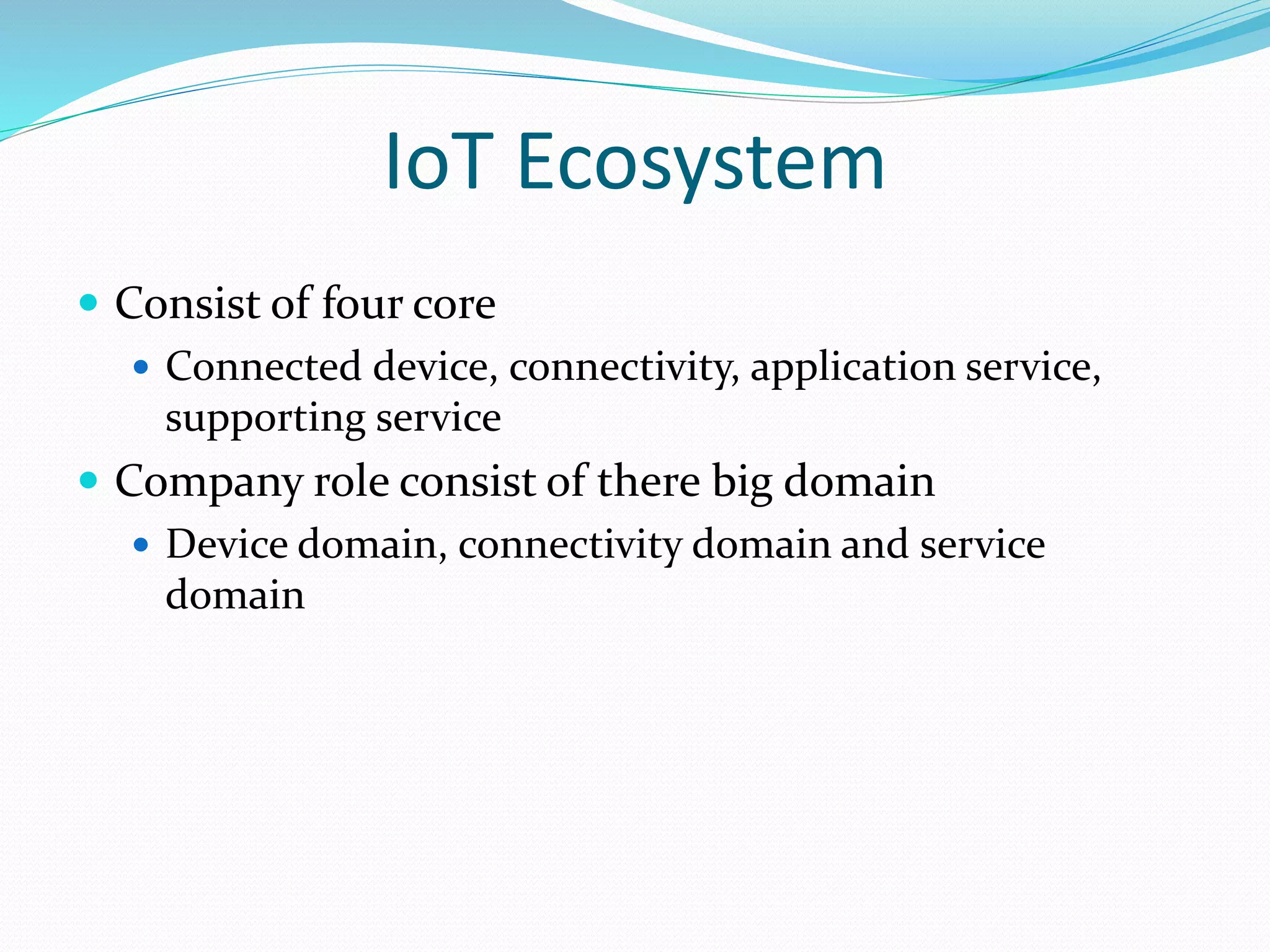
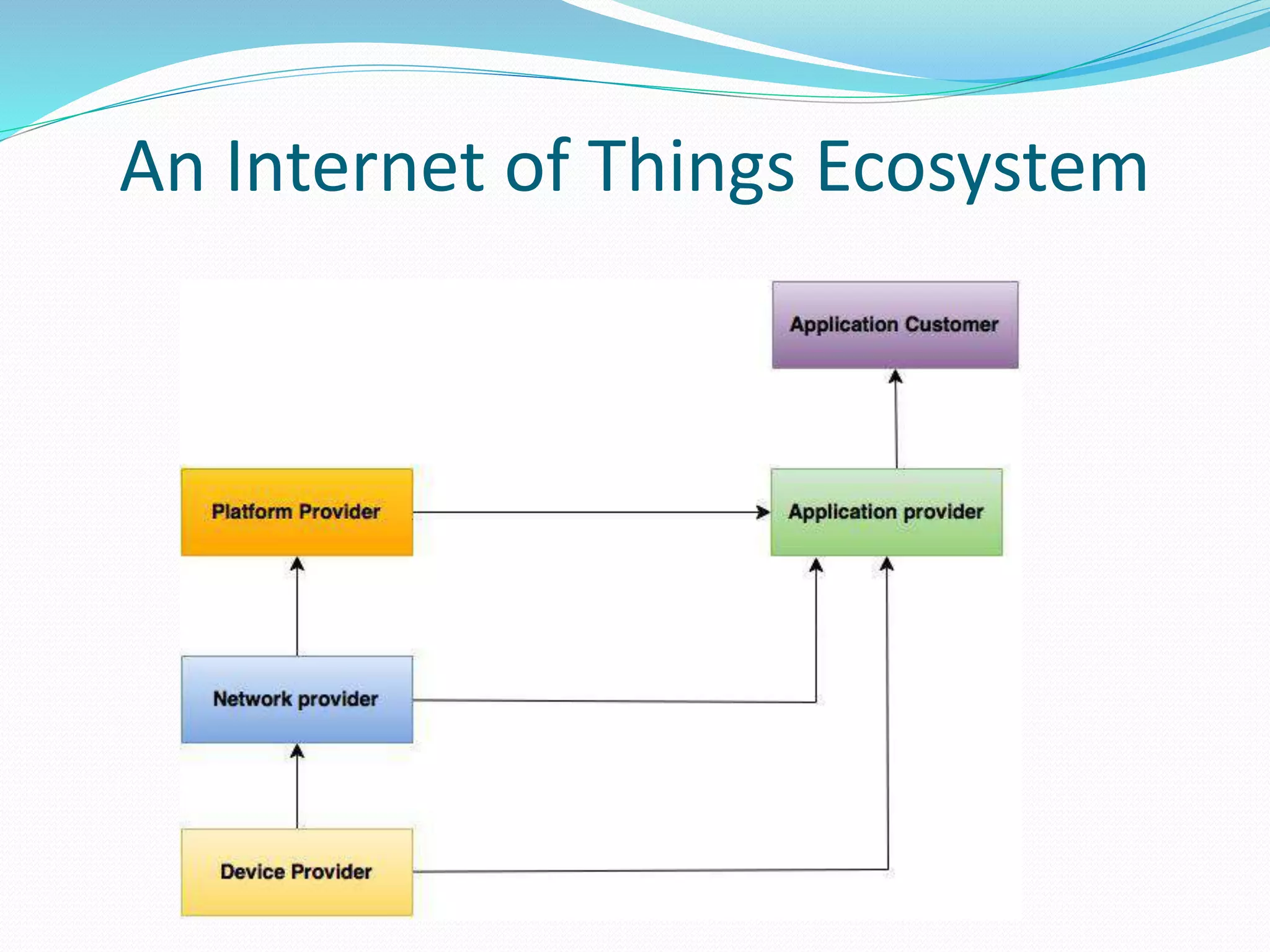
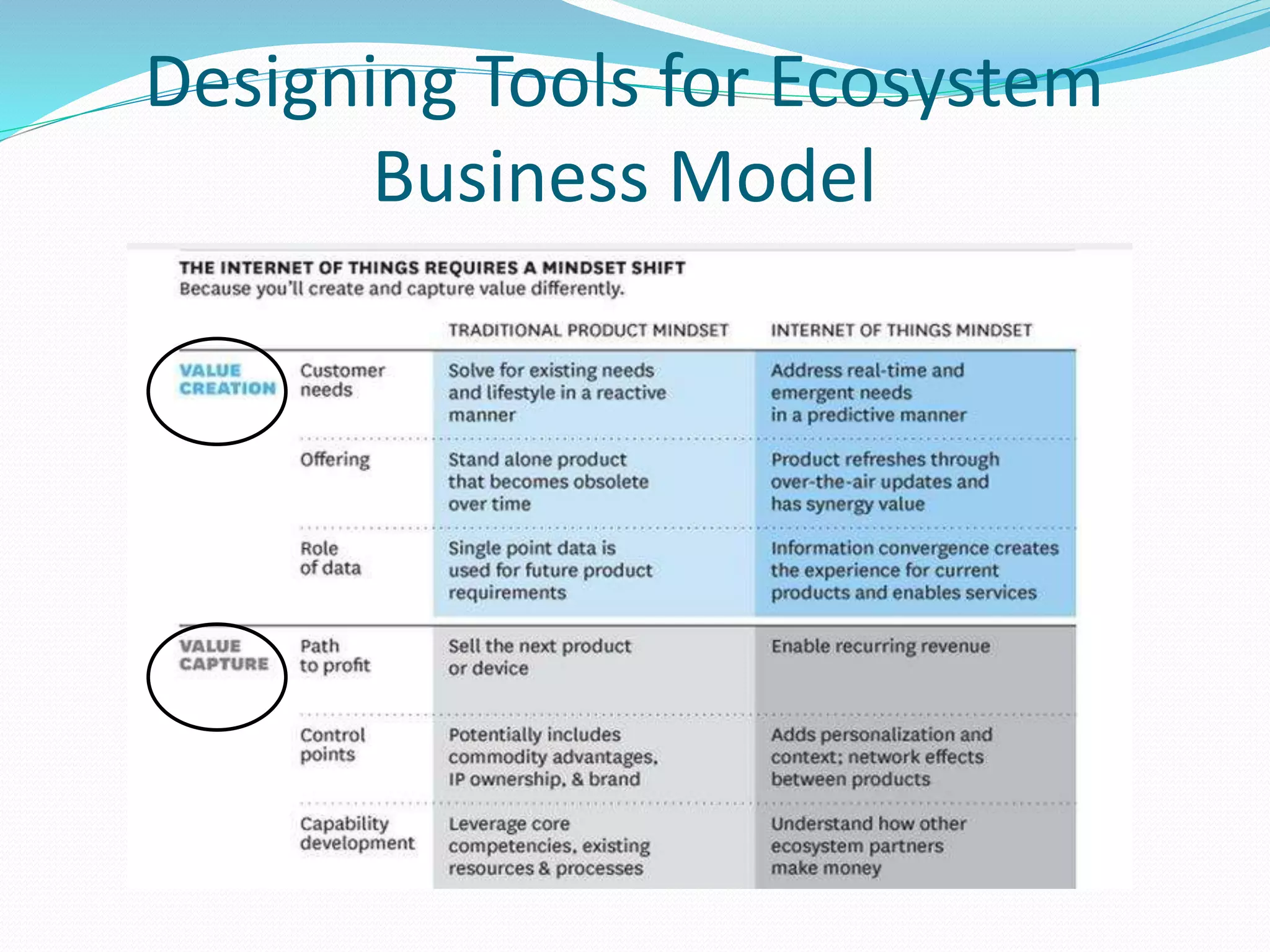
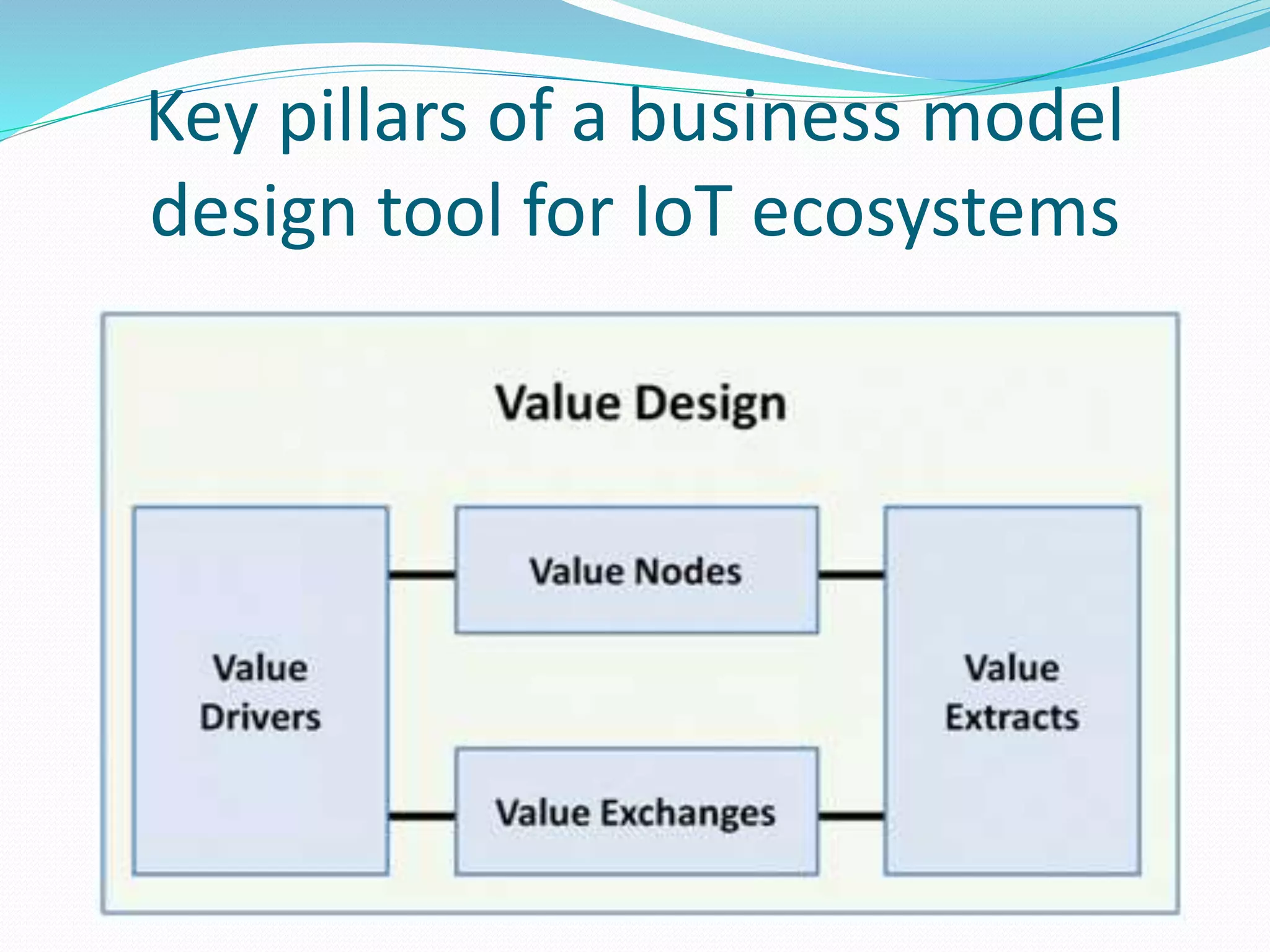
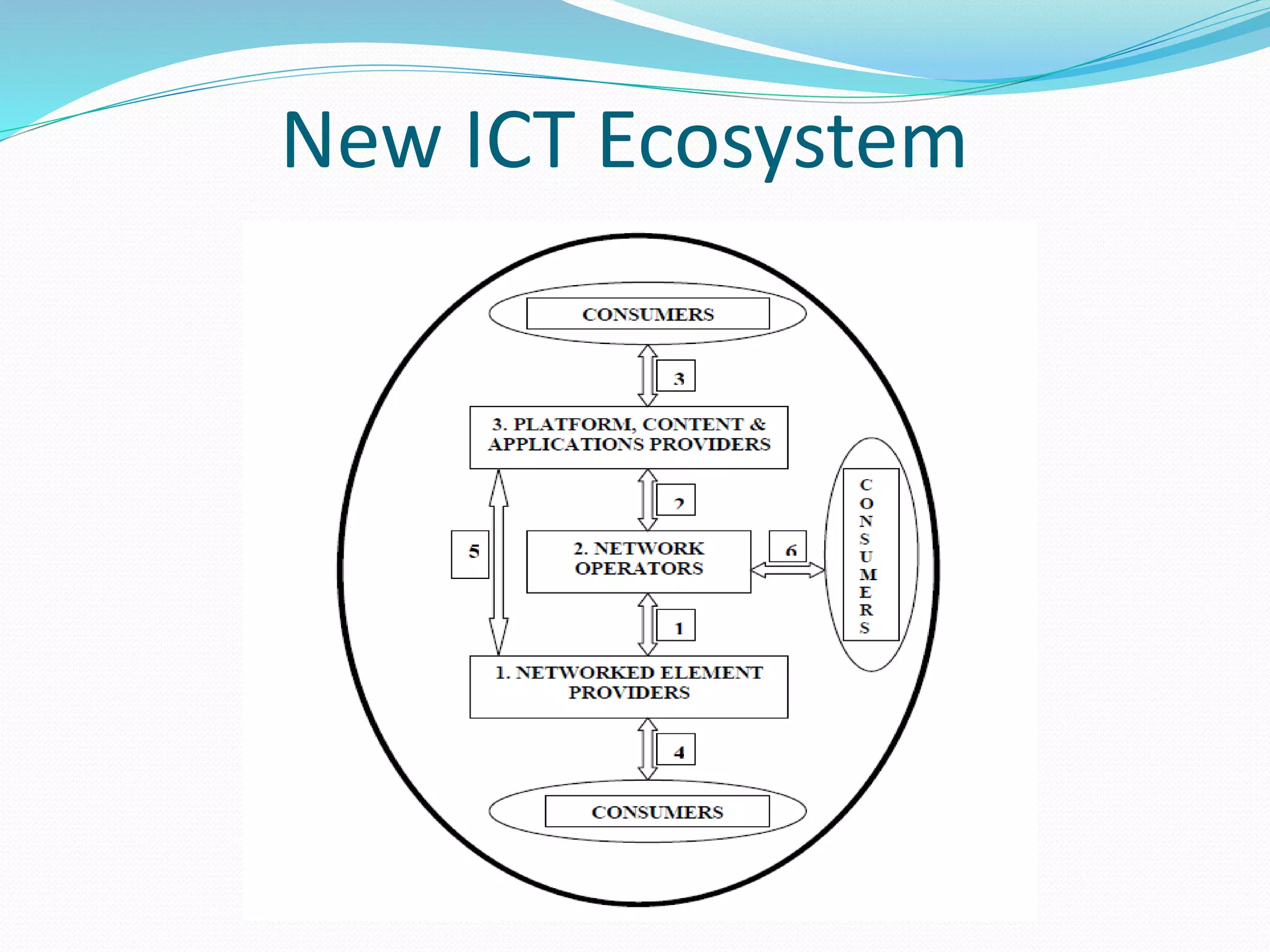
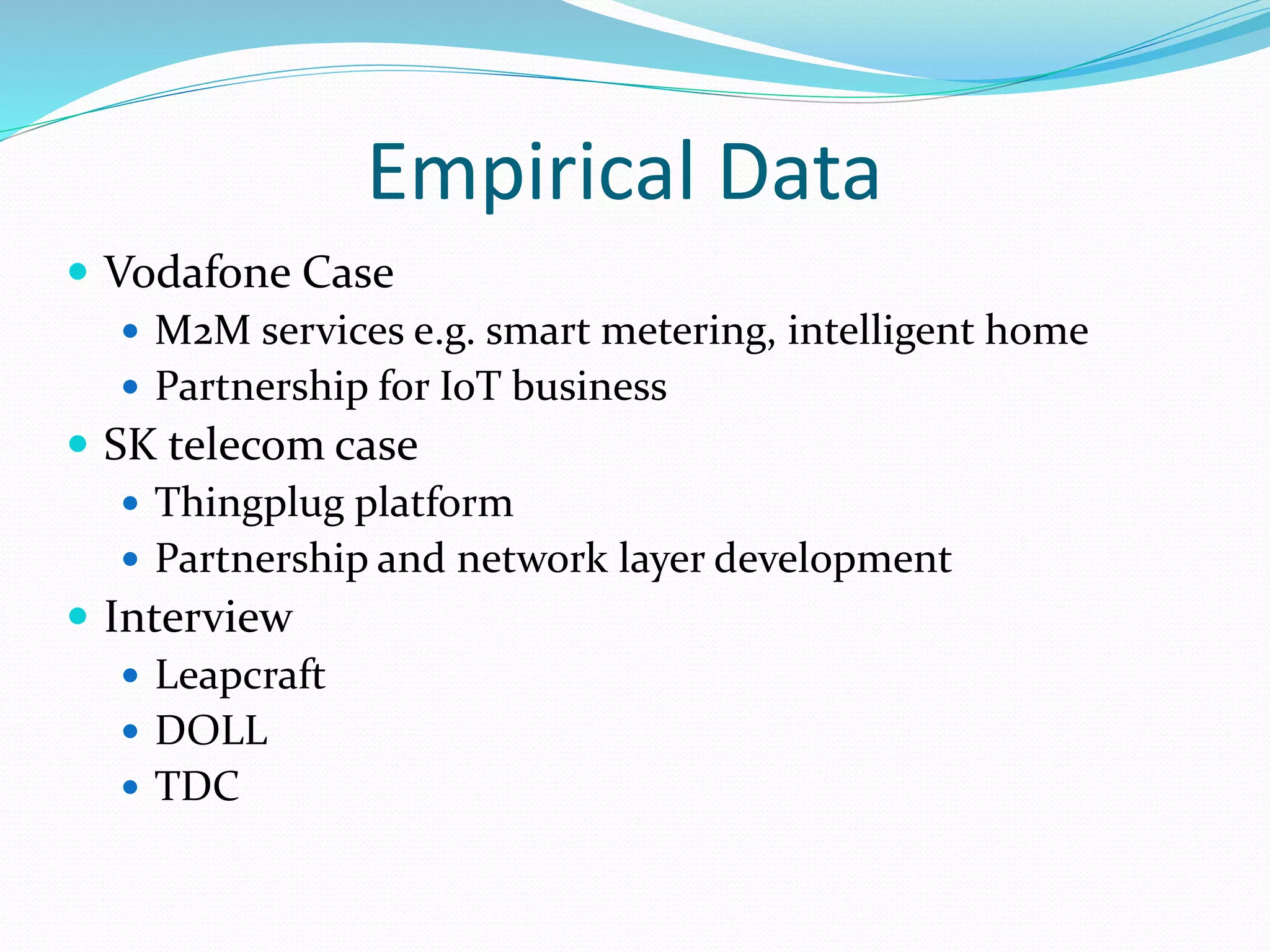
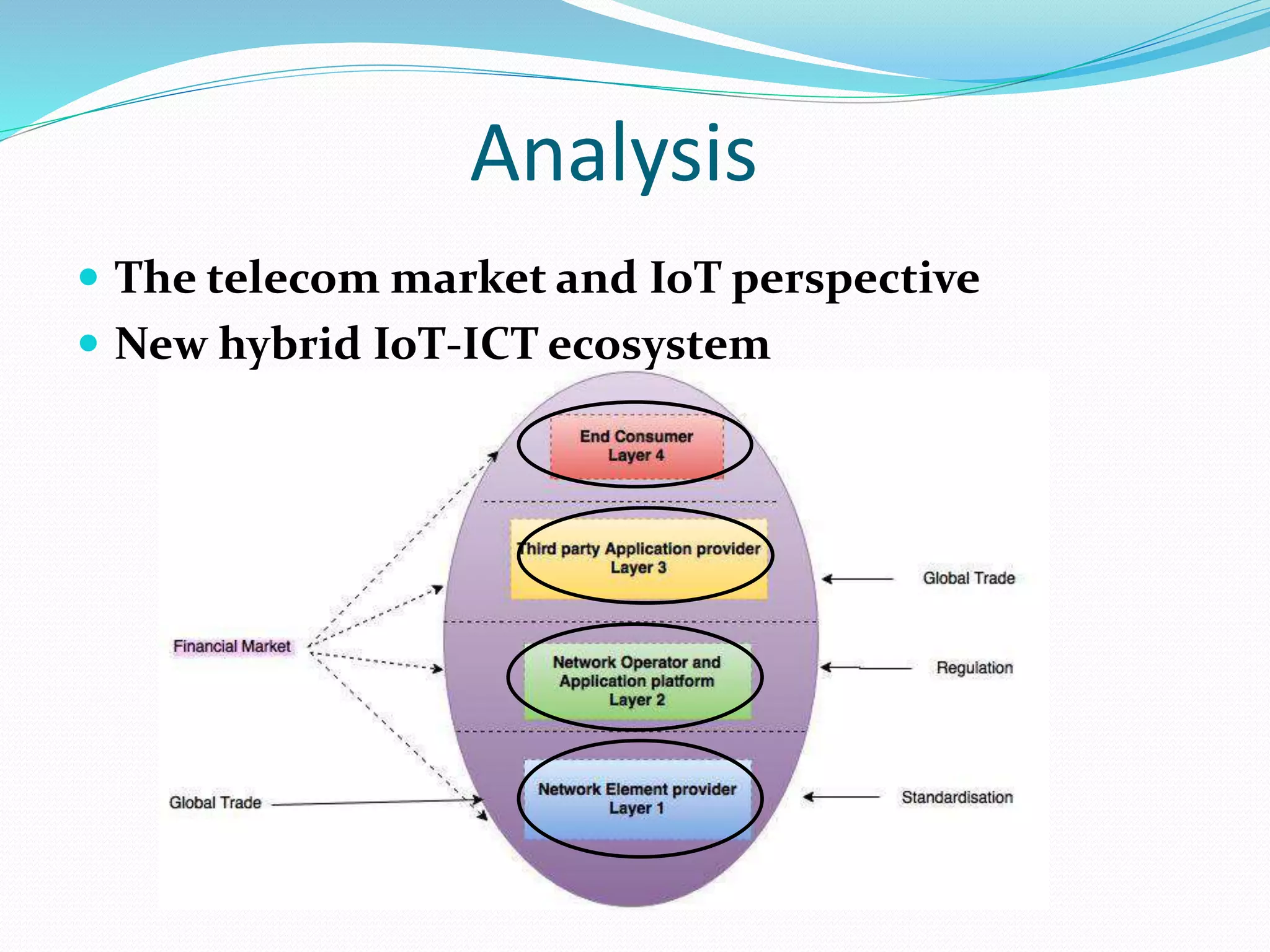
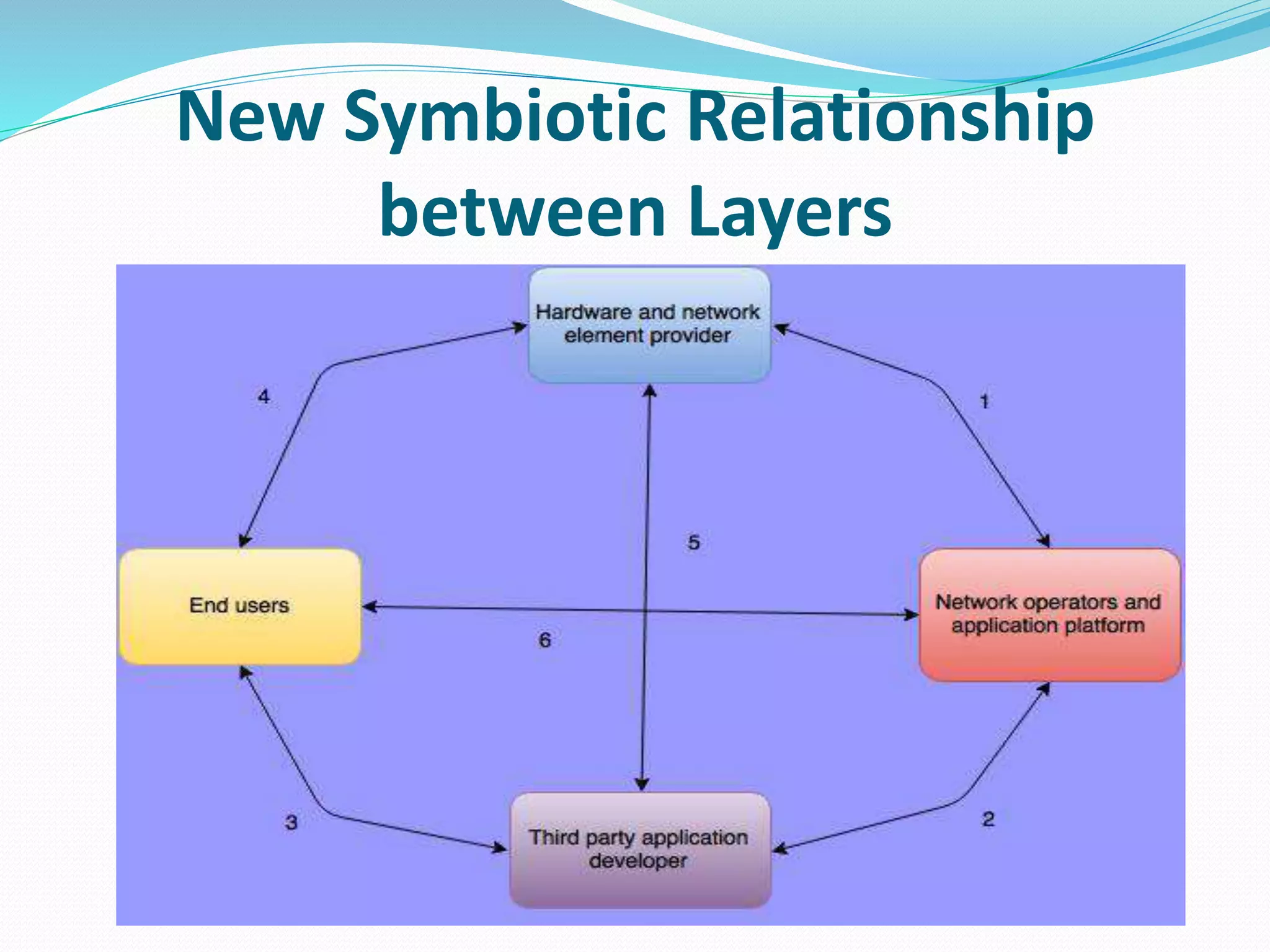
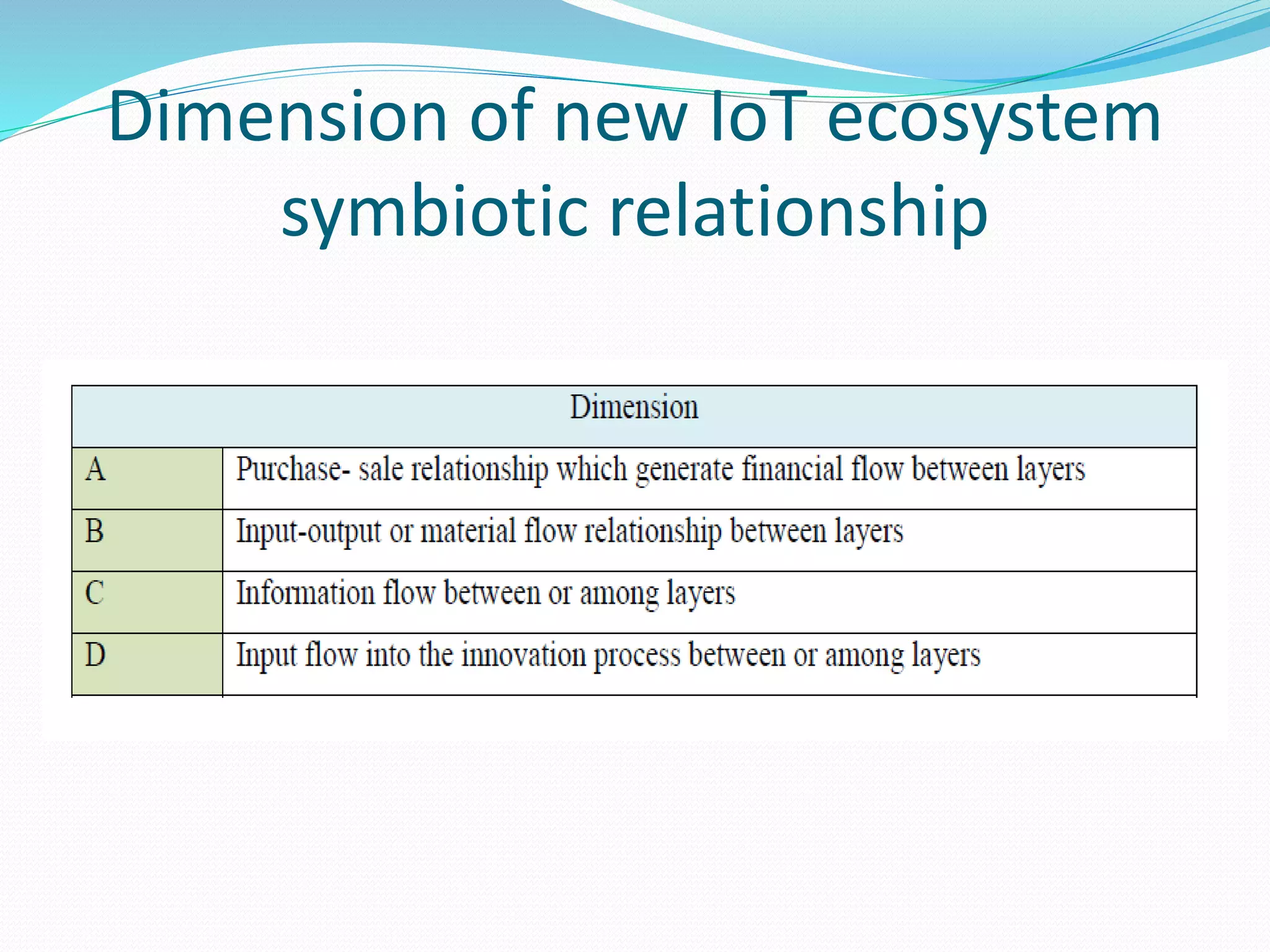
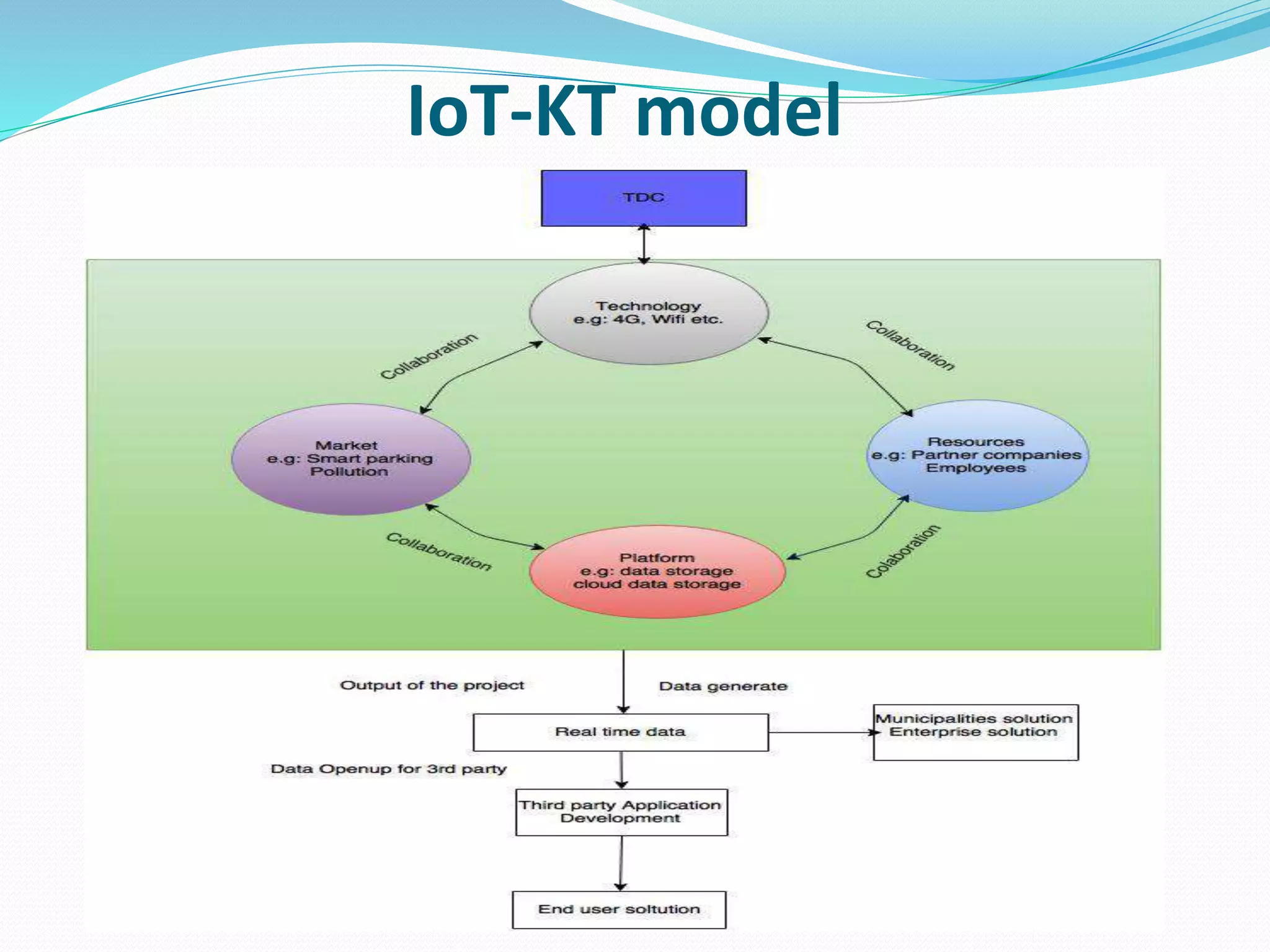
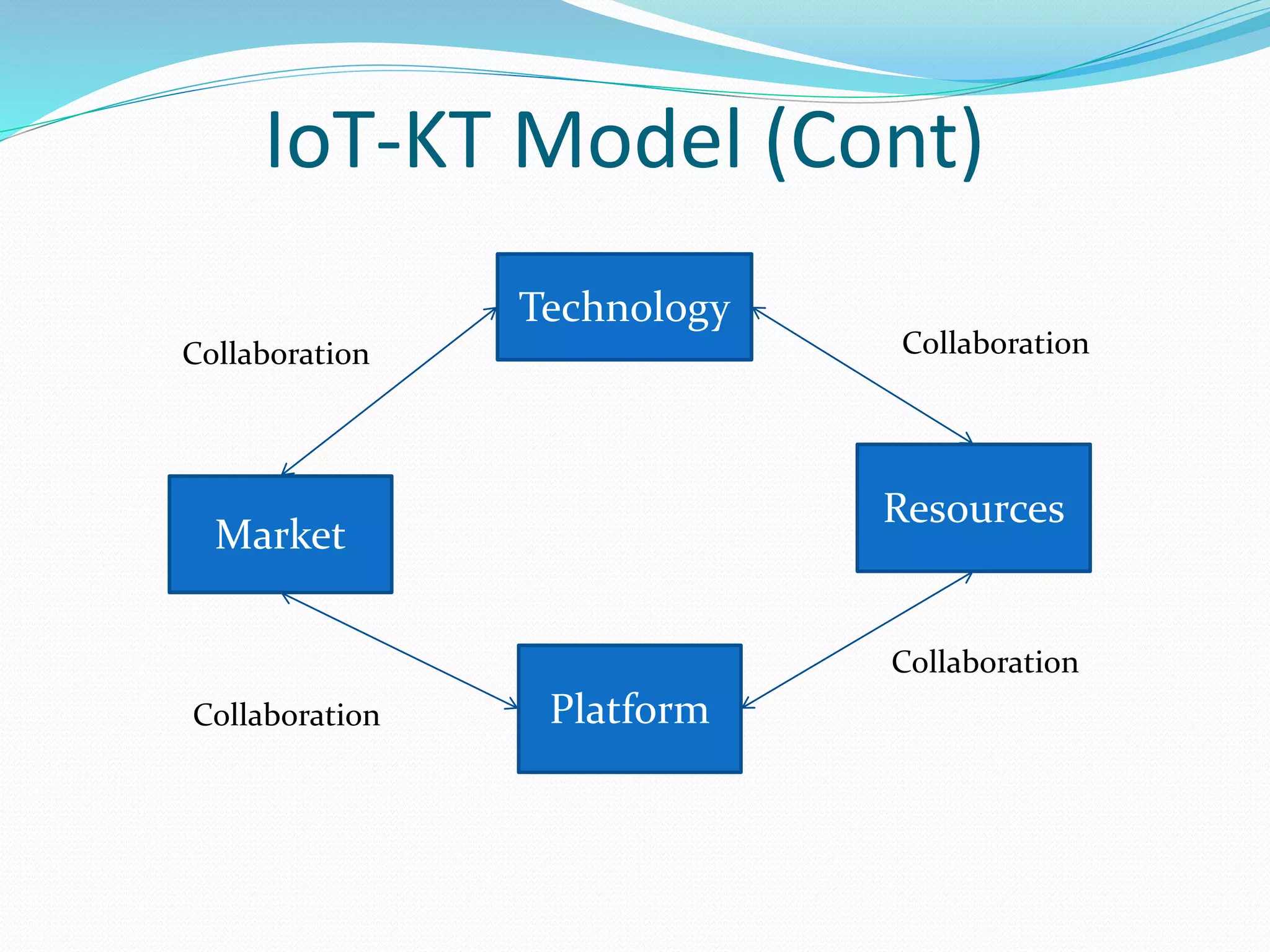
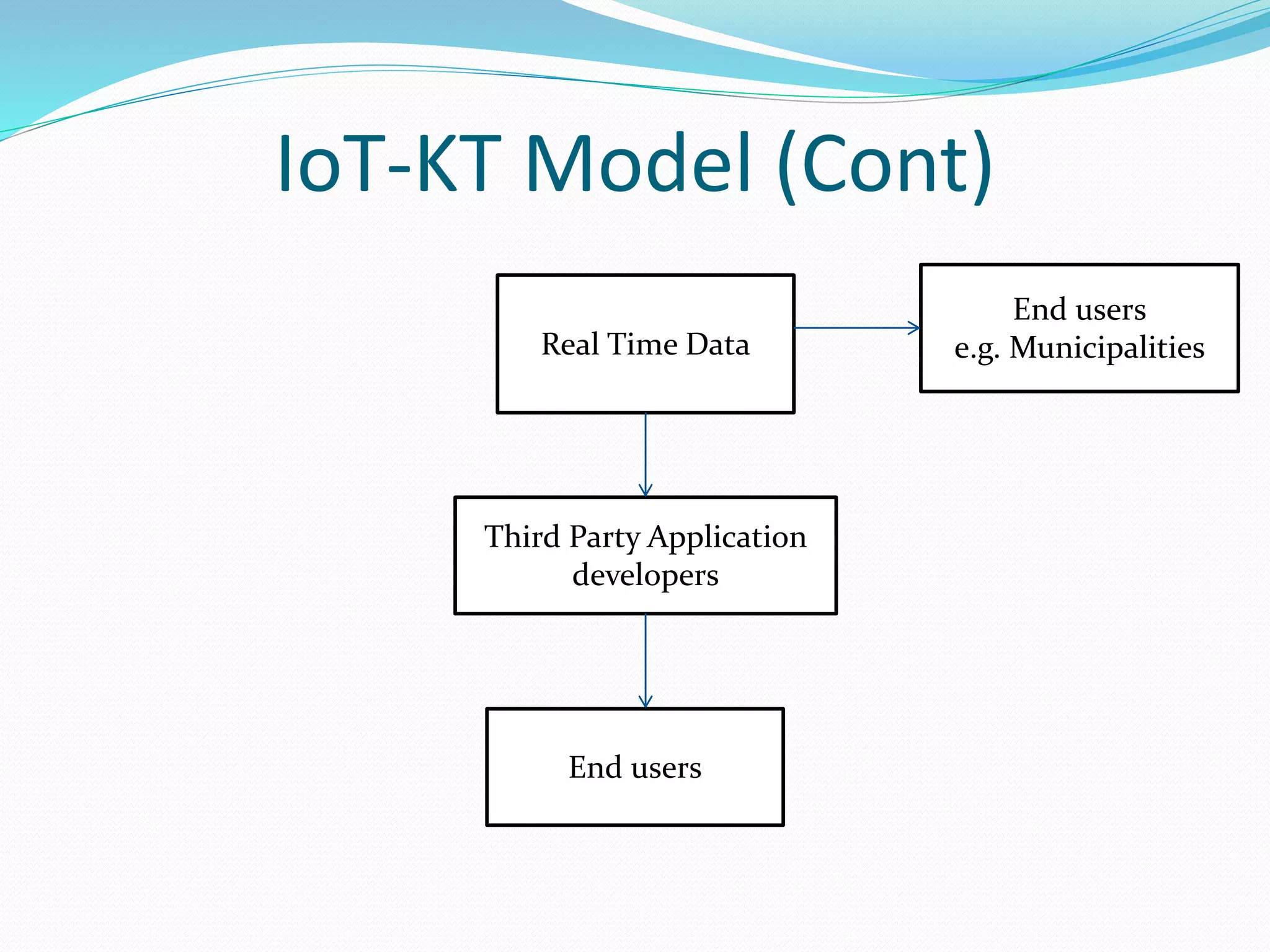
The document discusses Internet of Things (IoT) and TDC's potential future role in the IoT market in Denmark. It defines IoT and notes that the number of connected devices is expected to grow dramatically by 2020 and 2025. It also discusses the potential economic impact of IoT globally. The document then examines TDC's role in the evolving IoT ecosystem in Denmark, how TDC can create value and generate profit through partnerships and by providing connectivity and services. It identifies key market areas like consumer, public, and business where TDC can expand its IoT business.