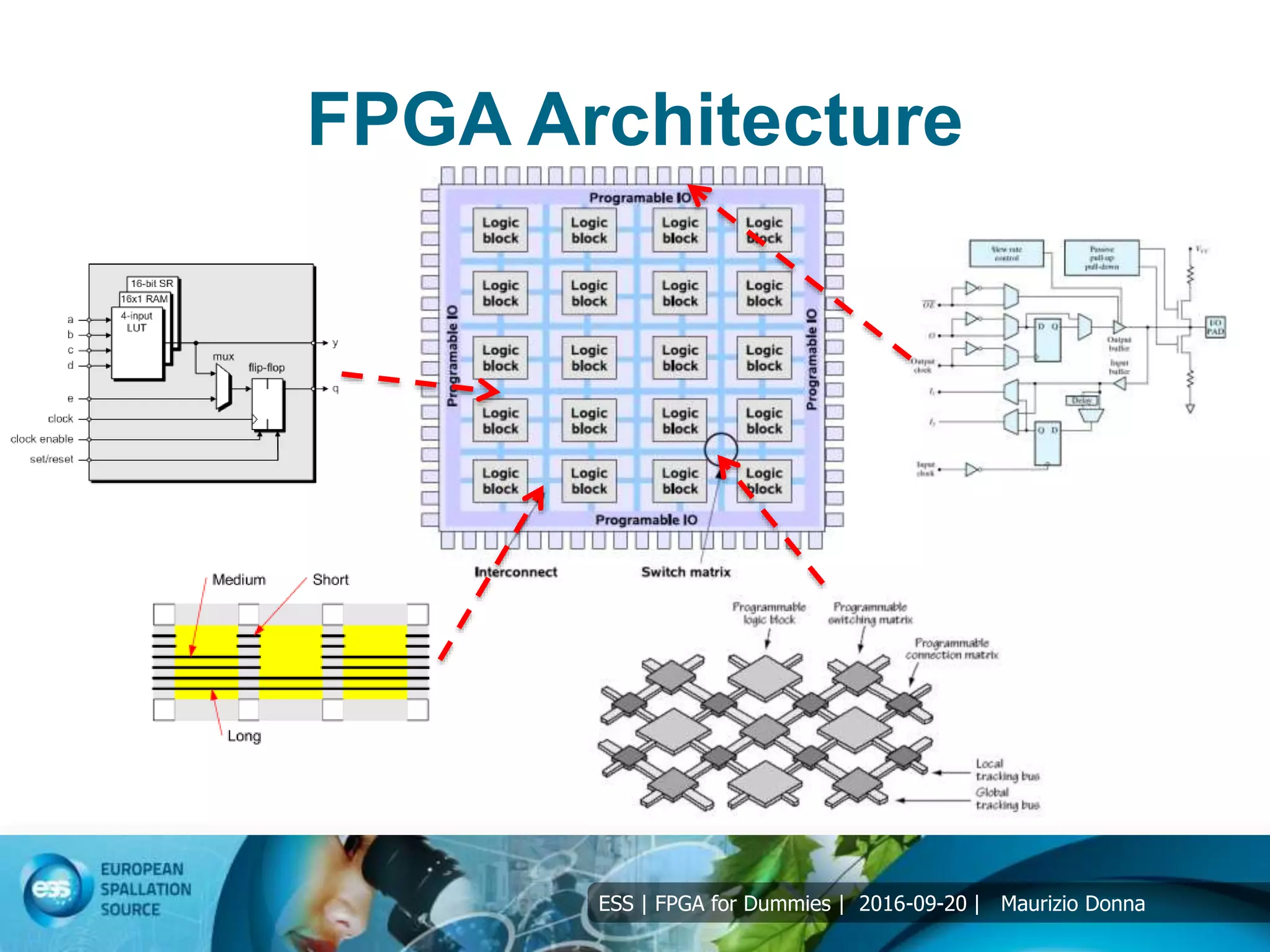
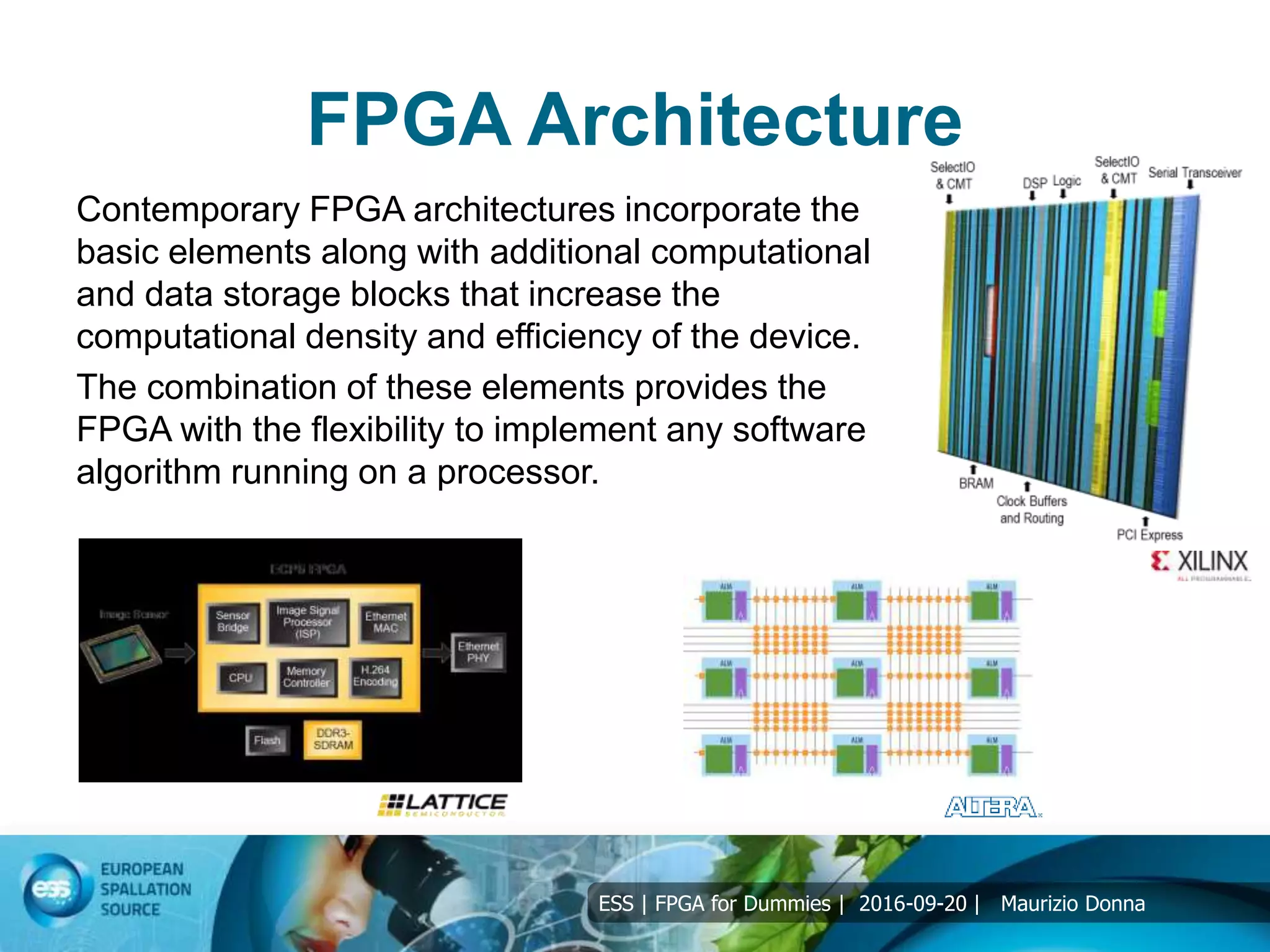
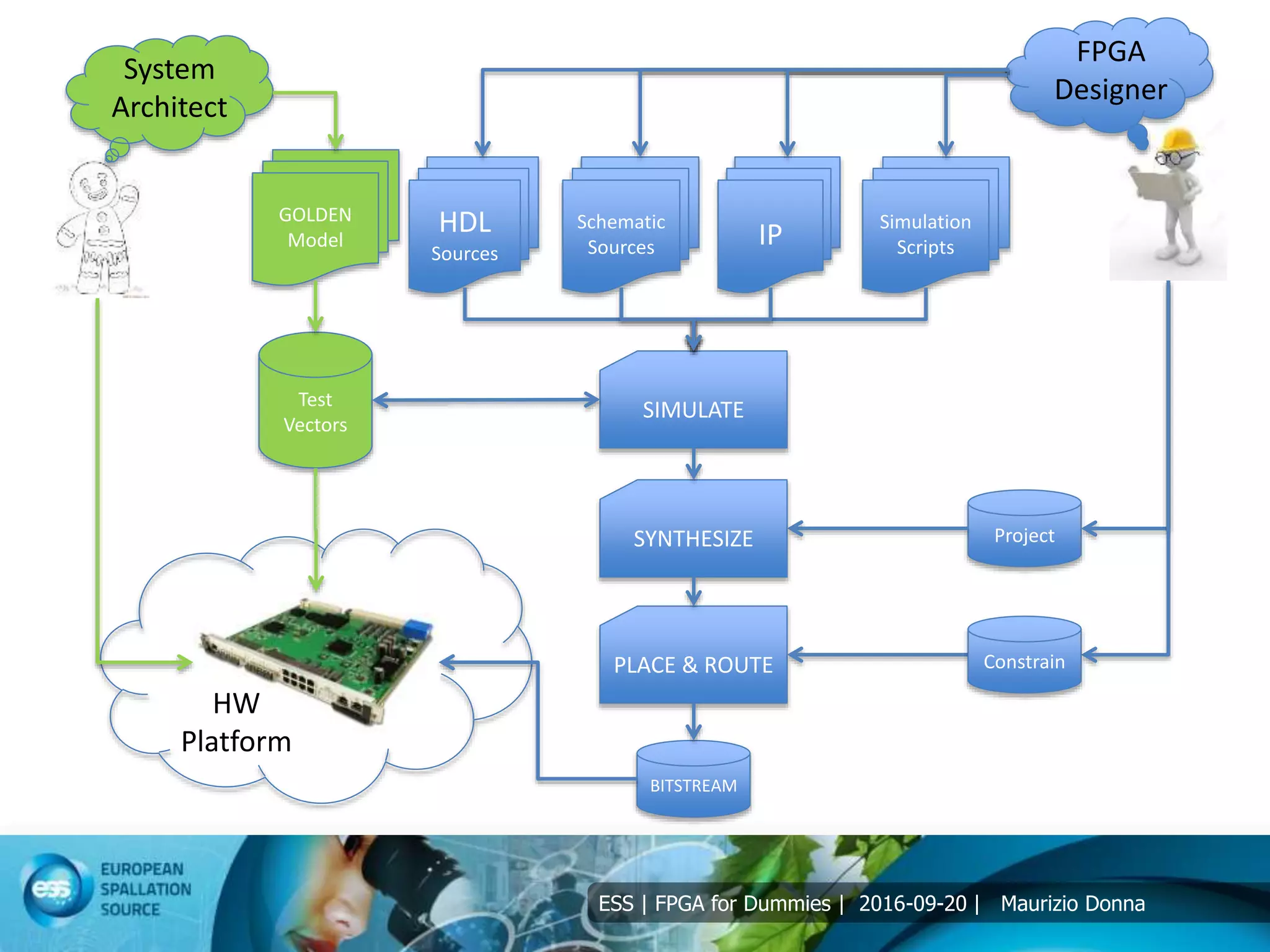
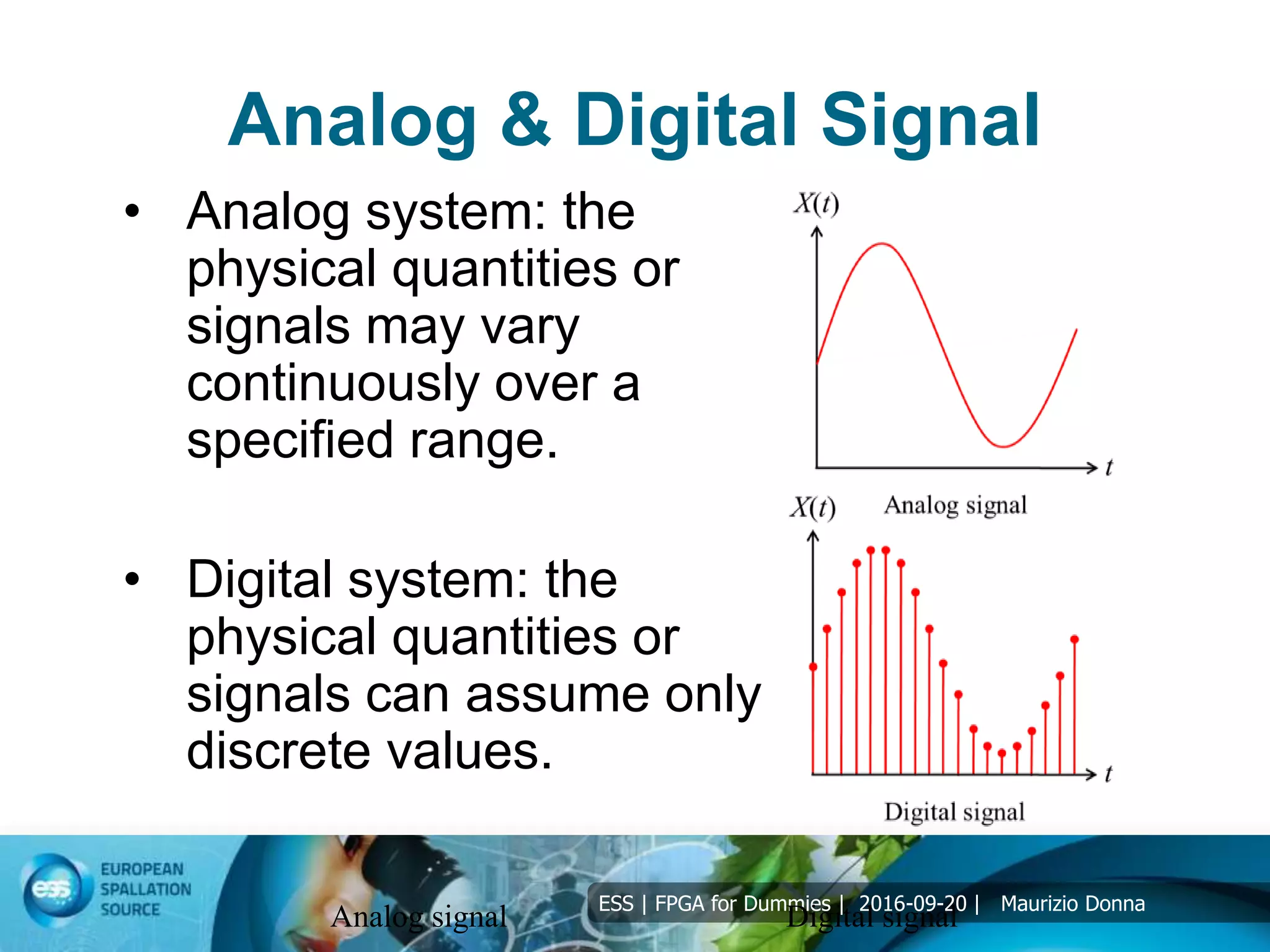
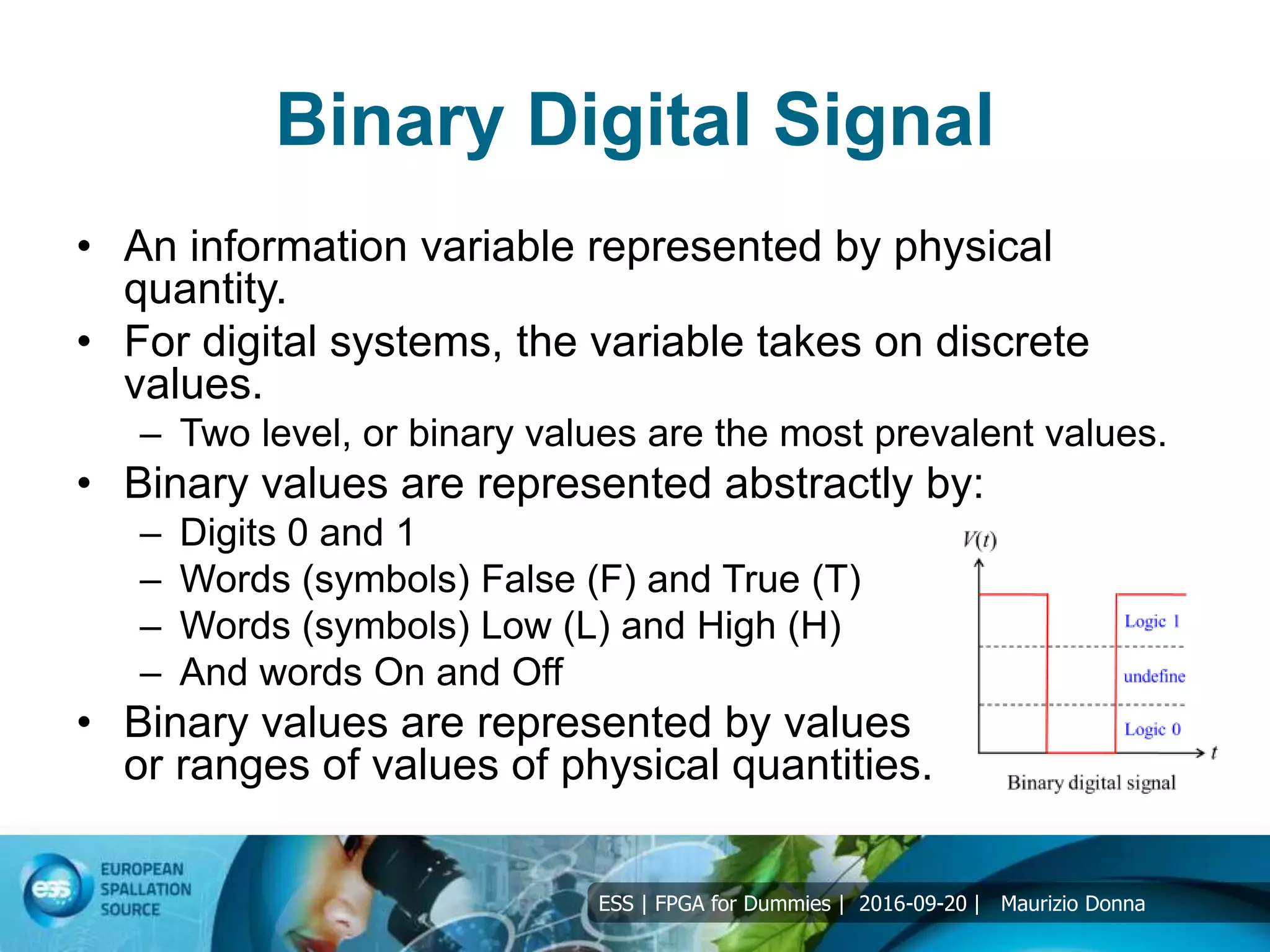
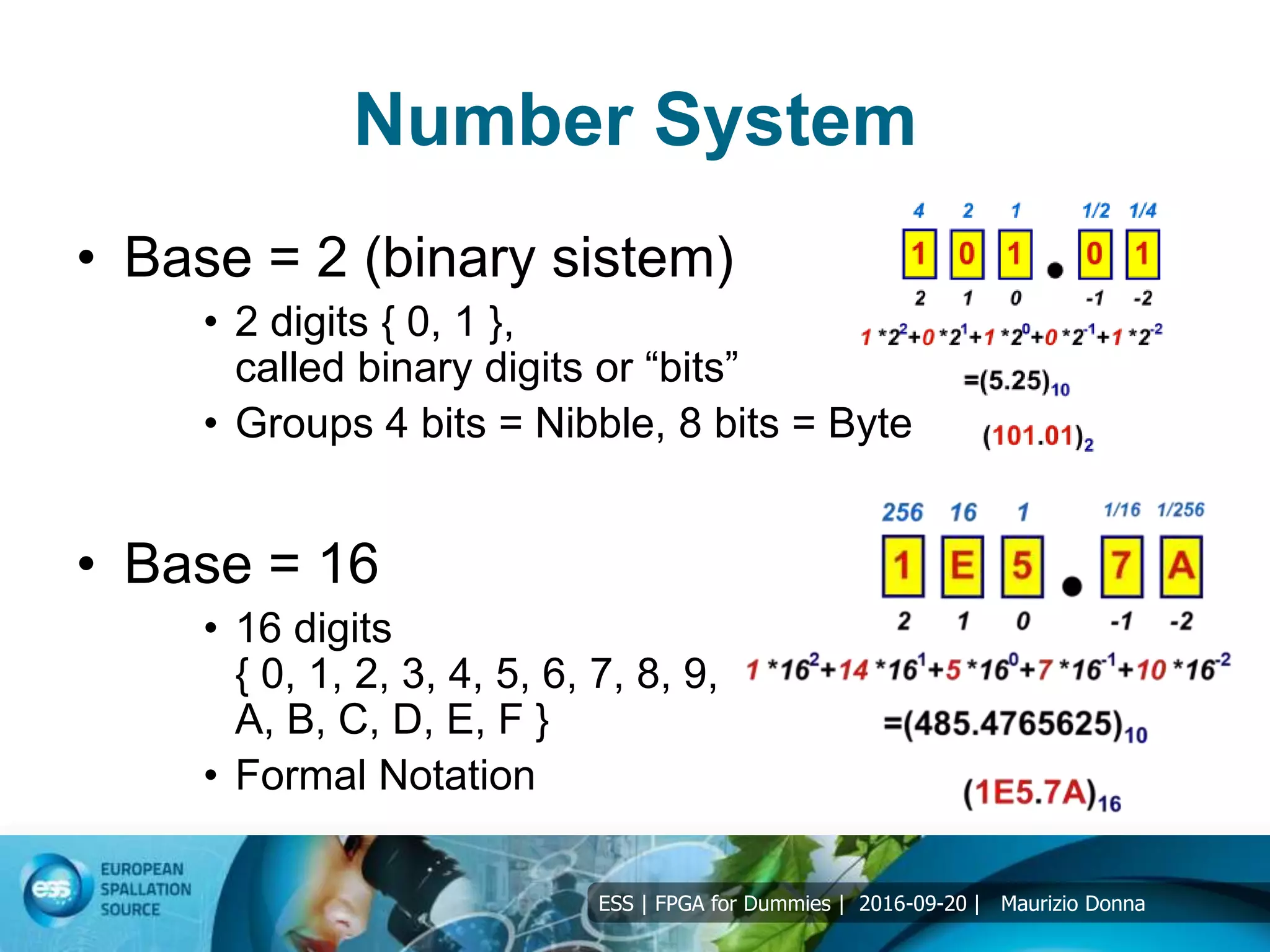
The document discusses FPGAs and their architecture. It covers FPGA programming using HDL languages and design flows. It also discusses FPGA DSP capabilities like arithmetic operations, FFTs, and filters. Basic FPGA elements are logic blocks, flip-flops, wires and I/O pads. Modern FPGAs add blocks for computations and storage. HDLs describe hardware structures and behaviors using extensive parallel operations. Common HDLs are synthesized into FPGAs using design tools to implement algorithms in programmable logic.


![ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2016-09-20 | Maurizio Donna
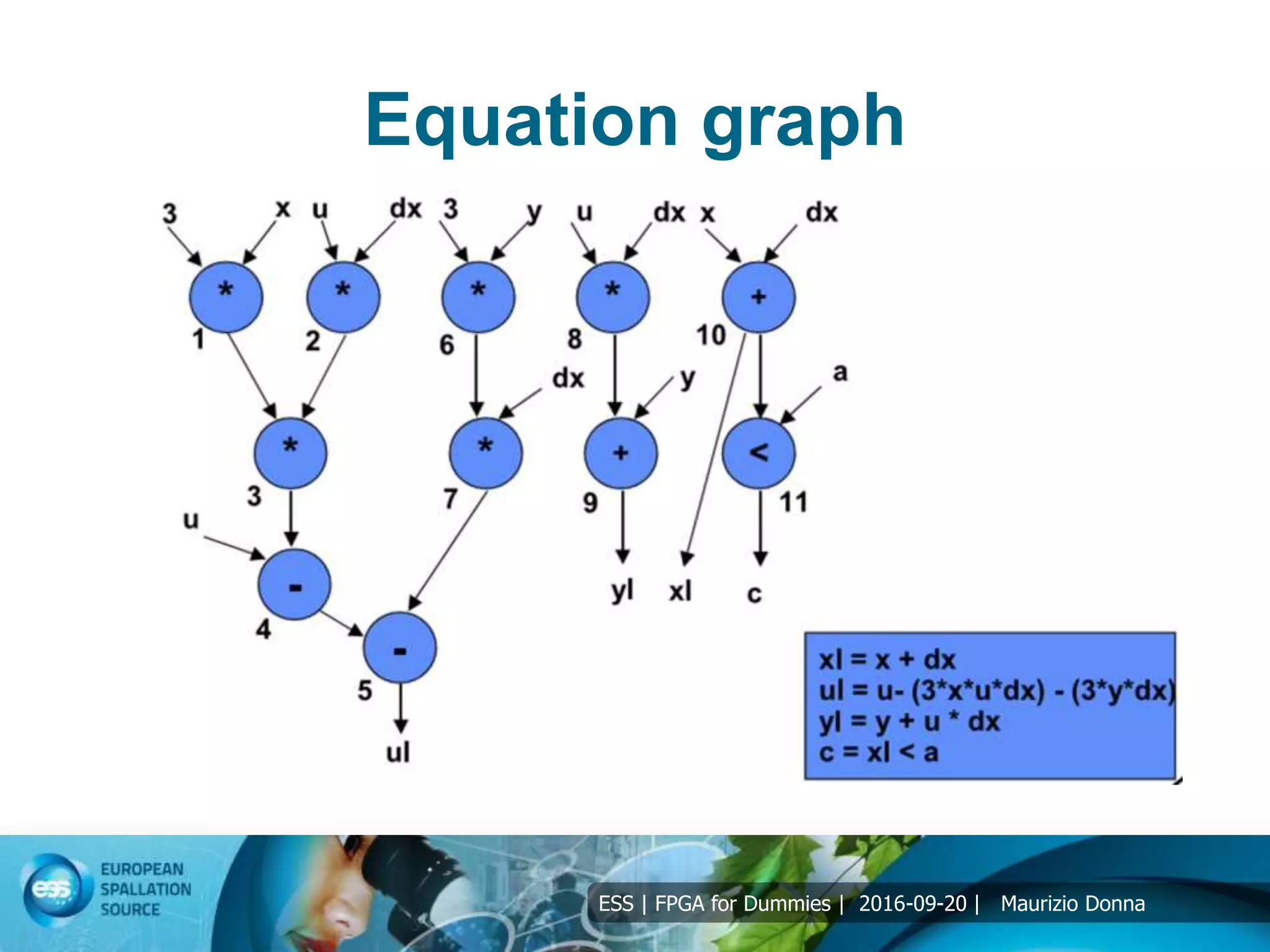
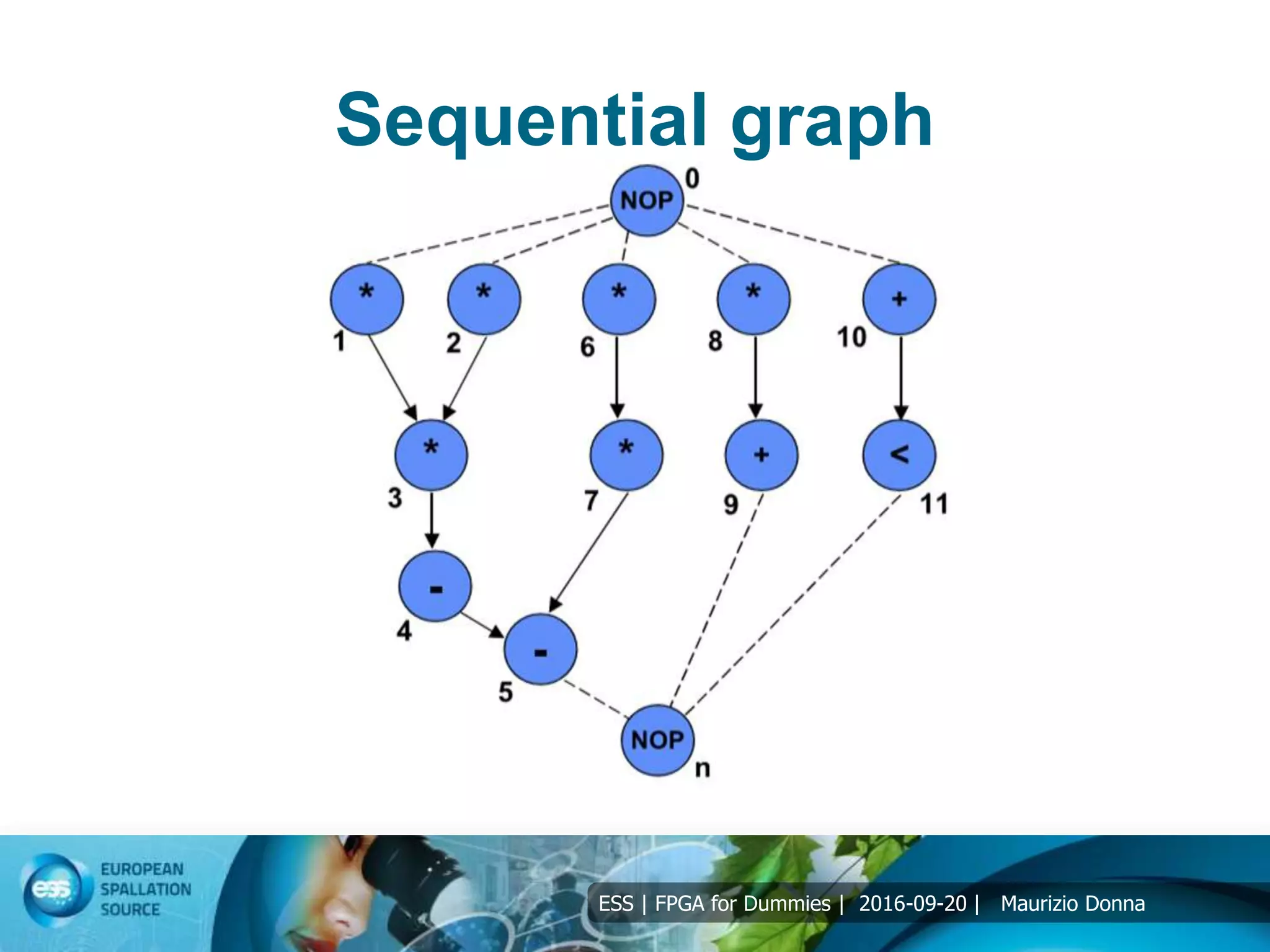
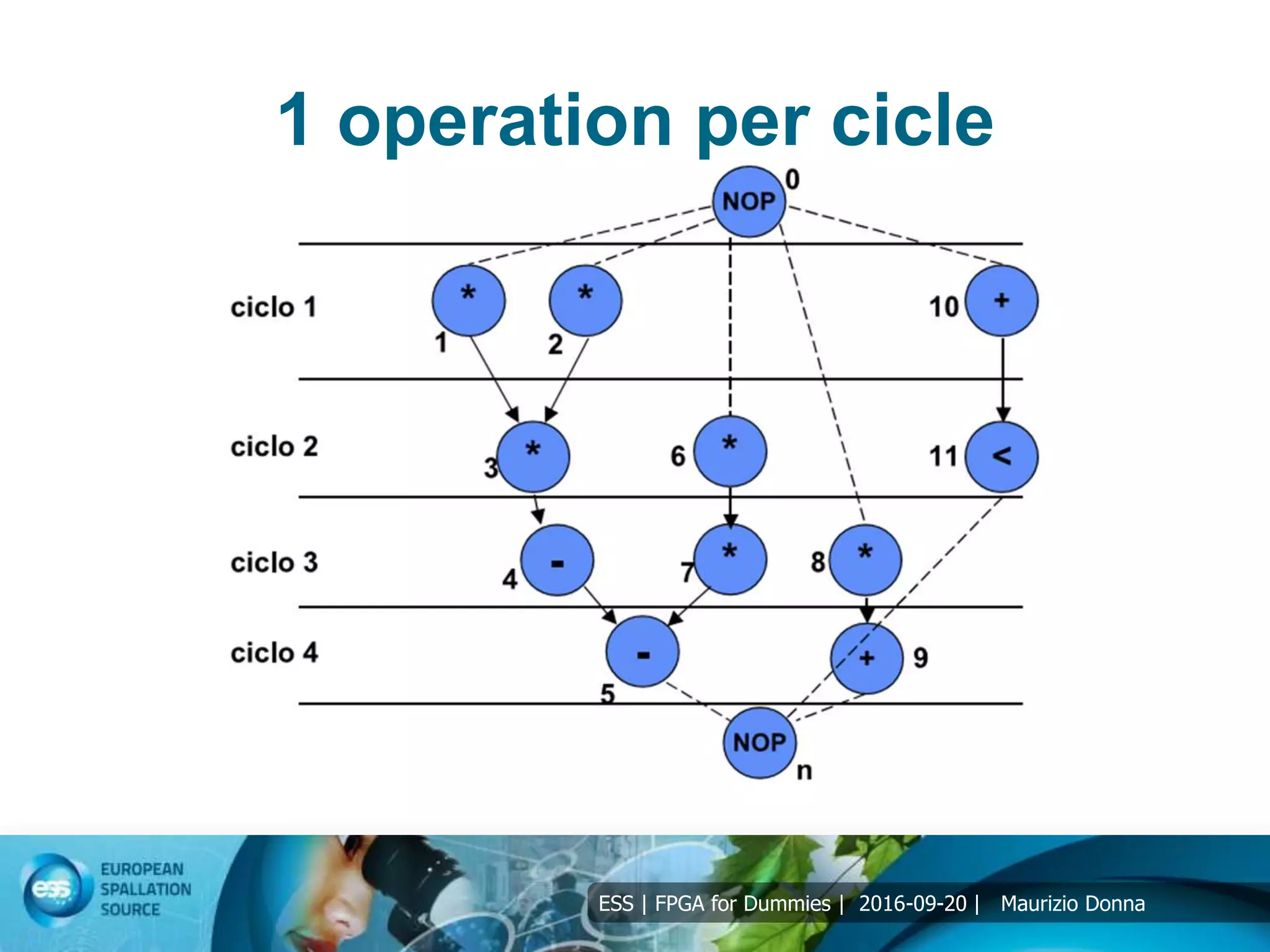
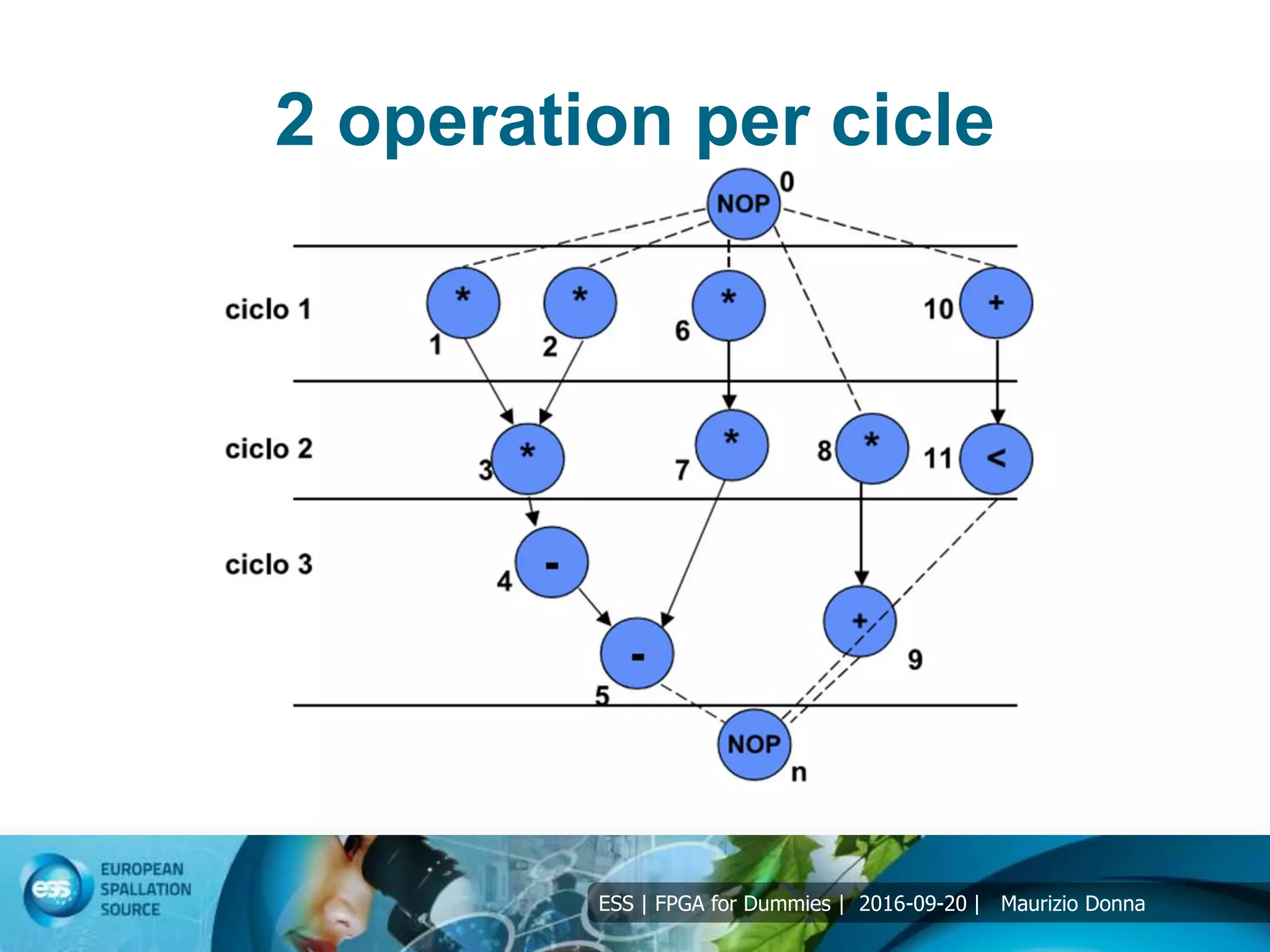
Resource allocation
4 operation: +, -, *, <>=
Example of solution of differential equation:
y” + 3*x*y’ + 3*y = 0;
Interval [0, a], integration Δx;
Initial values x(0)= 0, y(0)=y, y’(0)=u;
Solution using Forward Euler:
xn+1 = xn + Δx;
un+1 = un – Δx*(3*xn*un + 3*yn);
yn+1 = yn + un*Δx;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-191031132900/75/5-FPGA-for-dummies-DSP-12-2048.jpg)