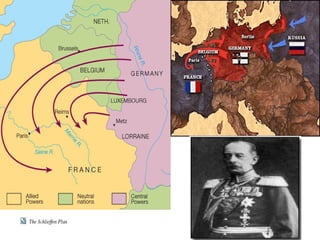
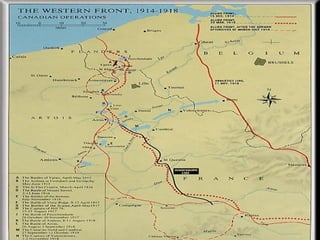
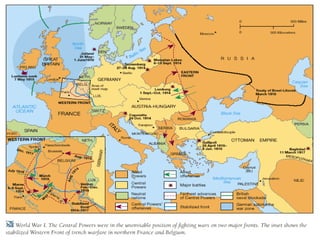
The Schlieffen Plan called for Germany to quickly defeat France before turning east to face Russia. Germany pushed through Belgium in 1914 but could not defeat France fast enough. By late 1914, the Western Front was locked in trench warfare that lasted for years. Russia initially had successes against Austria-Hungary and Germany but faced devastating losses. Turkey joining the war in late 1914 further strained Russia. The Russian Revolution in 1917 took Russia out of the war. The US entry into the war in 1917 helped balance Russia's exit and provided resources that aided the Allied powers. After years of brutal trench warfare, the Hundred Days Offensive in late 1918 pushed the Germans back and led to the armistice ending the war.