Embed presentation
Download to read offline



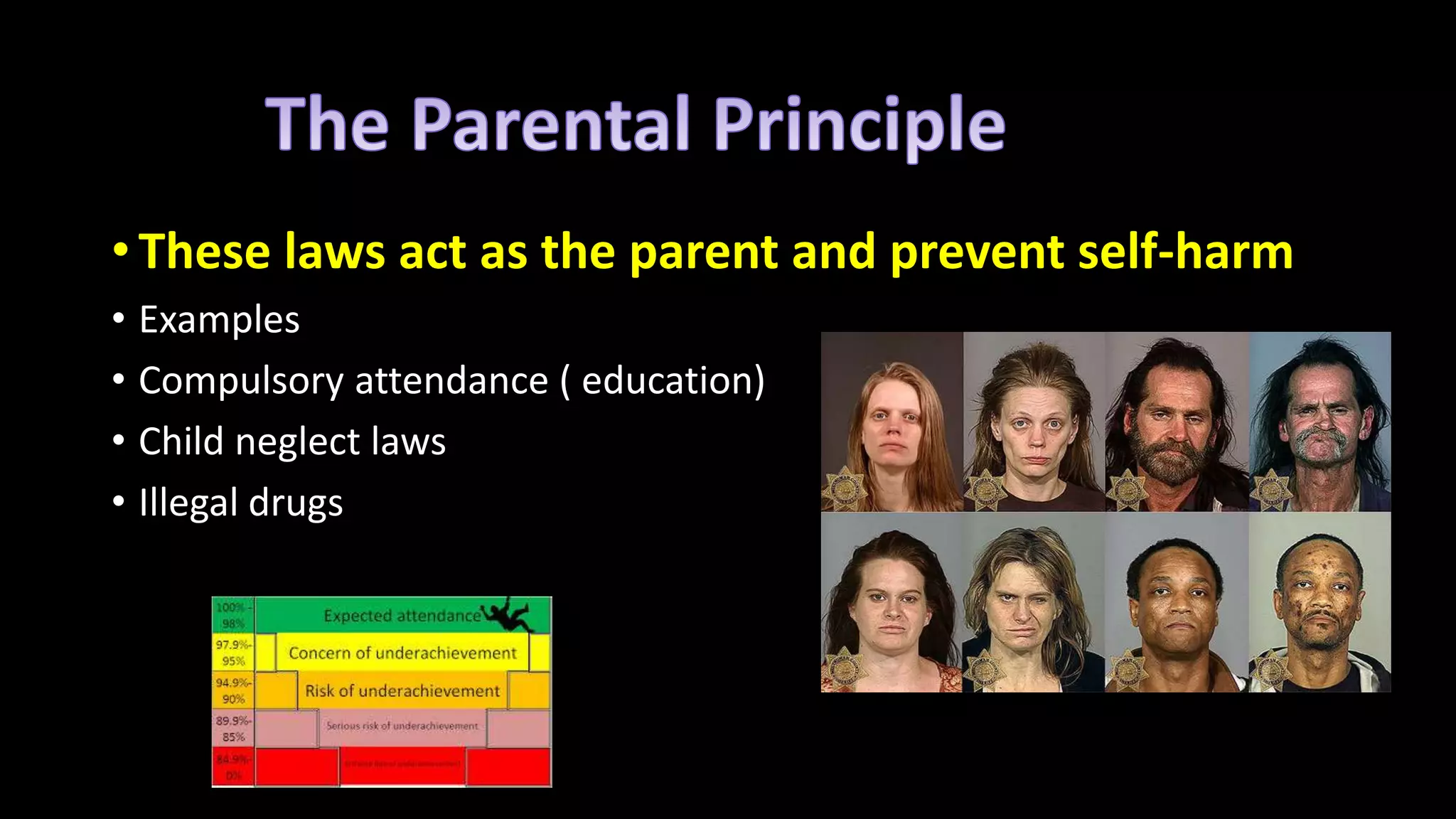
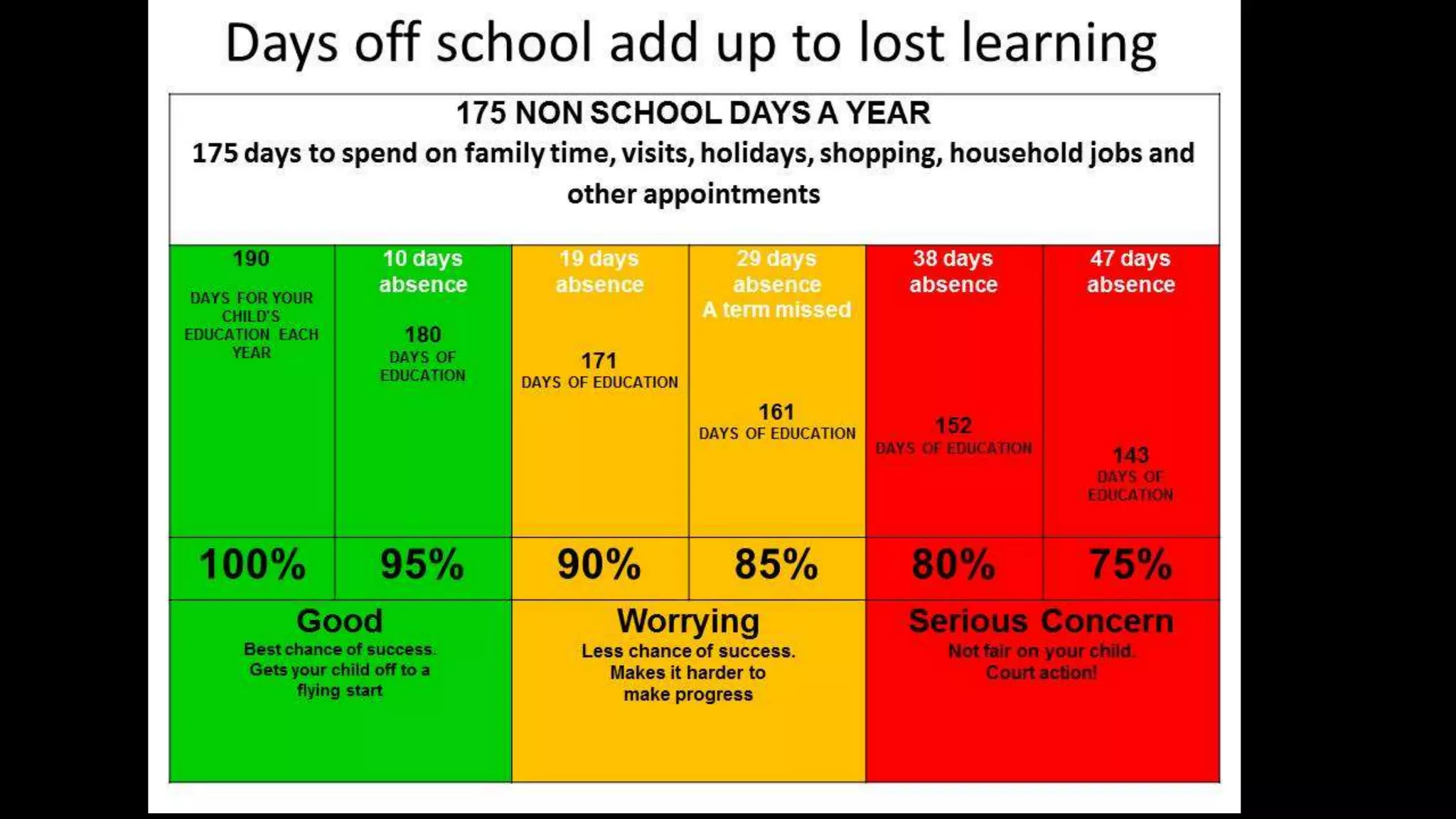



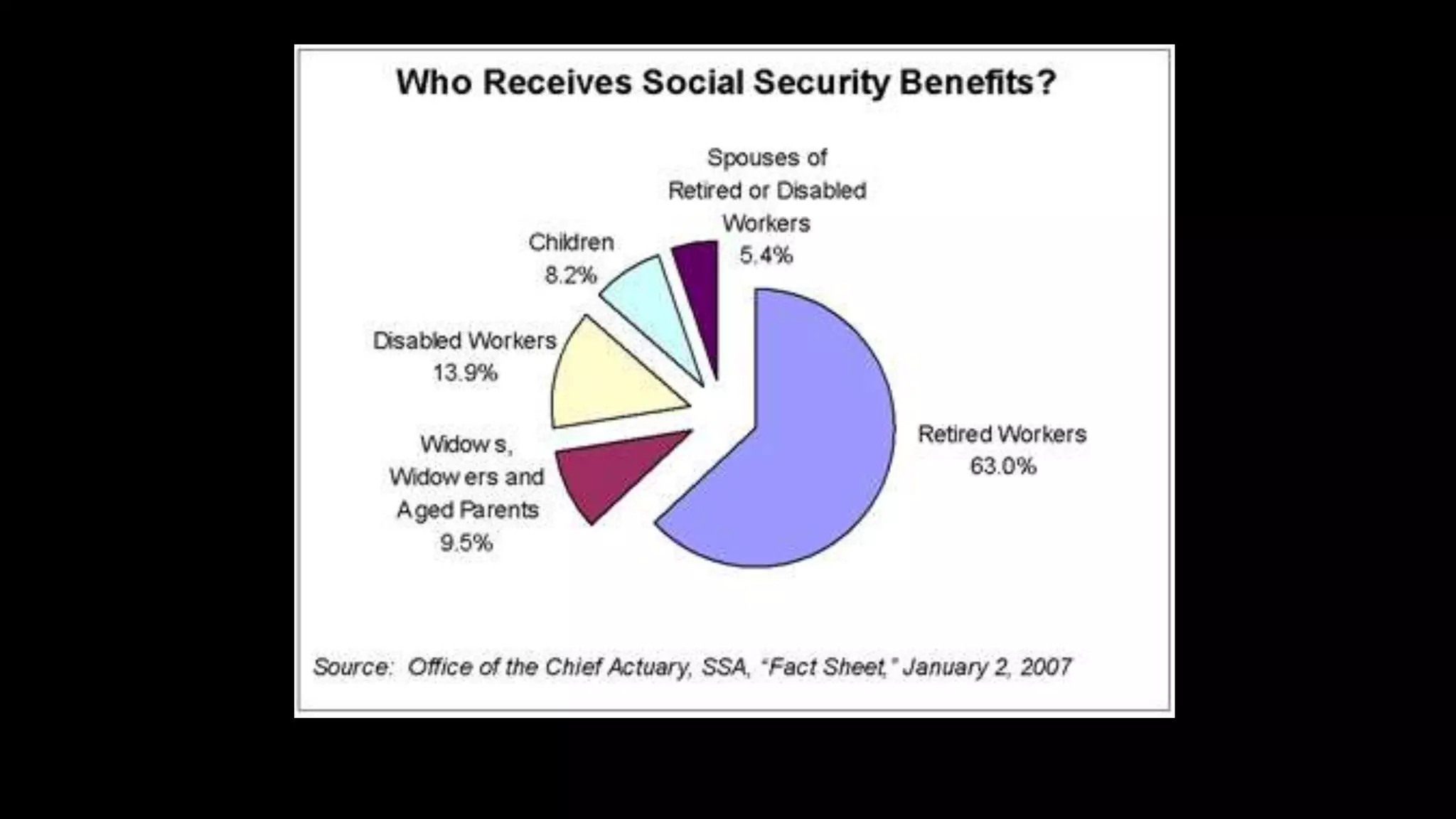

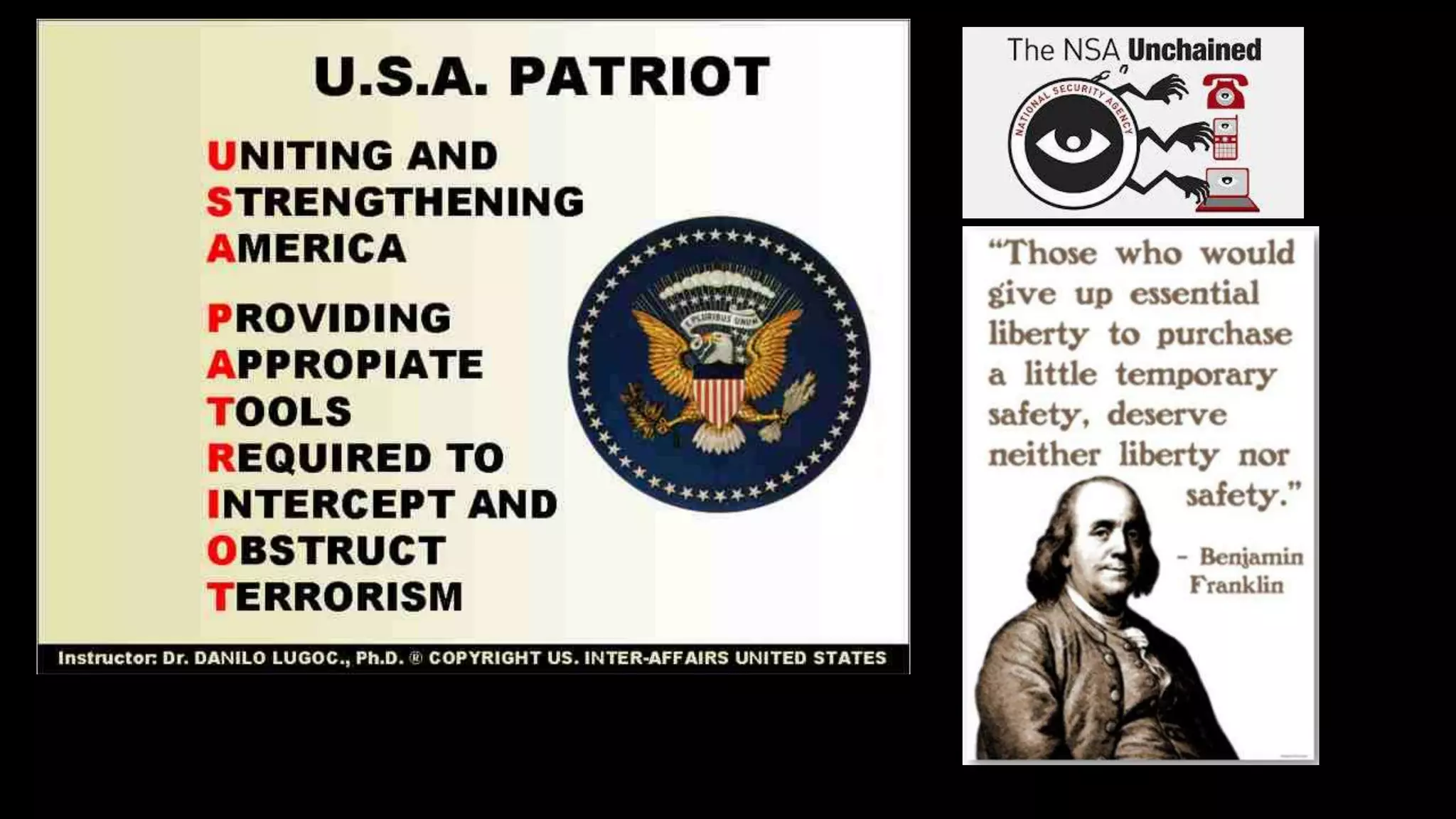


John Locke believed that in the state of nature life was without laws or government and it was a survival of the fittest. He argued that all persons have natural rights to life, liberty, and property. Locke's social contract theory holds that individuals give up some rights and freedoms to join society and enjoy safety by following laws. The document then discusses four principles of law: the harm principle which protects people from harm by others through laws like those against murder; the donation principle which provides public services through taxes; the personal morality principle which can be based on religion and cover things like hate speech; and the statist principle intended to protect government through laws against treason but which can threaten civil liberties.











