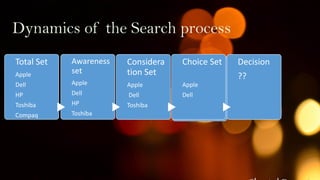
The document outlines the 5 stages that consumers go through in the buying process: 1) problem recognition, 2) information search, 3) evaluation of alternatives, 4) purchase decision, and 5) post-purchase behavior. It describes each stage in detail, including how internal and external stimuli can trigger problem recognition, the different sources of information consumers use in their search, and how they evaluate alternatives based on attributes and form attitudes. The document also discusses factors that can influence the purchase decision and the importance of satisfying consumers in the post-purchase stage through reinforcement of their choice.