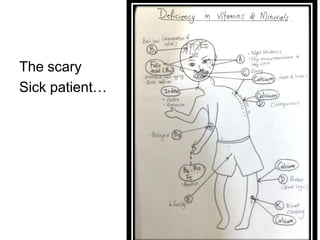
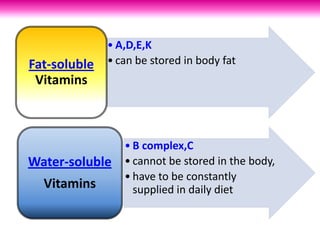
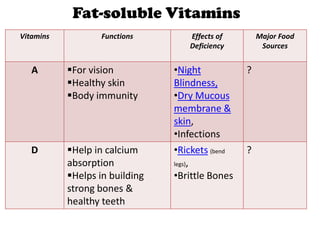
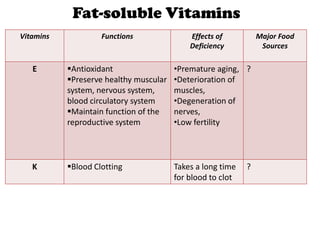
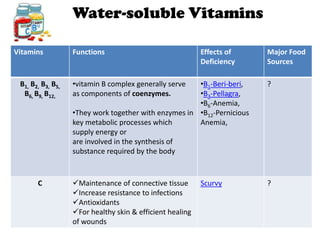
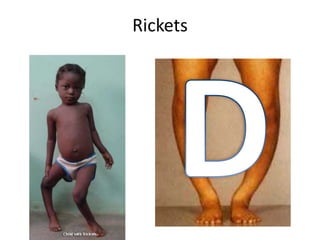
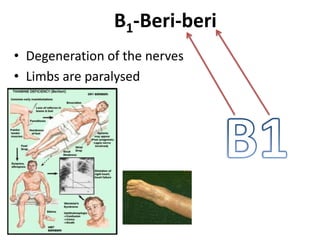
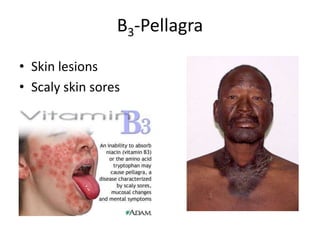
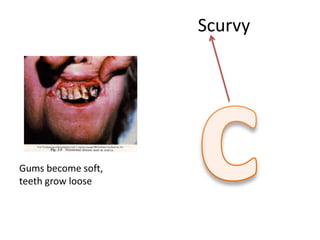
The document outlines the learning outcomes related to vitamins, emphasizing their importance in maintaining health, sources, and the effects of deficiencies and overdoses. It categorizes vitamins into fat-soluble and water-soluble groups, detailing their functions and associated deficiency diseases. Overall, the document serves as a guide for understanding vitamins' roles in the diet and their impact on human health.