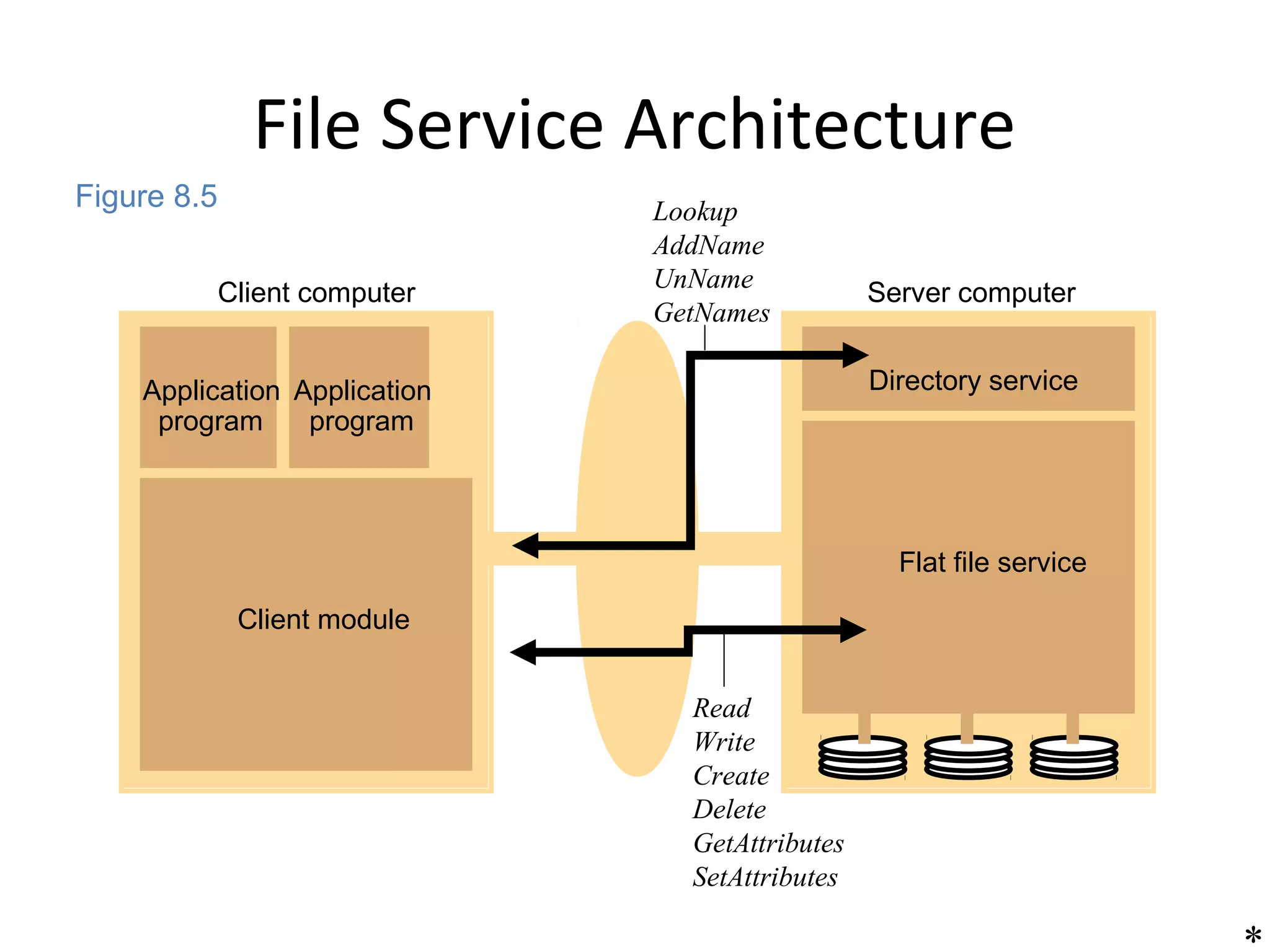
This document discusses distributed file systems (DFS), which provide access to files across a network. It describes the typical architecture of a DFS including flat file services, directory services, and client modules. Flat file services implement operations like read, write, create and delete on file contents. Directory services provide name to identifier mappings and support functions for adding/removing files from directories. The client module provides a unified interface to applications and knows the locations of file and directory servers.