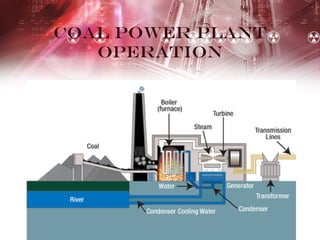
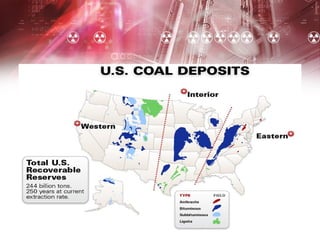
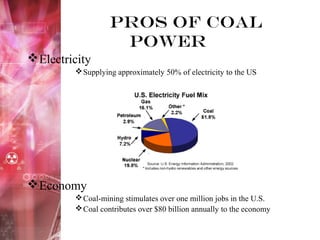
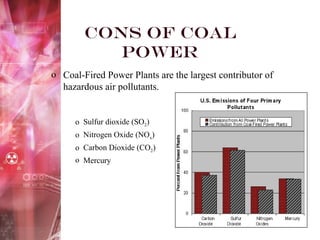
Coal-fired power plants present both benefits and risks. They provide a cheap, abundant source of electricity but also emit several hazardous air pollutants. Coal is burned in large furnaces to create steam that spins turbines connected to generators. The steam is then condensed and recycled. While coal supplies over 50% of US electricity and supports many jobs, the carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides and mercury released contribute to acid rain, smog, and health issues like heart attacks and respiratory illness. The future of coal may involve cleaner technologies and complying with environmental regulations to reduce these harmful emissions.