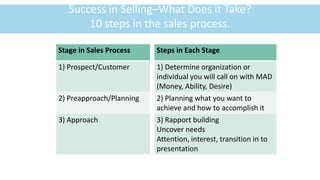
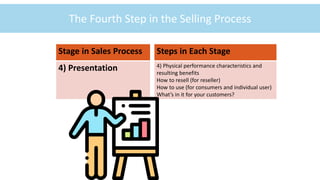
This document provides an overview of the life and career of a professional salesperson. It defines selling as the personal communication of information to unselfishly persuade others to buy something that satisfies their needs. The core principles of professional selling are to unselfishly serve buyers while also representing the interests of the selling organization. The 10 steps of the sales process are outlined, including prospecting, planning, approaching customers, presenting, handling objections, closing the sale, and following up. The document emphasizes that successful salespeople demonstrate knowledge of customers' needs and altruism through caring for others.