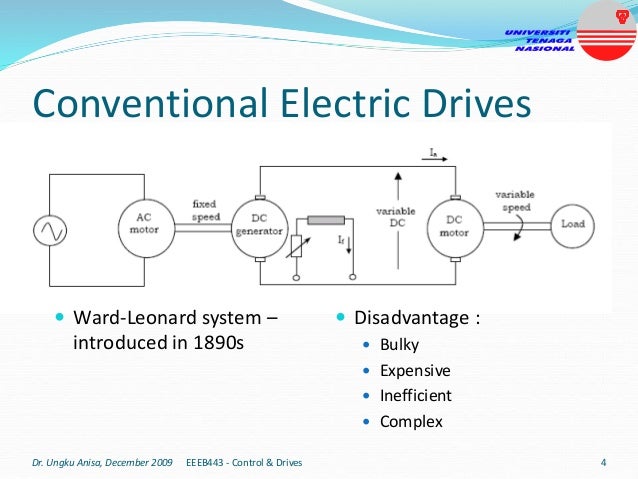
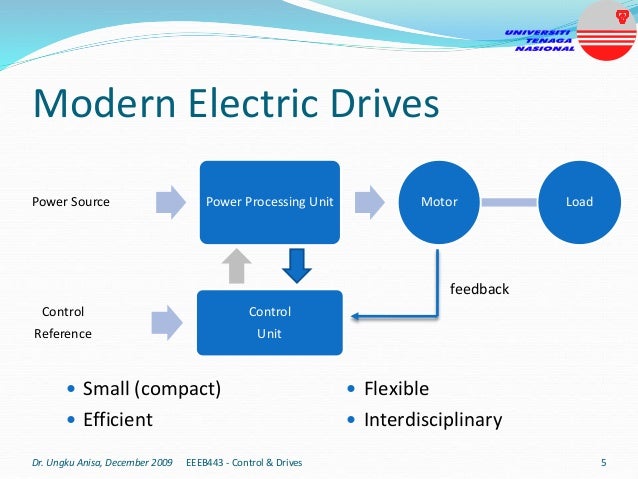
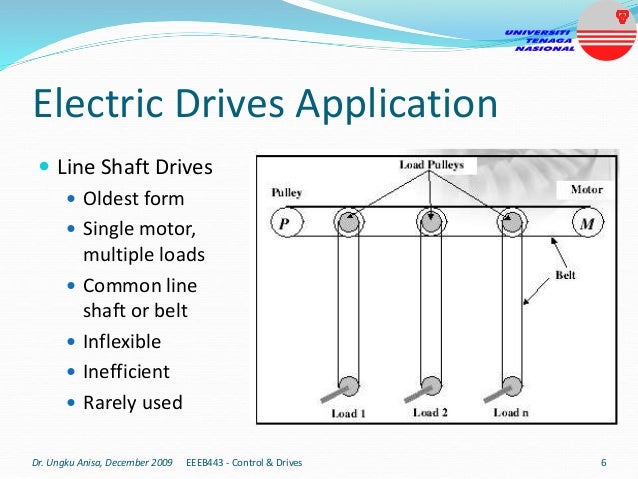
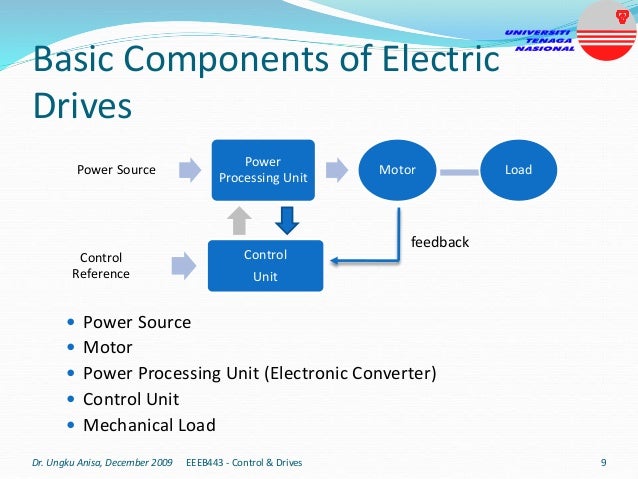
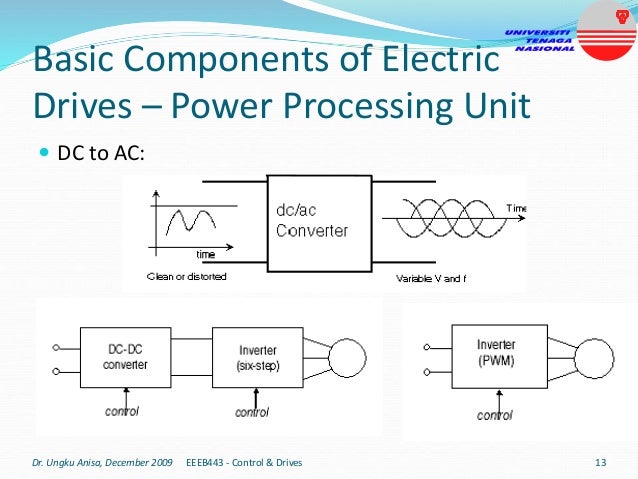
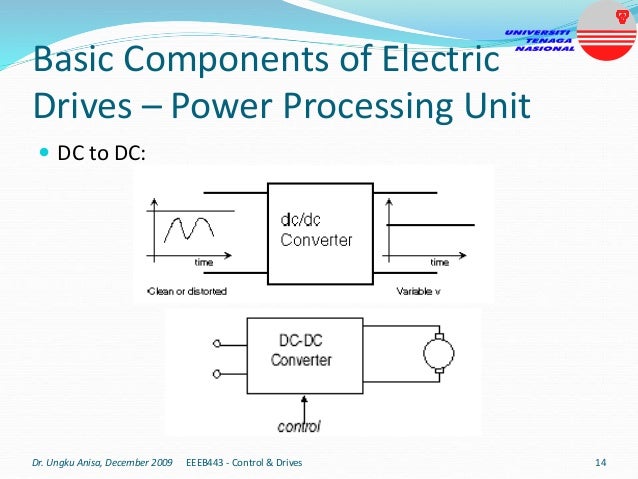
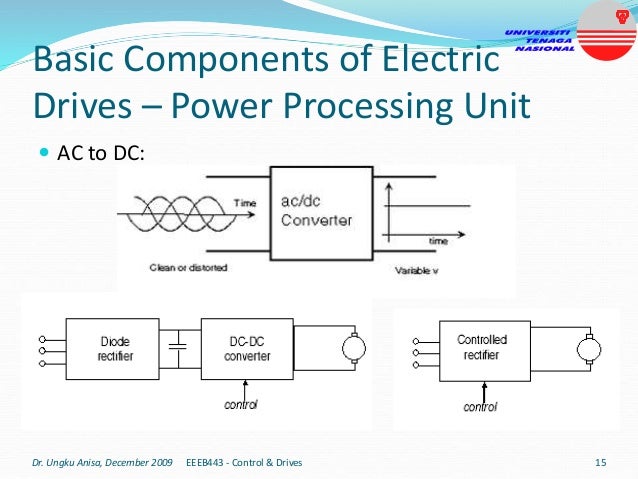
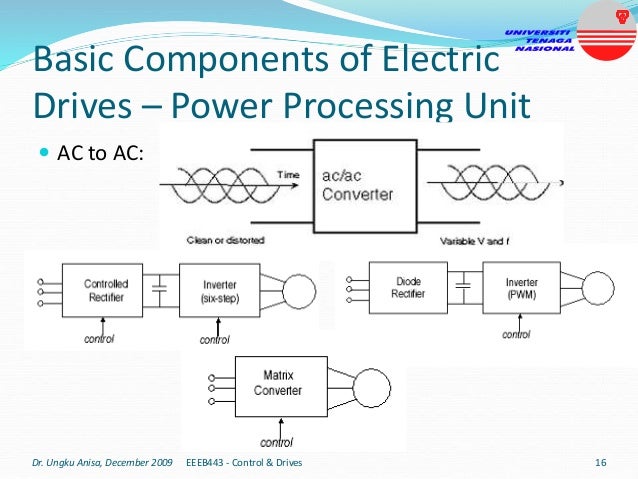
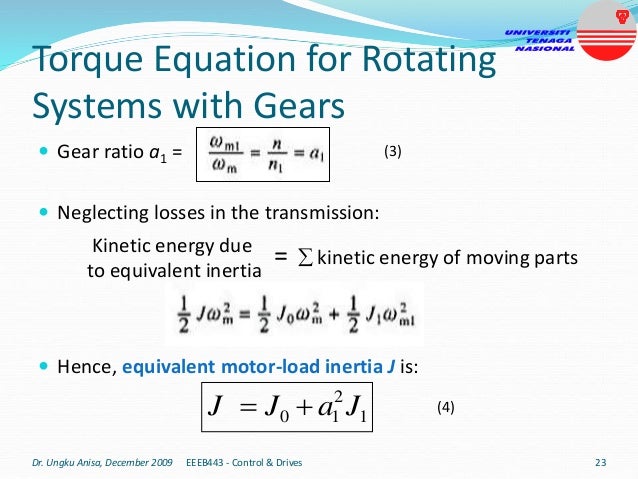
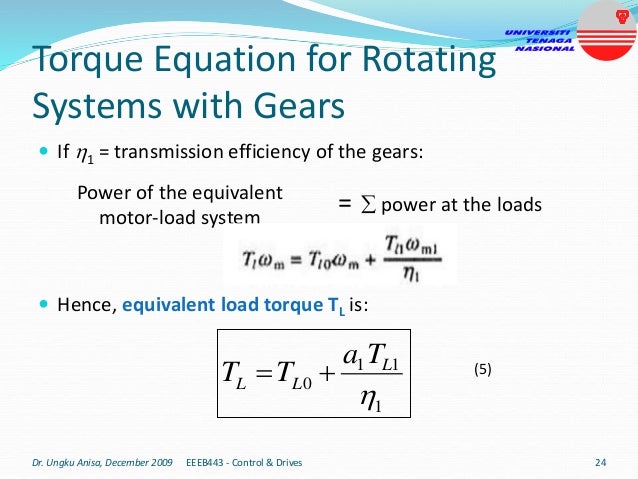
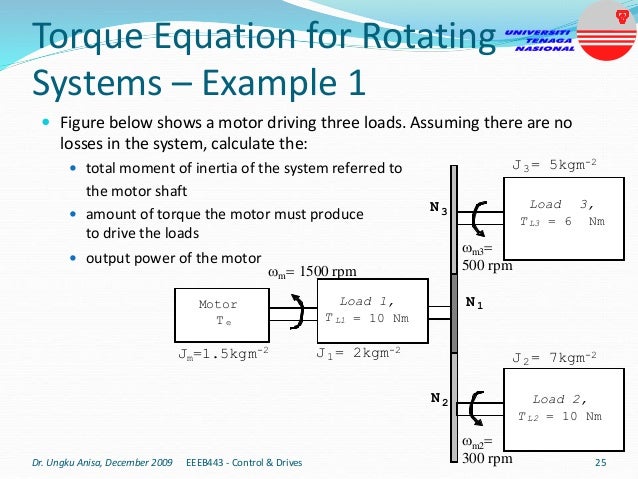
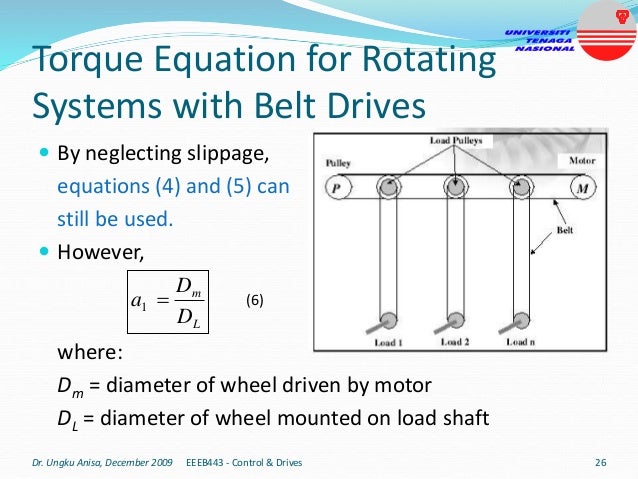
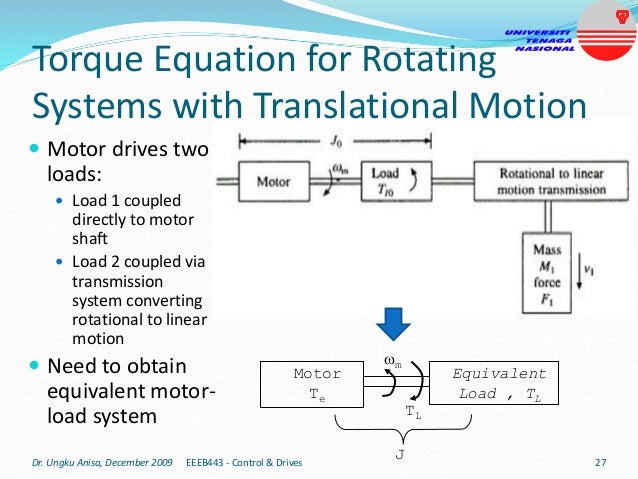
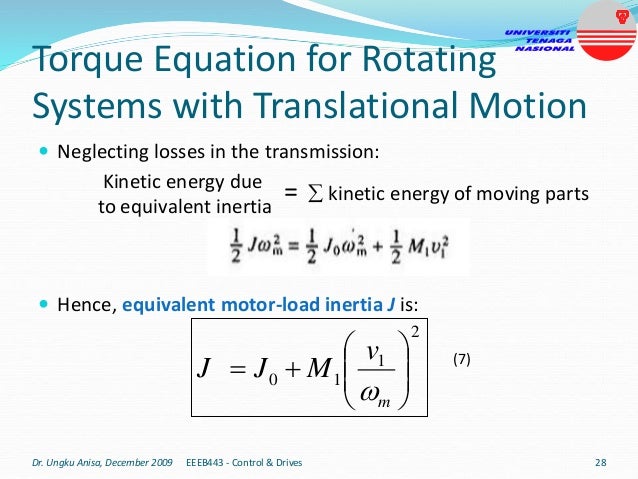
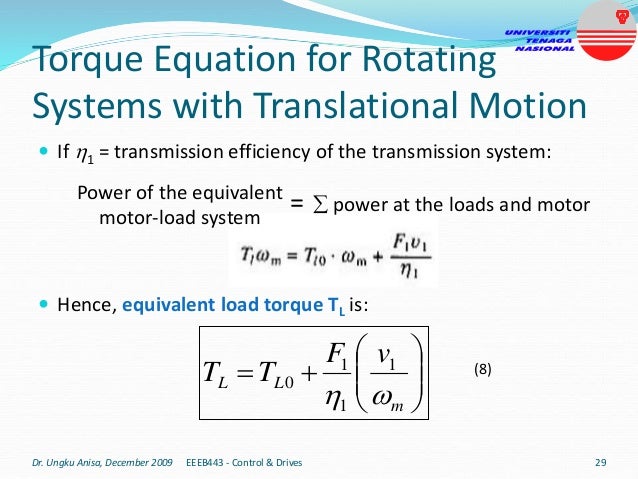
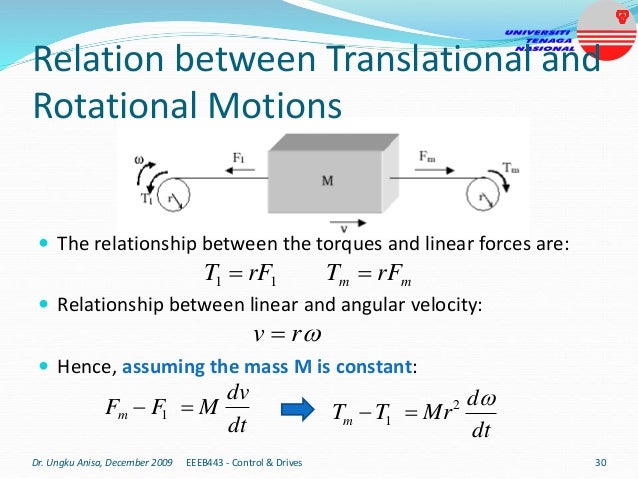
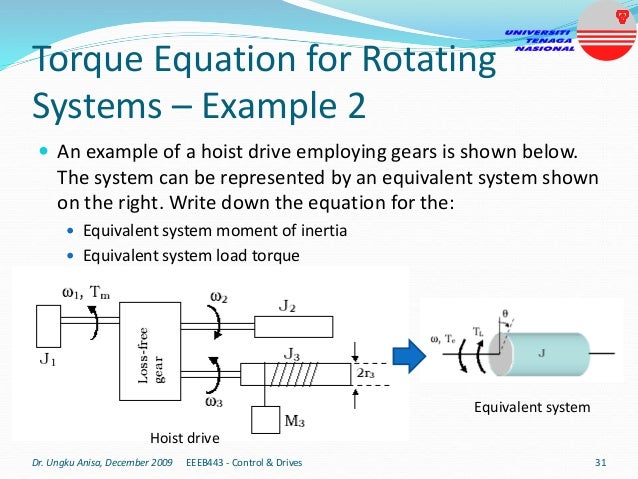
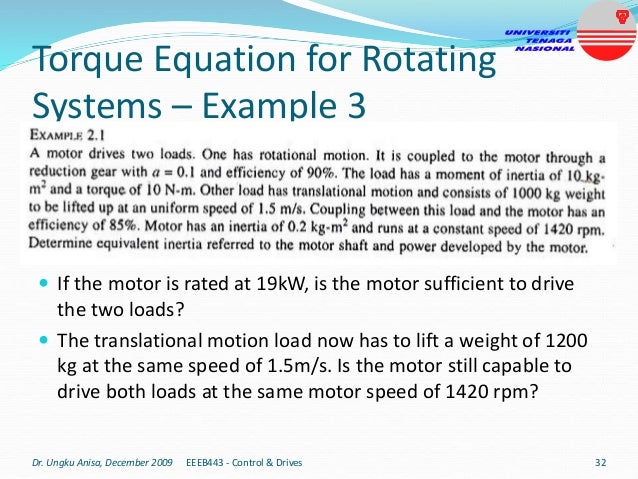
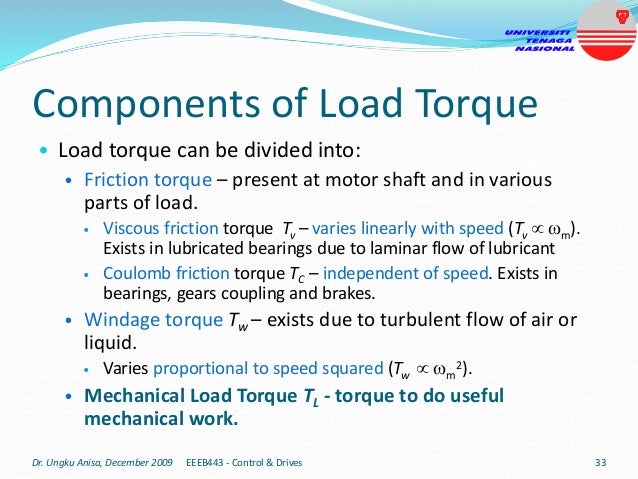
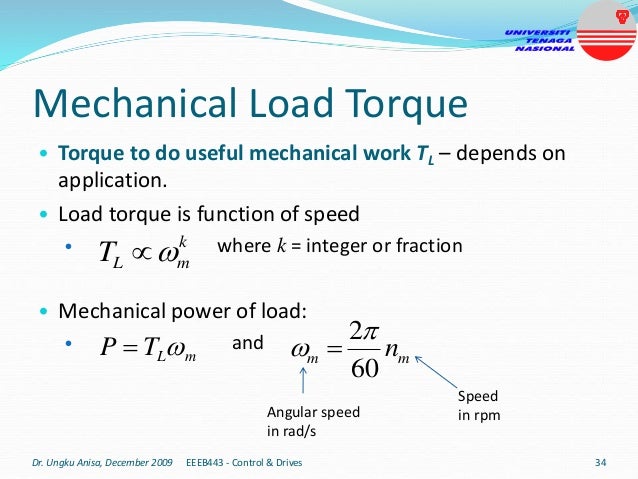
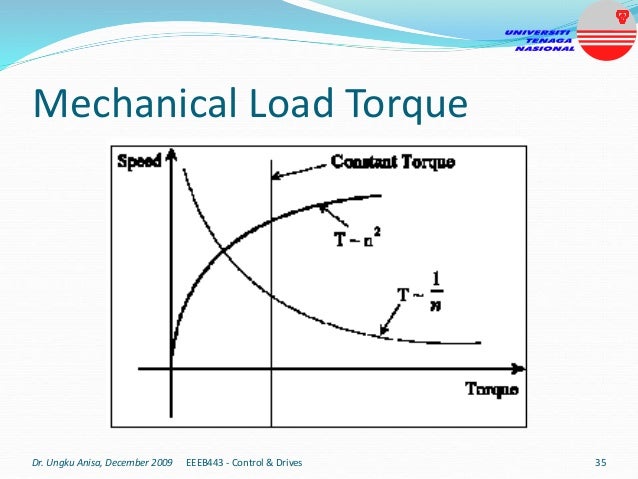
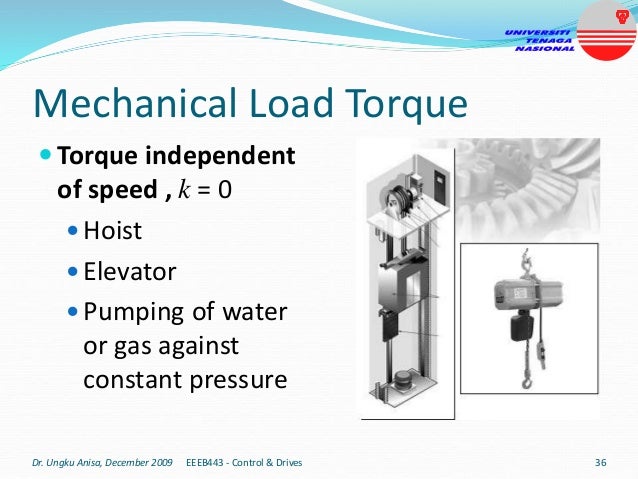
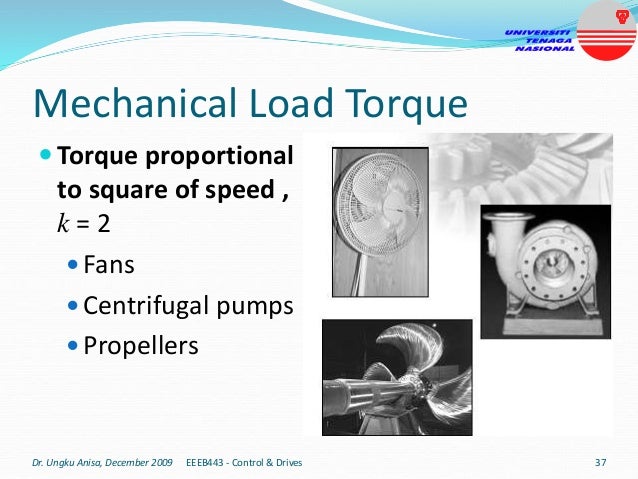
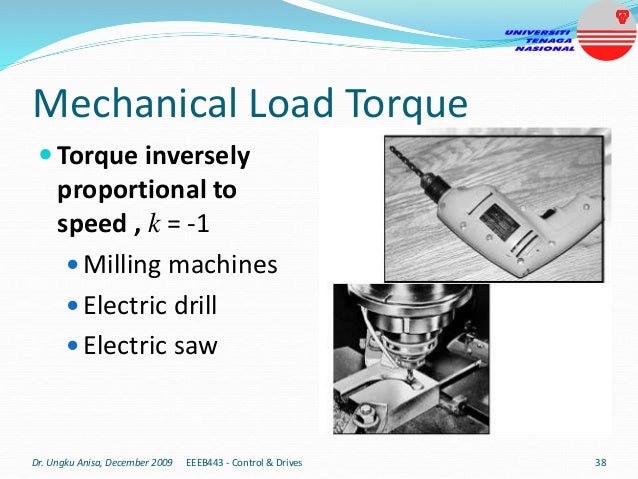
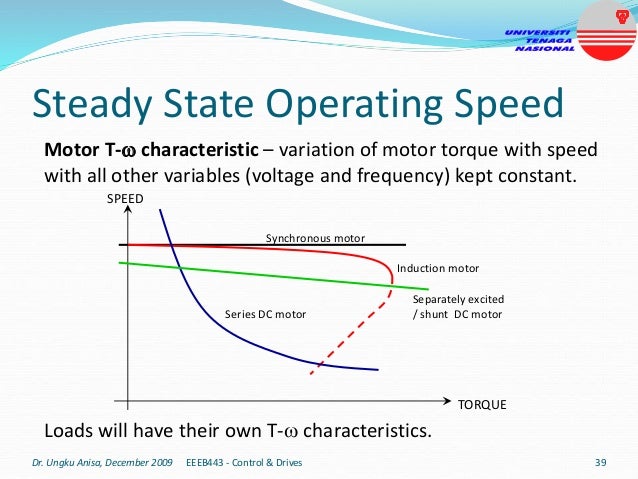
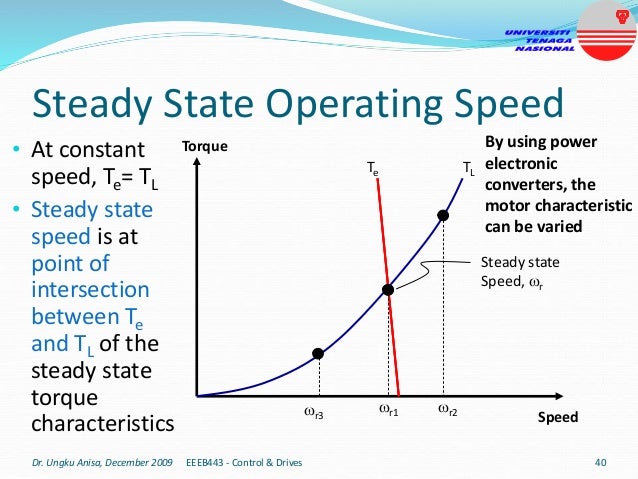
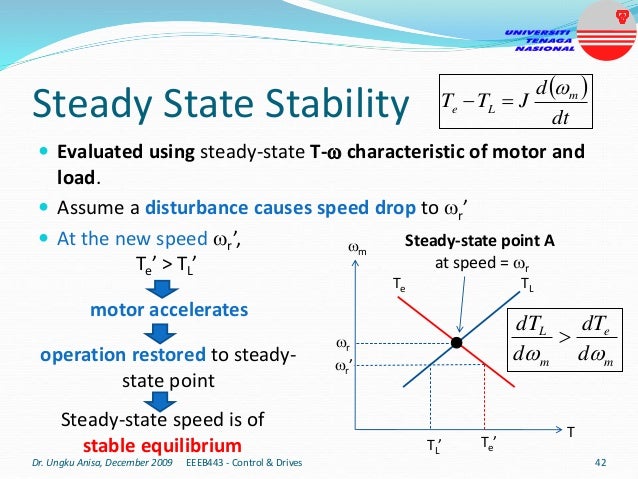
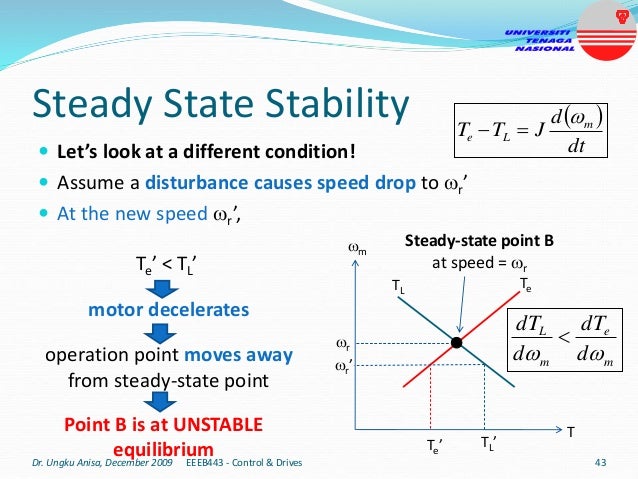
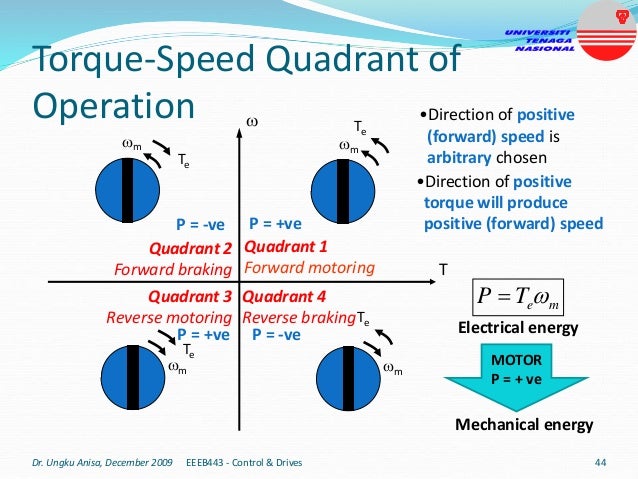
This document provides an introduction to electrical drives. It defines electrical drives as systems that employ electric motors as prime movers for motion control. The advantages of electrical drives include flexible control, wide speed and torque ranges, high efficiency, and operation in all four torque-speed quadrants. Modern electric drives are more compact, efficient and flexible compared to conventional drives due to use of power electronics. Electric drives find applications in line shaft drives, single motor-single load drives, and multimotor drives. The basic components of an electric drive system are the power source, motor, power processing unit, control unit, and mechanical load.