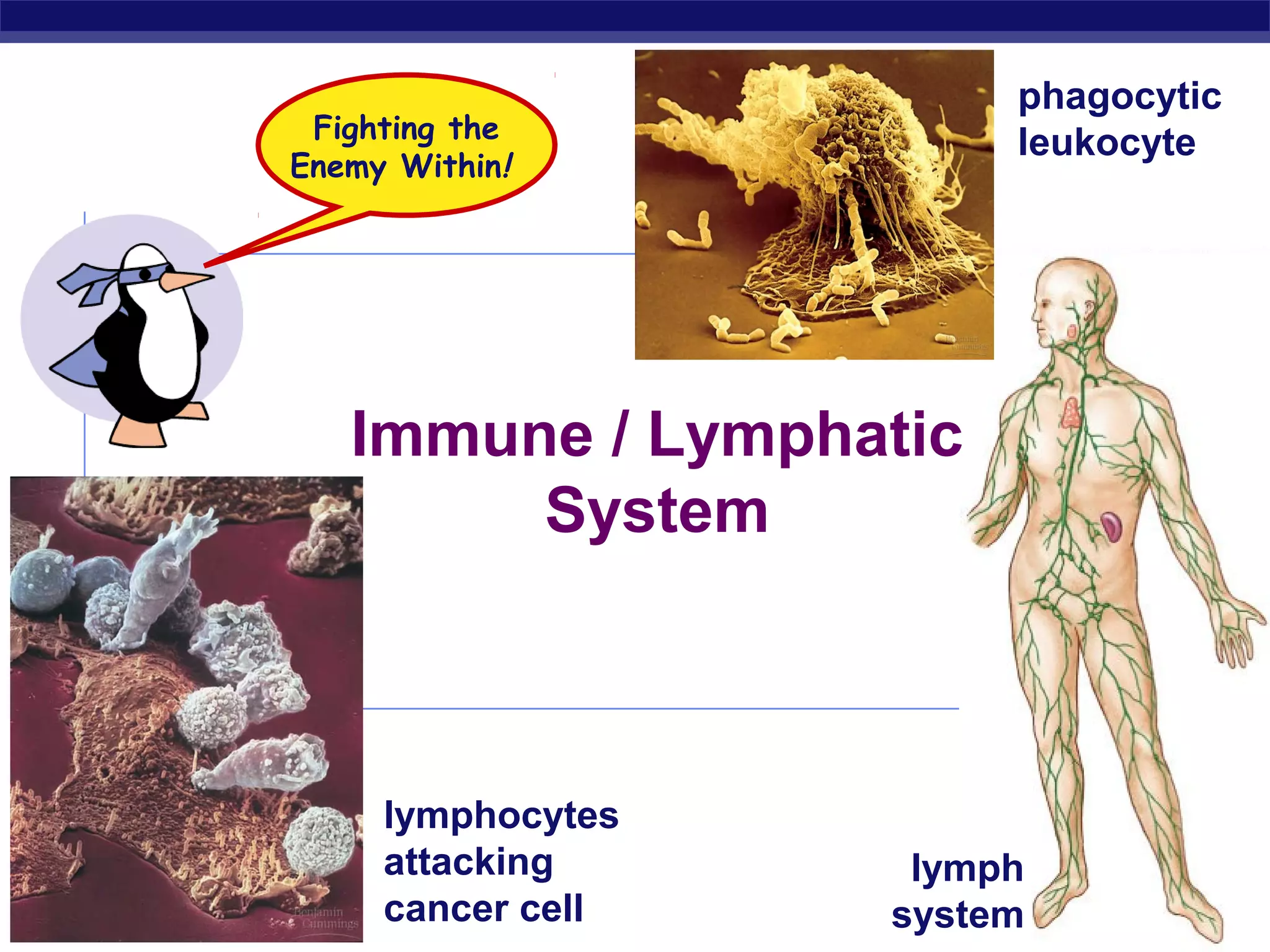
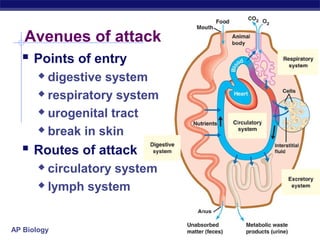
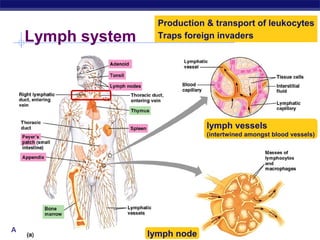
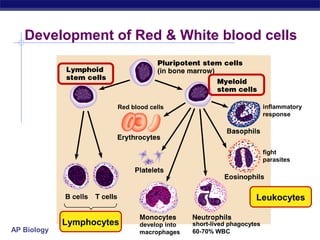
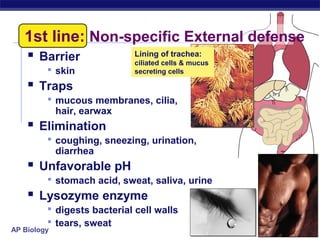
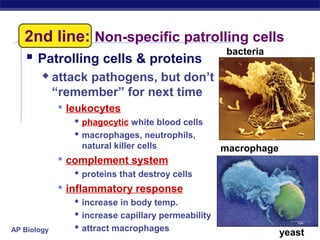
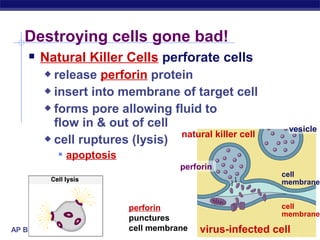
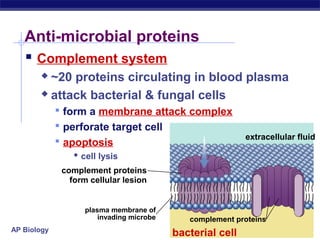
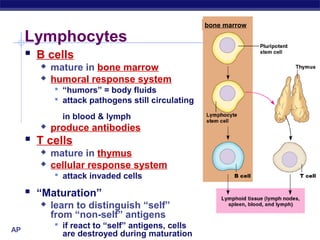
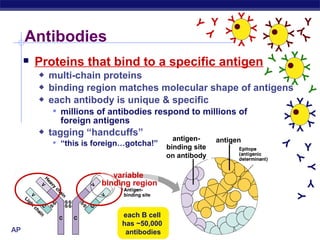
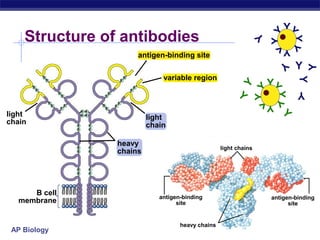
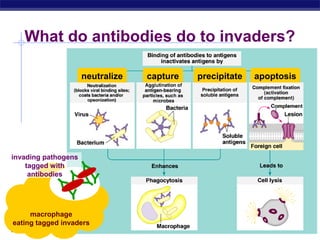
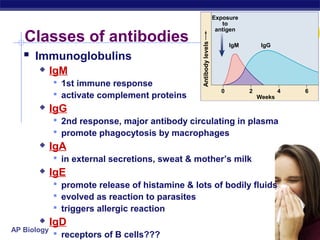
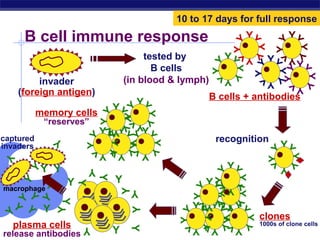
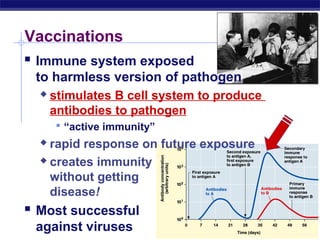
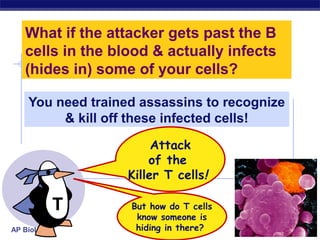
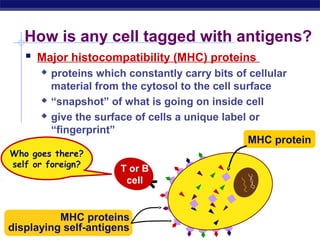
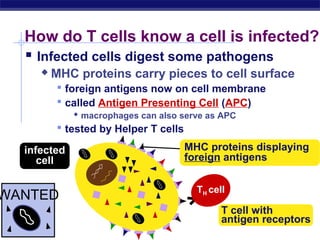
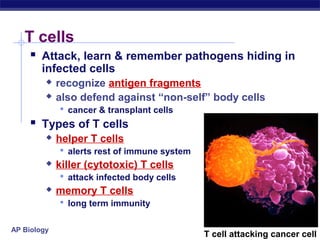
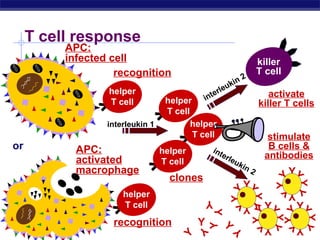
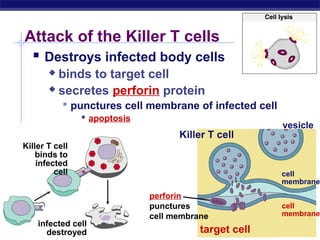
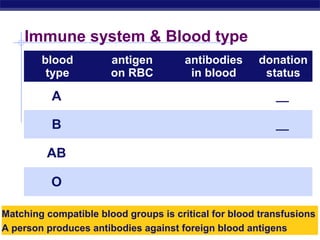
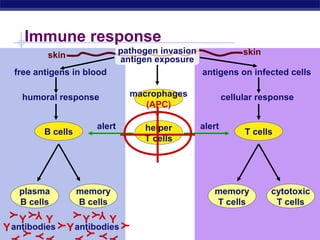
The document describes the immune system's lines of defense against pathogens, including non-specific barriers, leukocytes, lymphocytes, antibodies, and T cells. It explains how pathogens are recognized through antigens and presented by antigen presenting cells to activate helper T cells and recruit other immune responses. The immune system uses both non-specific responses and acquired immunity through B cells and T cells to identify and destroy invading pathogens through various targeted mechanisms.