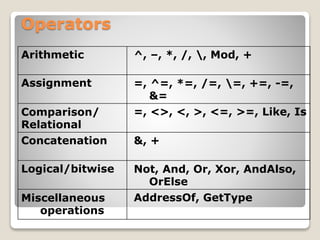
This document discusses operators, functions, and options in .NET. It describes unary and binary operators that take one or two operands. It covers arithmetic, assignment, comparison/relational, logical/bitwise, and miscellaneous operators. It also discusses functions like vbCrLf and InputBox. The document explains options like Option Explicit and Option Strict that control variable declaration and type conversion. Finally, it provides an example of using the With...End With block to set multiple properties of a control.





![Comparison / Relational
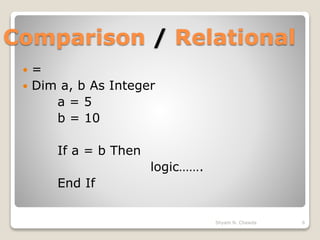
Dim ans As Boolean
ans = "F" Like "F"
ans = "F" Like "f"
ans = "F" Like "FFF"
ans = "aBBBa" Like "a*a"
ans = "F" Like "[A-Z]"
ans = "F" Like "[!A-Z]"
ans = "a2a" Like "a#a"
ans = "aM5b" Like "a[L-P]#[!c-e]"
9Shyam N. Chawda](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4operator-140322094744-phpapp01/85/Operators-Functions-and-Options-in-VB-NET-9-320.jpg)