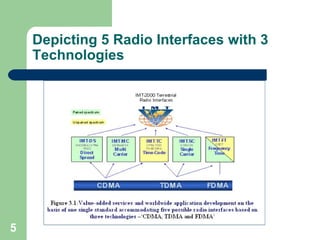
The document outlines the evolution and deployment strategy of cellular telephony, focusing on the growth from first generation (1G) analog systems to fourth generation (4G) networks, including the characteristics and branding of 3G technology. It describes the features of 3G, such as compatibility with 2G, affordability, and flexibility, as well as spectrum allocation strategies for network deployment. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of market research and financial models in selecting technology while highlighting the mutual benefits for users and service providers.