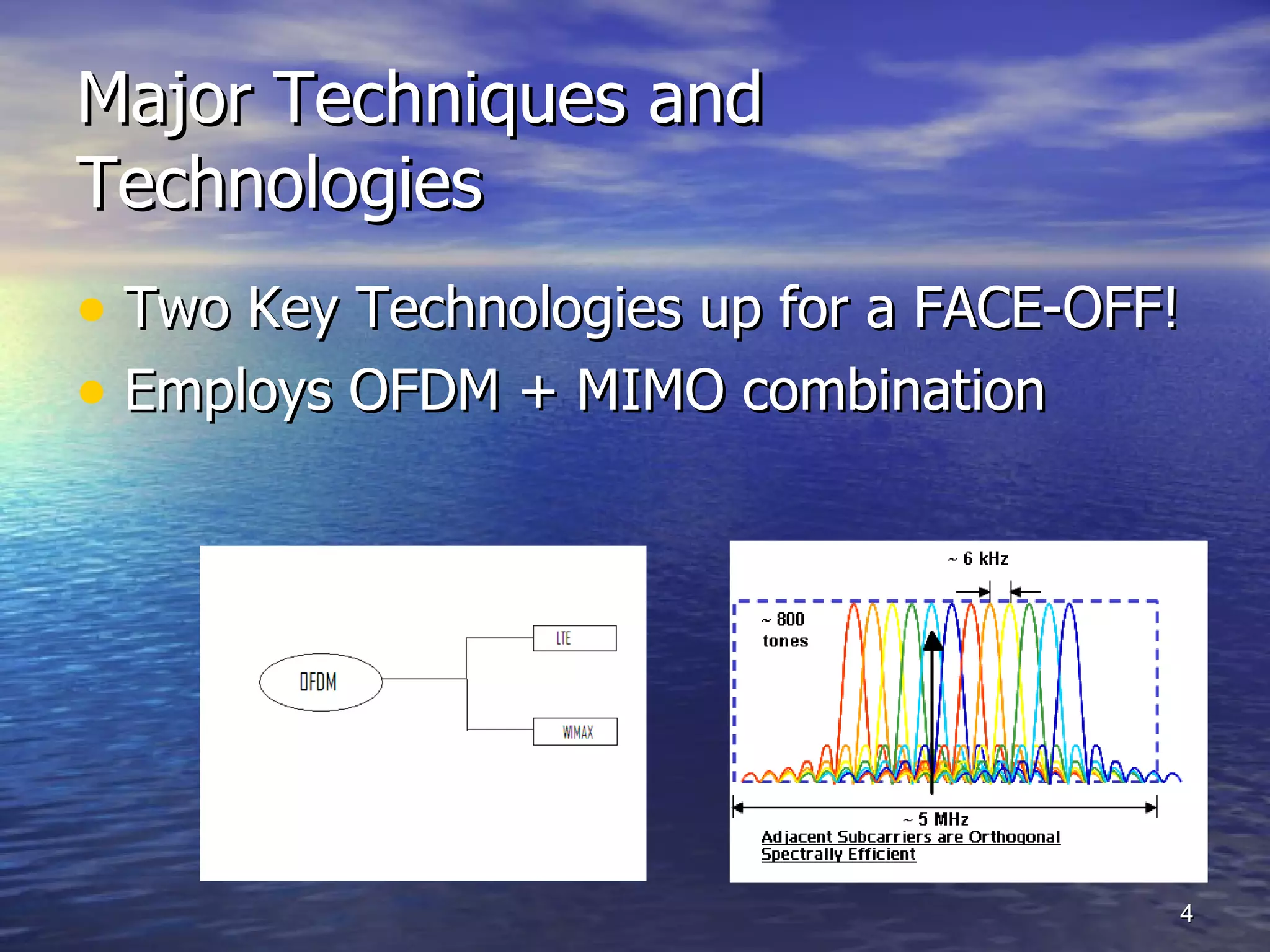
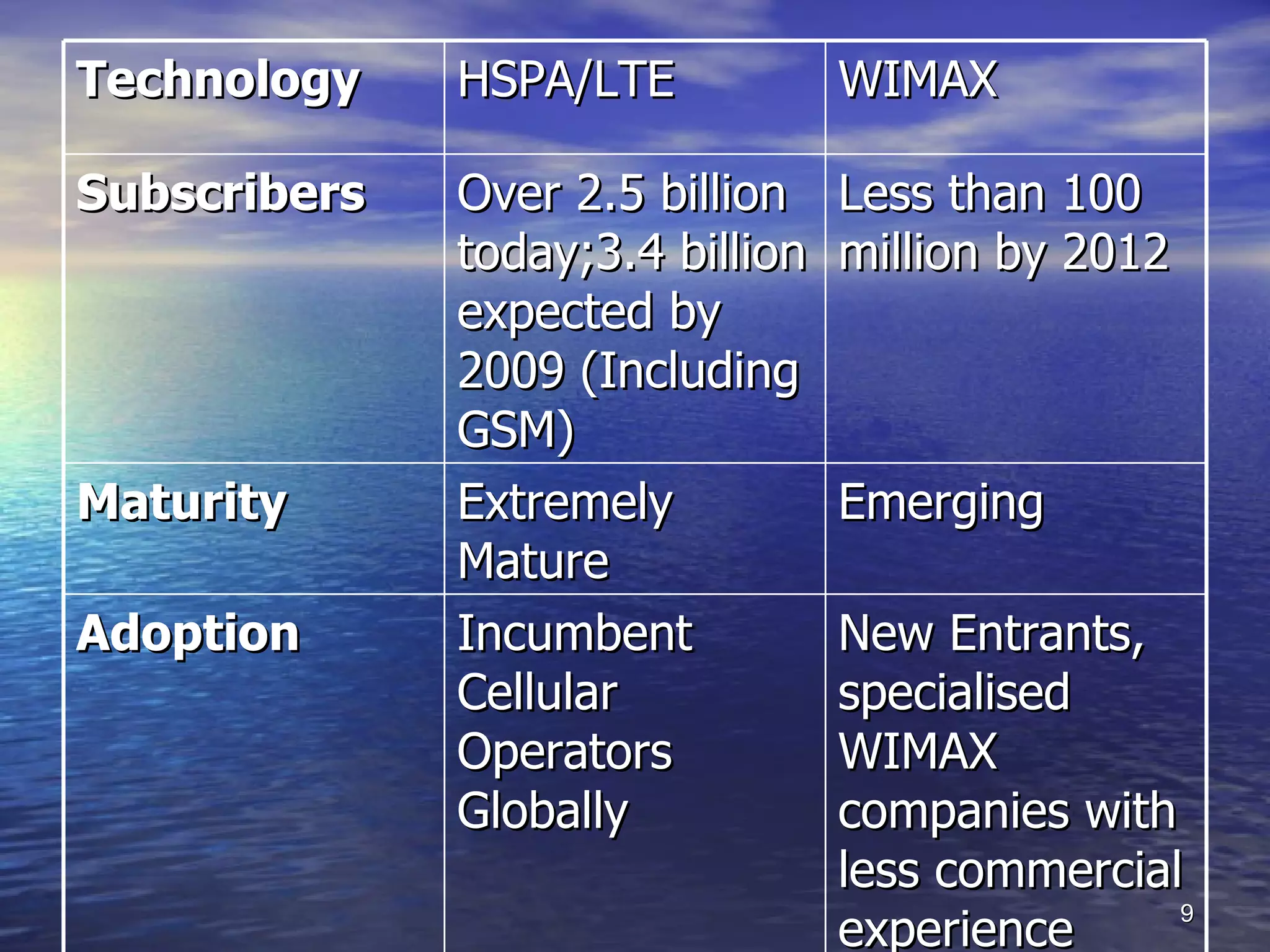
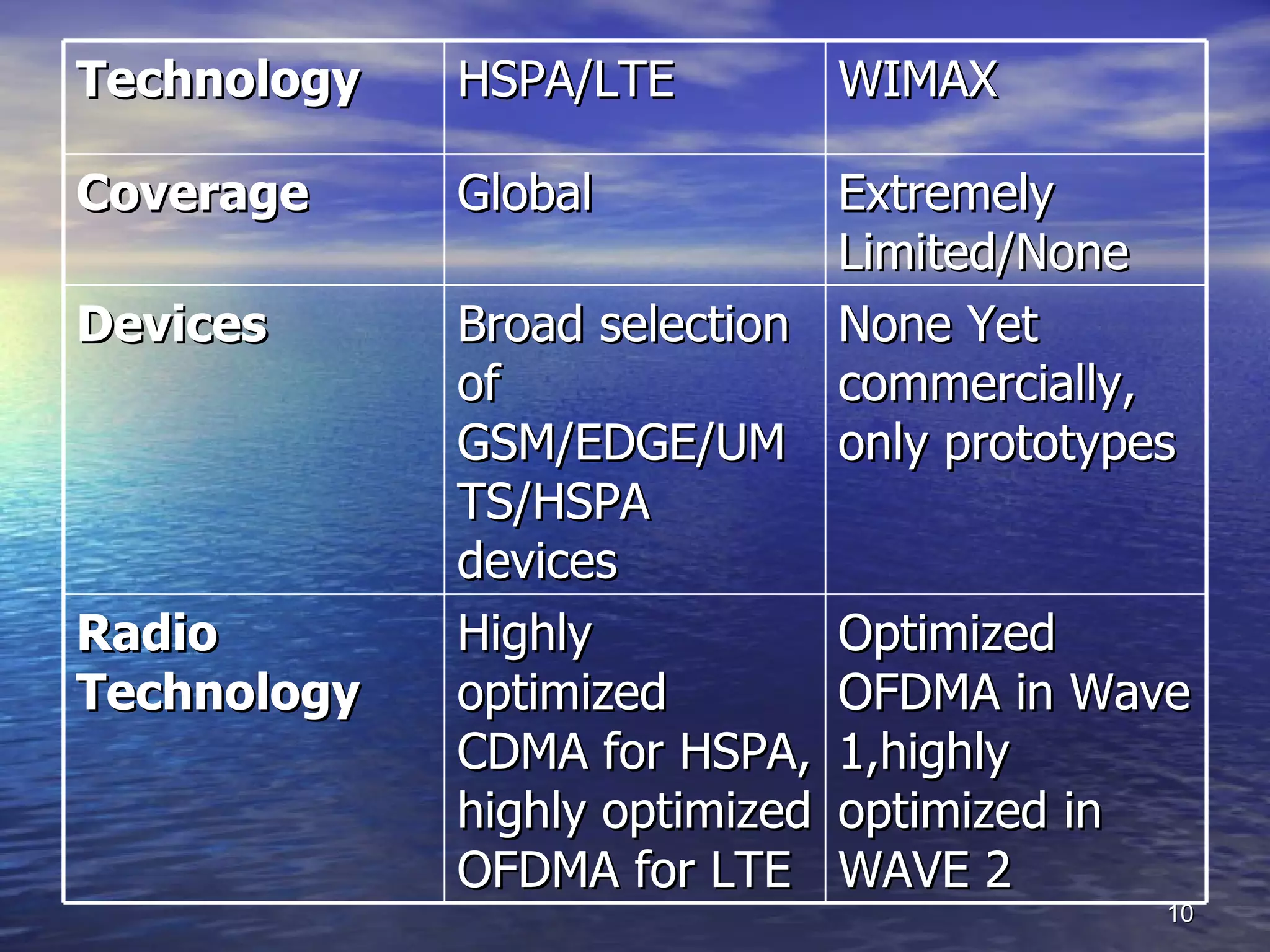
4G technologies like LTE and WiMAX aim to improve wireless services by providing better coverage, voice quality, data speeds, and revenue for operators. LTE employs OFDM and MIMO to achieve high spectrum efficiency and handle multipath fading, while WiMAX uses OFDM and is optimized for developing markets with limited wired infrastructure but available spectrum. Both technologies have strengths and weaknesses and may coexist, though LTE has broader device and network support currently from major mobile operators.





![WHY GO MOBILE AND BROADBAND? Packet Data on the Rise Data ARPU increase from 5 to 20 % over last 5 years [ABI Research]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nextgenerationradiotechnologies-12583631441634-phpapp02/75/At-Analysys-Mason-2008-Next-Generation-Radio-Technologies-7-2048.jpg)

![Other Deployment and technical Issues Latency / Architecture Spectrum Spectrum Efficiency Throughput Capabilities [D/l and U/l] Coverage Back-Haul network (No Mismatch!) Cost Finally, Conceptualisation of LTE and WIMAX](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nextgenerationradiotechnologies-12583631441634-phpapp02/75/At-Analysys-Mason-2008-Next-Generation-Radio-Technologies-11-2048.jpg)
![Business Case WIMAX Developing Markets [Low Optics/wire line Infrastructure] Better Opportunity for new entrants depending upon Spectrum Sale Backhaul Network to Existing Wi-Fi networks Fixed and Mobile flavours available with LTE Developed Markets [Matured Wire and Optic Infrastructure] Natural Progression for Incumbent Operators as it is Backward compatible to GSM/UMTS family](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nextgenerationradiotechnologies-12583631441634-phpapp02/75/At-Analysys-Mason-2008-Next-Generation-Radio-Technologies-12-2048.jpg)


