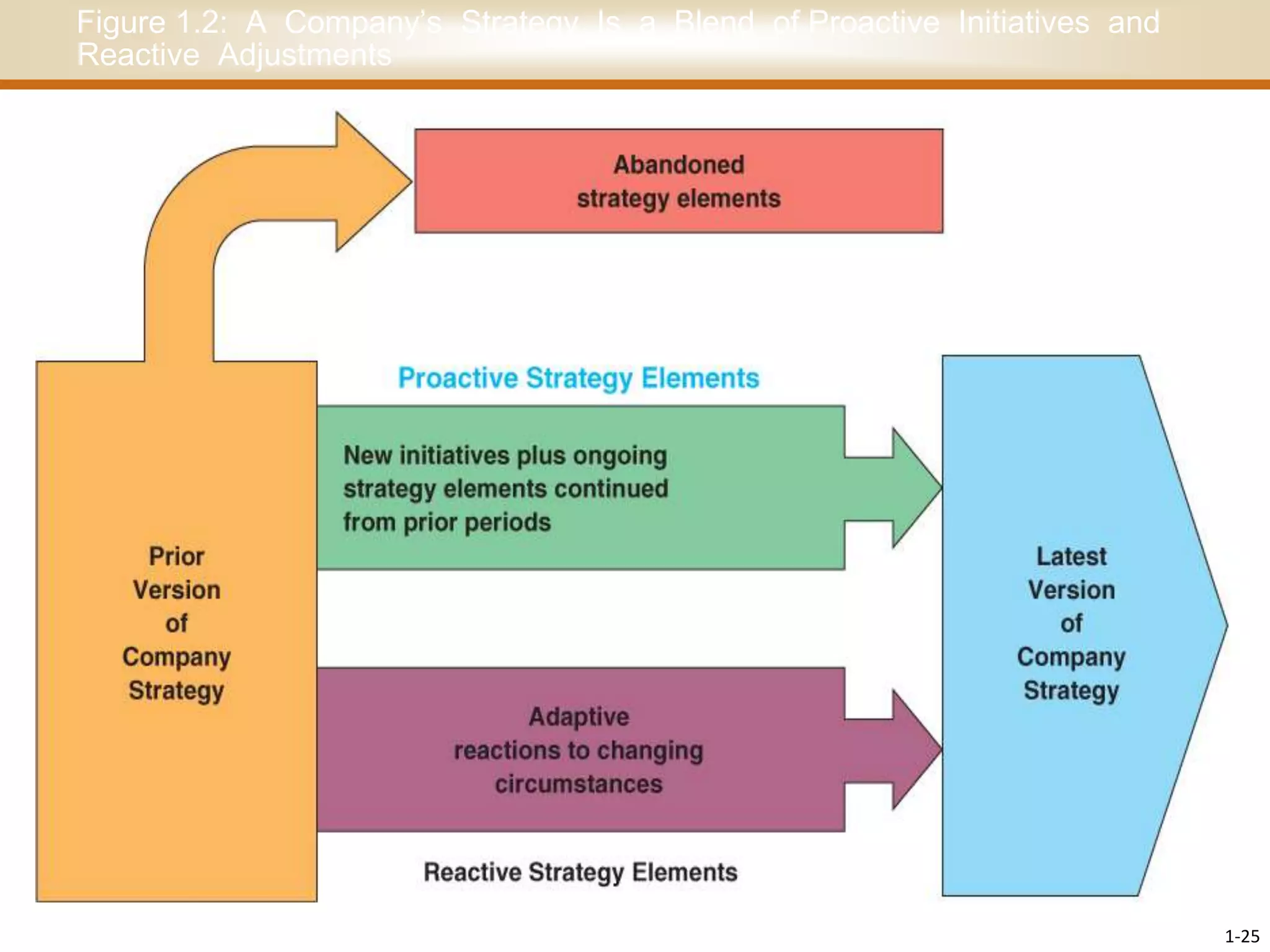
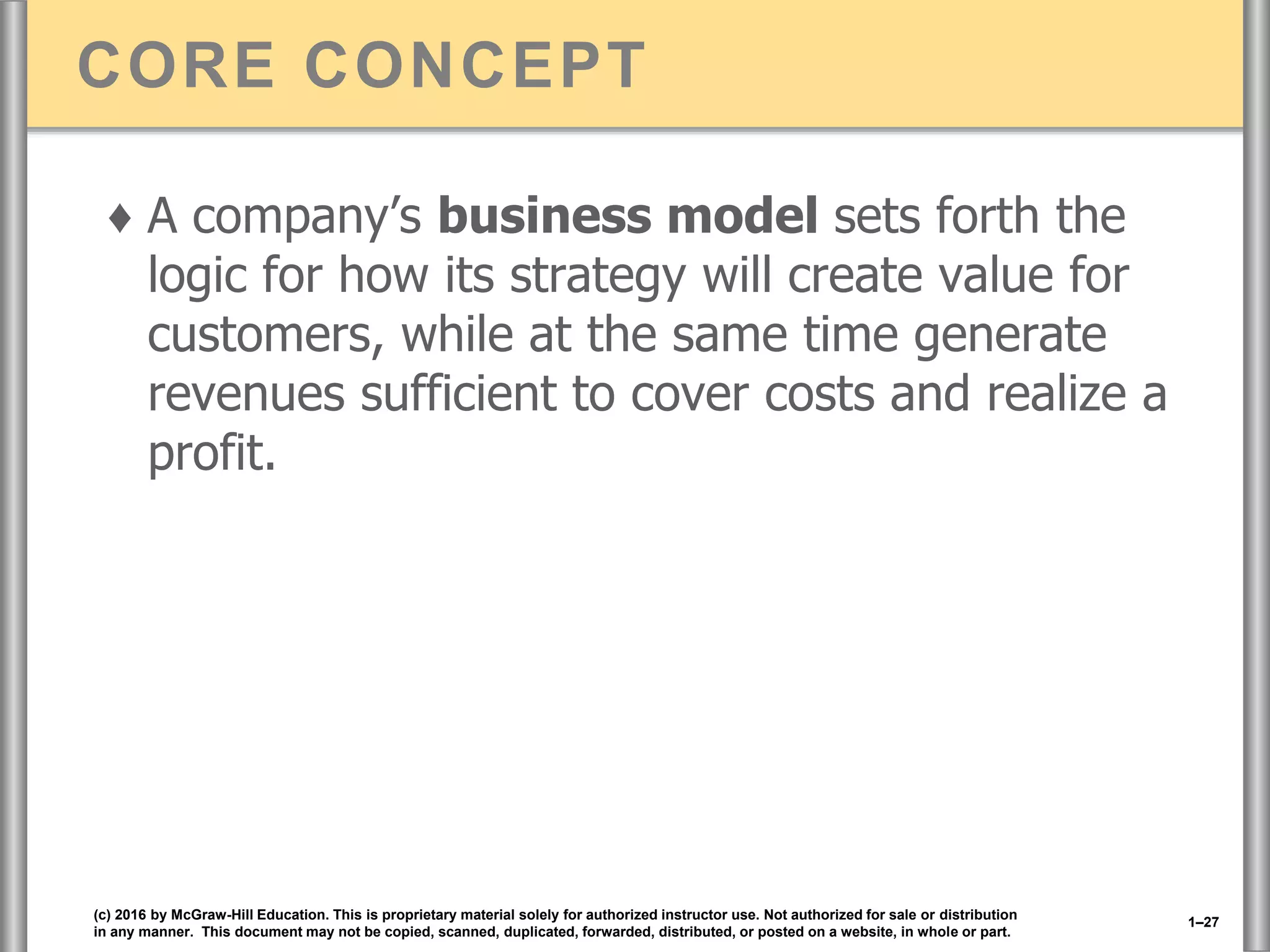
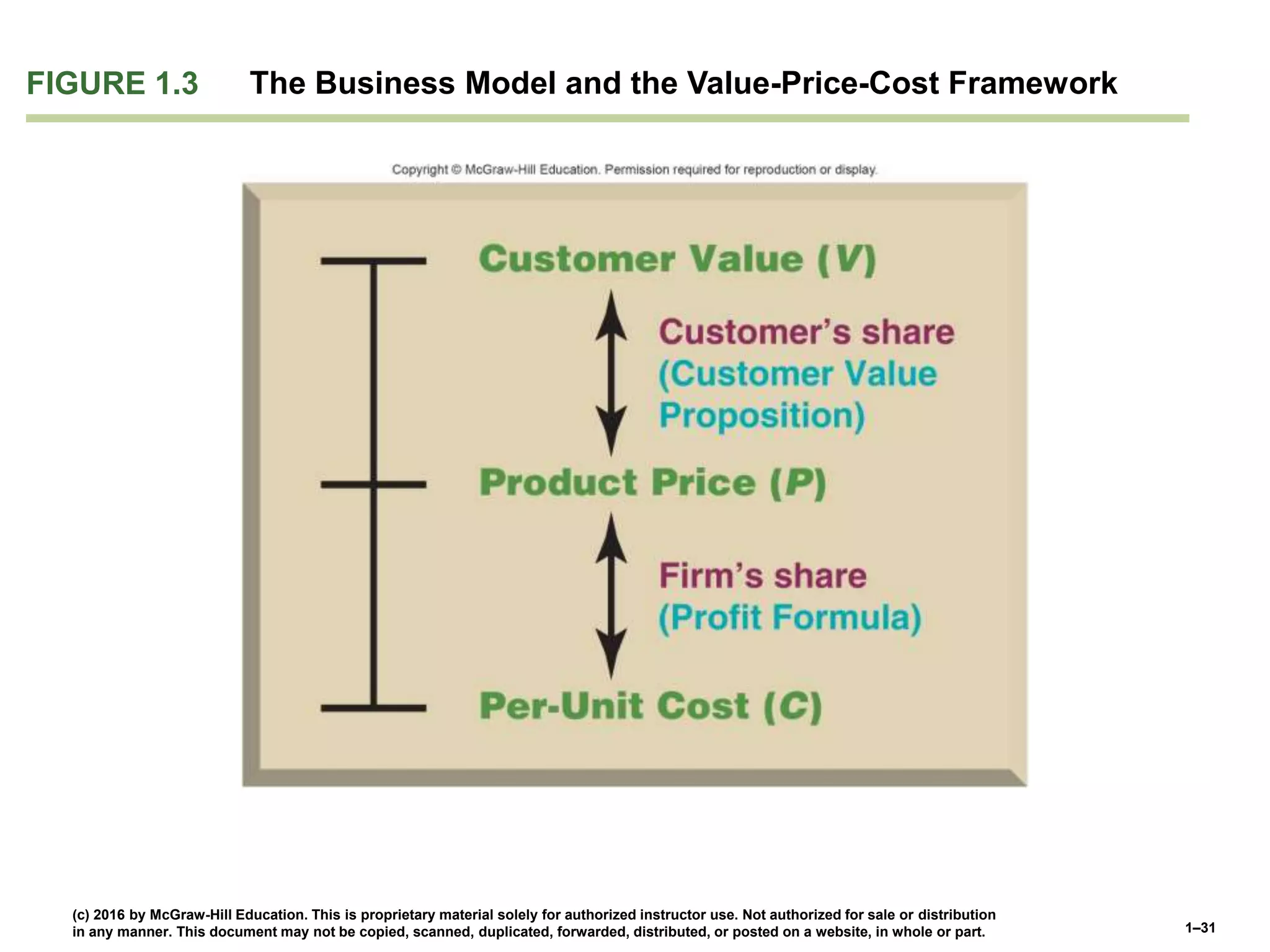
This document discusses the importance of strategy for companies. It defines strategy as the set of actions managers take to outperform competitors and achieve superior profitability. An effective strategy helps a company gain and sustain a competitive advantage over rivals by meeting customer needs better or more efficiently. There are different strategic approaches like becoming a low-cost provider, differentiating products, or focusing on a niche market. The goal of strategy is to develop valuable expertise and capabilities that cannot easily be copied, allowing long-term competitive advantage and above-average profits.