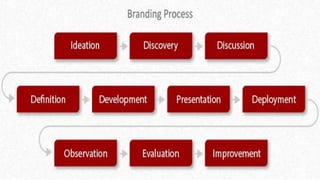
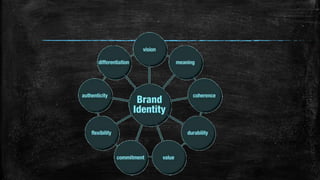
Branding is important for business success and involves establishing positive associations with a brand through tools like positioning, design, marketing and advertising. It should inform all business decisions. The branding process involves five phases - defining and assessing the brand, holistic strategic planning, developing a creative approach, executing the plan, and measuring results. Brand extensions involve using an existing brand name to enter new product categories or markets in order to leverage brand equity and increase profits, but they also carry risks like confusing consumers or hurting the parent brand's image if not executed properly.