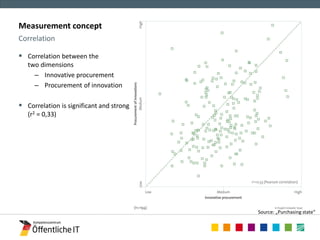
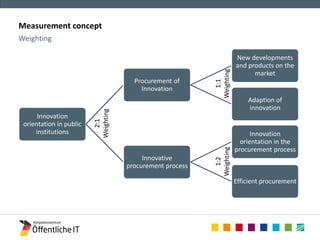
The document discusses the OECD workshop focused on measuring the link between public procurement, R&D, and innovation, highlighting insights from the 'Purchasing State' research project. It emphasizes the significance of effective measurement concepts and data analysis in understanding innovative procurement processes and outcomes in Germany. Lessons learned indicate the importance of comprehensive data access and modern analytical tools for enhancing procurement practices.