IB Biology 3.3 meiosis
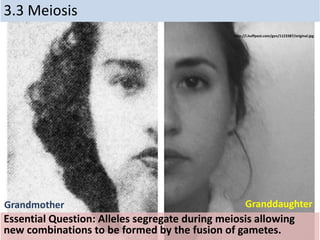
- 1. 3.3 Meiosis Essential Question: Alleles segregate during meiosis allowing new combinations to be formed by the fusion of gametes. http://i.huffpost.com/gen/1123387/original.jpg Grandmother Granddaughter
- 2. Understandings Statement Guidance 3.3.U1 One diploid nucleus divides by meiosis to produce four haploid nuclei. 3.3U2 The halving of the chromosome number allows a sexual life cycle with fusion of gametes. 3.3.U3 DNA is replicated before meiosis so that all chromosomes consist of two sister chromatids. 3.3.U4 The early stages of meiosis involve pairing of homologous chromosomes and crossing over followed by condensation. [The process of chiasmata formation need not be explained.] 3.3.U5 Orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes prior to separation is random. 3.3 U6 Separation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in the first division of meiosis halves the chromosome number. 3.3 U7 Crossing over and random orientation promotes genetic variation. 3.3 U8 Fusion of gametes from different parents promotes genetic variation.
- 3. Applications and Skills Statement Guidance 3.3 A1 Non-disjunction can cause Down syndrome and other chromosome abnormalities. 3.3 A2 Studies showing age of parents influences chances of non-disjunction. 3.3 A3 Description of methods used to obtain cells for karyotype analysis e.g. chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis and the associated risks. 3.3 S1 Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells. [Drawings of the stages of meiosis do not need to include chiasmata. Preparation of microscope slides showing meiosis is challenging and permanent slides should be available in case no cells in meiosis are visible in temporary mounts.]
- 4. 3.3 U1 One diploid nucleus divides by meiosis to produce four haploid nuclei. http://cis.payap.ac.th/wp-content/uploads/2011/11/142.png • Cells divide twice • Result: 4 daughter cells, each with half as many chromosomes as parent cell
- 5. • What if a complex multicellular organism (like us) wants to reproduce? – joining of egg + sperm • Do we make egg & sperm by mitosis? 46 46+ 92 egg sperm zygote What if we did, then…. Doesn’t work! No! 3.3 U.2 The halving of the chromosome number allows a sexual life cycle with fusion of gametes.
- 6. 3.3 U.2 The halving of the chromosome number allows a sexual life cycle with fusion of gametes. http://lh6.ggpht.com/n2T0xB_8BXE/UY4bhlV52uI/AAAAAAAABxg/7ZjWF QMBfx4/s1600-h/Humanlifecycle9.jpg Sexual life cycle • Meiosis: reduces # of chromosomes creating gametes (n) • Fertilization: combine gametes (sperm + egg) creating a fertilized egg or zygote (2n)
- 7. Duplication of Chromosomes During S stage of Interphase Single chromosome (called chromatin during Interphase) Two identical sister chromatids joined by a centromere DNA replication during S stage of Interphase 3.3 U.3 DNA is replicated before meiosis so that all chromosomes consist of two sister chromatids. .
- 8. Crossover • Red and Blue chromosomes are a homologous pair. • They have replicated during the interphase and each copy is held together by the centromere (black dot) 3.3 U.4 The early stages of meiosis involve pairing of homologous chromosomes and crossing over followed by condensation. [The process of chiasmata formation need not be explained.]
- 9. •The chromosomes overlap and exchange lengths of DNA. •The chiasmata are the points at which the red and blue chromosomes overlap. •At a molecular level the exchange has to be exact avoiding loss of bases. Such an error would have profound effect on the genes. 3.3 U.4 The early stages of meiosis involve pairing of homologous chromosomes and crossing over followed by condensation. [The process of chiasmata formation need not be explained.]
- 10. • At anaphase I the homologous pairs are separated. • Notice that sections of DNA have been exchanged. • These will mean that the alleles on these section have also been exchanged • Crossing over, Independent Assortment, combined with Fertilization: A couple can produce over 64 trillion (8.3 million x 8.3 million) different combinations in a zygotes during fertilization 3.3 U.4 The early stages of meiosis involve pairing of homologous chromosomes and crossing over followed by condensation. [The process of chiasmata formation need not be explained.]
- 11. 3.3 U.5 Orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes prior to separation is random. http://cnx.org/resources/9d7cd91abd65e9c7fa857cf6c6d133ec/Figure_08_03_06.jpg Independent assortment of chromosomes • meiosis introduces genetic variation in several ways • gametes of offspring do not have same combination of genes as gametes from parents
- 12. 3.3 U.6 Separation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in the first division of meiosis halves the chromosome number. • Each individual has a pair chromosomes both chromosomes of a pair carry “matching” genes control same inherited characters homologous = same information • To create sex cells the number of chromosomes must be reduce for Humans from 46 chromosomes to 23. Reduced by half. http://41.media.tumblr.com/4c08ea694bcf30c5a9d8423 187fba2de/tumblr_mx5zd49kWN1qjofuoo1_1280.jpg
- 13. 3.3 S.1 Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/5/54/Meiosis_diagram.jpg
- 14. Meiosis 1 • interphase • prophase 1 • metaphase 1 • anaphase 1 • telophase 1 Meiosis 2 • prophase 2 • metaphase 2 • anaphase 2 • telophase 2 2nd division of meiosis separates sister chromatids (1n 1n) * just like mitosis * 1st division of meiosis separates homologous pairs (2n 1n) “reduction division” 3.3 S.1 Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells.
- 15. Meiosis: Generates haploid gametes • Reduces the number of chromosomes by half. • Also produces genetic variability, each gamete is different, ensuring that two offspring from the same parents are never identical. • Two divisions: Meiosis I and meiosis II. Chromosomes are duplicated in interphase prior to Meiosis I. 3.3 S.1 Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells.
- 16. Meiosis I: Separation of Homologous Chromosomes 1. Prophase I: • Chromatin condenses into chromosomes. • Nuclear membrane disappear. • Centrosomes move to opposite poles of cell and microtubules attach to chromatids. • Synapsis: Homologous chromosomes pair up and form a tetrad of 4 sister chromatids. 3.3 S.1 Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells.
- 17. Prophase I: Crossing Over Between Homologous Chromosomes Crossing over combined with Fertilization: A couple can produce over 64 trillion (8.3 million x 8.3 million) different combinations in a zygotes during fertilization. 3.3 S.1 Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells.
- 18. Meiosis I: 2. Metaphase I: 3. Anaphase I: 4. Telophase I and Cytokinesis: 3.3 S.1 Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells.
- 19. Random Assortment of Homologous Chromosomes During Meiosis I Generates Many Possible Gametes
- 20. Meiosis II: Separation of Sister Chromatids During interphase that follows meiosis I, no DNA replication occurs. Interphase may be very brief or absent. Meiosis II is very similar to mitosis. 1. Prophase II: • Very brief, chromosomes reform. • No crossing over or synapsis. • Spindle forms and starts to move chromosomes towards center of the cell. 3.3 S.1 Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells.
- 21. Meiosis II: Separation of Sister Chromatids 2. Metaphase II: • Very brief, individual chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. 3. Anaphase II: • Chromatids separate and move towards opposite ends of the cell. 3.3 S.1 Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells.
- 22. Meiosis II: Separation of Sister Chromatids 4. Telophase II: • Nuclei form at opposite ends of the cell. • Cytokinesis occurs. Product of meiosis: Four (4) haploid gametes, each genetically different from the other. 3.3 S.1 Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells.
- 23. • Independent assortment of chromosomes – meiosis introduces genetic variation – gametes of offspring do not have same combination of genes as gametes from parents • random assortment in humans produces 223 (8,388,608) different combinations in gametes from Dadfrom Mom offspring new gametes made by offspring 3.3 U.7 Crossing over and random orientation promotes genetic variation.
- 24. Fertilization Sources of Genetic Variation – Human Sperm + Human Egg come together to produce 8 million X 8 million = 64 trillion combinations! 3.3 U8 Fusion of gametes from different parents promotes genetic variation. http://news.bbcimg.co.uk/media/images/63005000/jpg/_63005 026_p6480029-sperm_fertilizing_egg-spl.jpg http://worms.zoology.wisc.edu/dd2/echino/fert/files/page19_2.gif
- 25. • Sperm + Egg = ? – any 2 parents will produce a zygote with over 70 trillion (223 x 223) possible diploid combinations 3.3 U8 Fusion of gametes from different parents promotes genetic variation. http://worms.zoology.wisc.edu/dd2/e chino/fert/files/page19_2.gif
- 26. Sexual reproduction allows us to maintain both genetic similarity & differences. Baldwin brothers Jonas Brothers 3.3 U8 Fusion of gametes from different parents promotes genetic variation. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/ff/Jonas_Brothers_2009.jpg Martin & Charlie Sheen, Emilio Estevez
- 27. 3.3 A.1 Non-disjunction can cause Down syndrome and other chromosome abnormalities. Accidents During Meiosis Can Cause Chromosomal Abnormalities – Nondisjunction: Chromosomes fail to separate. – Gametes (and zygotes) will have an extra chromosome, others will be missing a chromosome. • Trisomy: Individuals with one extra chromosome, three instead of pair. Have 47 chromosomes in cells. • Monosomy: Missing a chromosome, one instead of pair. Have 45 chromosomes in cells. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/3/31/Mitotic_nondisjunction.png
- 28. 3.3 A.2 Studies showing age of parents influences chances of non-disjunction. http://knowgenetics.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/DownSyndromeRisk.png • Weakening of cohesive ties holding together chromosomes in sex cells may contribute to maternal age- related errors. • The loss of cohesion may contribute to incorrect microtubule attachment during meiotic divisions
- 29. 3.3 A.3 Description of methods used to obtain cells for karyotype analysis e.g. chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis and the associated risks. http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/healthlibrary/GetImage.aspx?ImageId=161385 • Amniocentesis medical procedure used in prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities and also used for sex determination. • A small amount of amniotic fluid, which contains fetal tissues, is sampled from the amniotic sac surrounding a developing fetus, and the fetal DNA is examined for genetic abnormalities.
