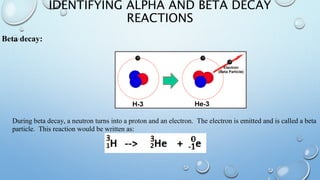
The document discusses radioactivity and nuclear chemistry concepts. It defines radioactivity as the spontaneous decay of unstable atomic nuclei. There are three main types of decay: alpha particles which are helium nuclei, beta particles which are electrons, and gamma rays which are electromagnetic waves. Alpha particles have a low penetrating power but strongly ionize atoms, while gamma rays have a high penetrating power but do not directly ionize atoms. Isotope notation includes extra information about an isotope's nucleus. Unstable atoms undergo alpha or beta decay to become more stable elements in decay chains. Nuclear fission and fusion are also discussed, as well as the concept of half-life which determines the rate of radioactive decay.