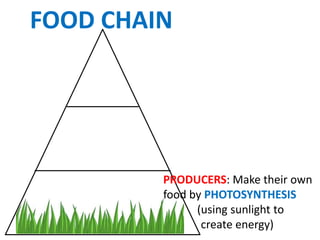
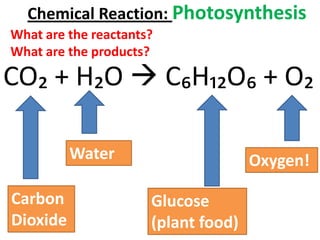
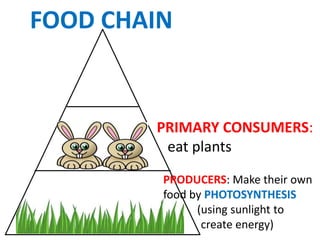
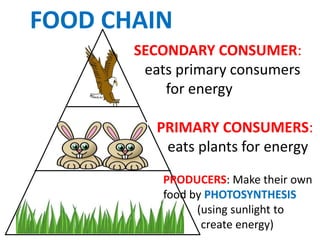
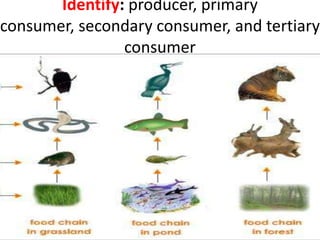
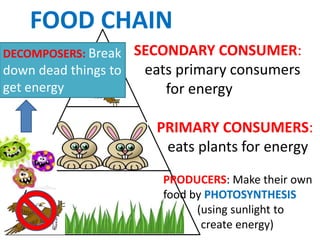
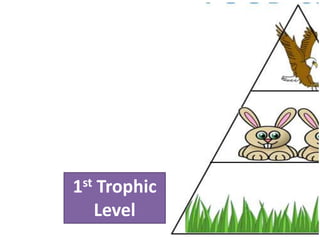
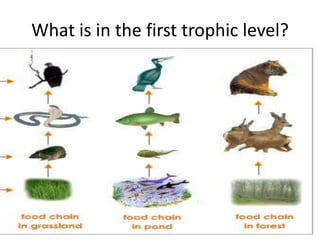
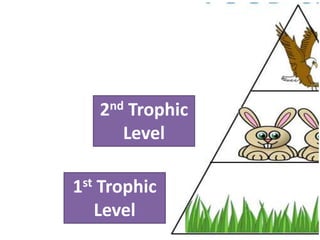
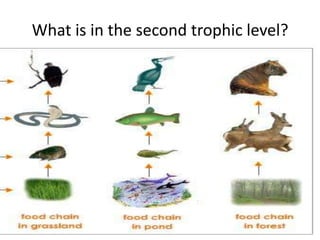
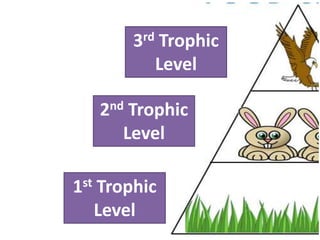
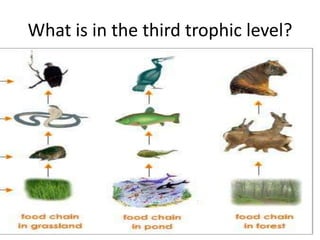
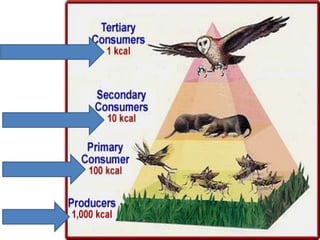
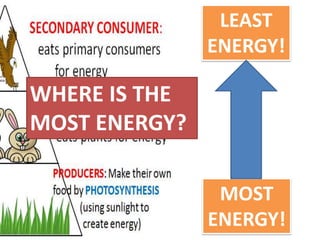
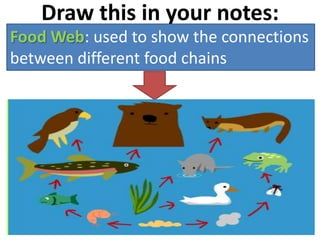
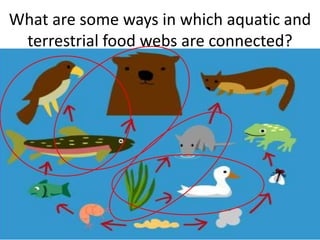
This document provides information about aquatic and terrestrial food webs. It discusses producers that get energy from photosynthesis, primary and secondary consumers that eat other organisms, and examples of connections between aquatic and land-based food chains like bears eating salmon. The document also notes that the first trophic level contains the most energy and that energy decreases at each subsequent trophic level as it is transferred between organisms in a food web.
![3/12/12 A/B Day
LEQ: How are aquatic and terrestrial
food webs connected?
1. What is a wetland?
2. What is a tributary?
3. What is a watershed?
4. How are estuaries and wetlands similar?
How are they different?
5. Copy and complete: Most of our freshwater
is located [underground/in lakes and
rivers/frozen in glaciers and polar ice caps]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/312-120320202927-phpapp02/75/3-12-12-1-2048.jpg)